Exam 1 Key
advertisement

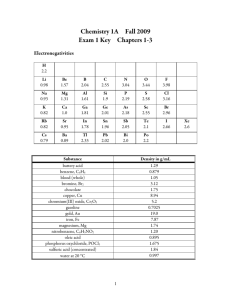
CHEMISTRY 1A SPRING 2011 EXAM 1 KEY CHAPTERS 1-4 You might find the following useful. Electronegativities H 2.2 Li 0.98 Be 1.57 B 2.04 C 2.55 N 3.04 O 3.44 F 3.98 Na 0.93 Mg 1.31 Al 1.61 Si 1.9 P 2.19 S 2.58 Cl 3.16 K 0.82 Ca 1.0 Ga 1.81 Ge 2.01 As 2.18 Se 2.55 Br 2.96 Rb 0.82 Sr 0.95 In 1.78 Sn 1.96 Sb 2.05 Te 2.1 I 2.66 Cs 0.79 Ba 0.89 Tl 2.33 Pb 2.02 Bi 2.0 Po 2.2 Xe 2.6 Densities Substance Density g/mL Substance Density g/mL battery acid 1.29 magnesium, Mg 1.74 benzene, C6H6 0.879 nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2 1.20 blood (whole) 1.05 oleic acid 0.895 bromine, Br2 3.12 sea water 1.025 copper, Cu 8.94 sodium chloride, NaCl 2.16 chromium(III) oxide, Cr2O3 5.2 sulfuric acid (concentrated) 1.84 gasoline 0.7025 triethylene glycol 1.12 Gold, Au 19.0 trinitrotoluene, TNT 1.654 Iron, Fe 7.87 water at 20 C 0.997 1 Answer the following by writing the word, words, letter, letters or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (1 point each blank) 1. Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. 2. Electronegativity is a measure of the electron-attracting ability of an atom in a chemical bond. 3. A(n) oxyanion is a polyatomic ions with the general formula HaXbOcd-. (The a can be 0.) 4. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. 5. Molar mass is the mass in grams of one mole of substance. 6. A(n) formula unit is a group represented by a substance’s chemical formula, that is, a group containing the kinds and numbers of atoms or ions listed in the chemical formula. It is a general term that can be used in reference to elements, molecular compounds, or ionic compounds. 7. The accepted SI unit for amount of substance is the mole, which has an abbreviation of mol. 8. The accepted SI base unit for energy is the joule with an abbreviation of J. 9. The chemical symbol for cobalt is Co, for potassium is K, and for silver is Ag. 10. The names of elements that correspond to the following symbols are sodium for Na, cadmium for Cd, and manganese for Mn. 11. The name of the group on the periodic table in which barium, Ba, is found is alkaline earth metal. Its group number is 2 or 2A. Barium is in the 6th period. It is a representative (or main-group) element (representative element, transition metal or inner transition metal). 12. The N-F bond is a(n) polar covalent (ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent) bond. 13. In the C-O polar covalent bond, the O atom has the partial negative charge. 14. Draw a reasonable Lewis structure for COBr2. (4 points) 2 15. Identify each of the following as a binary covalent compound, a binary ionic compound, a binary acid, an ionic compound with a polyatomic ion, an oxyacid, an alcohol, or a sugar. Write name for each. (8 points) Chemical Formula Type of Substance Name HNO2 oxyacid nitrous acid Co(ClO)3 ionic with polyatomic ion cobalt(III) hypochlorite C2H6 binary covalent (hydrocarbon) ethane Ca(HCO3)2 ionic with polyatomic ion calcium hydrogen carbonate 16. Identify each of the following as a binary covalent compound, a binary ionic compound, a binary acid, an ionic compound with a polyatomic ion, an oxyacid, an alcohol, or a sugar. Write formula for each. (8 points) Chemical Formula Type of Substance Formula ferrous sulfate ionic with polyatomic ion FeSO4 sulfur hexafluoride binary covalent SF6 hydrochloric acid binary acid HCl(aq) ethanol alcohol C2H5OH or CH3CH2OH 17. Complete the following table by (1) writing the name for the type of particle viewed as forming the structure of a solid, liquid, or gas of each of the following substances and (2) writing the name of the type of attraction holding these particles in the solid and liquid form. (9 point each box) Substance Particles to Visualize Type of Attraction CH3OH molecules hydrogen bonds NH4OH cations and anions ionic bonds sulfur molecules London forces cadmium cations in sea of e- metallic bonds neon atoms London forces C6H14 