Chemistry 1A Fall 2009 Exam 1 Key Chapters 1-3
advertisement

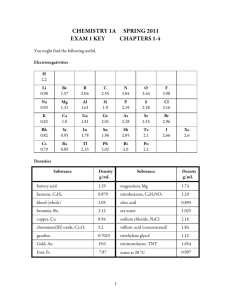
Chemistry 1A Fall 2009 Exam 1 Key Chapters 1-3 Electronegativities H 2.2 Li 0.98 Be 1.57 B 2.04 C 2.55 N 3.04 O 3.44 F 3.98 Na 0.93 Mg 1.31 Al 1.61 Si 1.9 P 2.19 S 2.