molecules London forces 3 18. Draw the Lewis structure for 2,2,4-trimethylpentane. (3 points) 19. Write the name for the compound represented by the Lewis structure below. (3 points) 3-ethylheptane For each of the following numerical problems, be sure to show your work. NOTE: Remember that there is part credit for each problem. Even if you cannot do all of a problem, be sure to set up as much of it as you can. 20. Chromium metal is used in metal alloys and as a surface plating on other metals to minimize corrosion. It can be obtained by reducing the chromium(III) in chromium(III) oxide, Cr2O3, to the uncharged metal with finely divided aluminum. What is the maximum mass, in pounds, of chromium that can be made from a sample of Cr2O3 with a volume of 2.00 m3 of Cr2O3? (8 points) 3 102 cm 1 mL 5.2 g Cr2O3 1 mol Cr2 O3 ? lb Cr = 2.00 m Cr2O3 3 1 m 1 cm 1 mL Cr2O3 151.990 g Cr2O3 3 2 mol Cr 51.9961 g Cr 1 lb 4 = 1.6 ×10 lb Cr 1 mol Cr2 O3 1 mol Cr 453.6 g 4 21. Potassium permanganate, KMnO4, a common oxidizing agent, is made from various ores that contain manganese(IV) oxide, MnO2. The following equation shows the net reaction for one process that forms potassium permanganate. 2MnO2 + 2KOH + O2 2KMnO4 + H2 a. What is the maximum mass, in kilograms, of KMnO4 that can be made from the reaction of 835.6 g of MnO2 with 585 g of KOH and excess oxygen gas? (8 points) 2 158.0339 g KMnO4 1 kg ? kg KMnO4 = 835.6 g MnO2 3 = 1.519 kg KMnO4 2 86.9368 g MnO2 10 g 2 158.0339 g KMnO4 1 kg ? kg KMnO4 = 585 g KOH 3 = 1.65 kg KMnO4 2 56.1056 g KOH 10 g b. Explain why the oxygen gas is in excess. (6 points) Because air contains oxygen gas, the oxygen is less expensive than the other reactants. It’s especially important that the manganese reactant is used most efficiently, so it is limiting. Oxygen is very safe, so we don’t mind having some left over. Because the O2 is a gas, it is easily separated from the solid product, KMnO4. c. If 1.18 kg of KMnO4 are isolated from the product mixture of the reaction of 835.6 g of MnO2 with 585 g of KOH and excess oxygen gas, what is the percent yield? (3 points) 1.18 kg KMnO4 actual yield % yield = 100 = 100 = 77.7% yield theoretical yield 1.519 kg KMnO4 d. Explain why the actual yield in a chemical reaction such as this one is less than the theoretical yield. (6 points) (1) Many chemical reactions are significantly reversible. Because there is a constant conversion of reactants to products and products to reactants, the reaction never proceeds completely to products. (2) It is common, especially in reactions involving organic compounds, to have side reactions. These reactions form products other than the desired product. (3) Sometimes a reaction is so slow that it has not reached the maximum yield by the time the product is isolated. (4) Even if 100% of the limiting reactant proceeds to products, the product still usually needs to be separated from the other components in the product mixture. (The other components include excess reactants, products of side reactions, and other impurities.) This separation generally involves some loss of product. 5 Answer the following in short answer form. 22. Consider the element bromine. (8 points) a. Describe the particles that form the basic structure of bromine. Bromine is composed of Br2 molecules, which consist of two bromine nuclei surrounded by a70 electron cloud. Each nucleus contains 35 protons and has a +35 charge. b. Is bromine a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature and pressure? liquid c. What is the approximate percentage of the volume of a sample of bromine that is actually occupied by particles? 70% d. What type of attractions hold bromine particles together? London forces e. Describe the motion of a typical bromine particle at room temperature and pressure. Particles are constantly moving. Attractions are strong but not strong enough to keep particles from moving throughout the liquid. Constant collisions that lead to changes in direction and velocity. 6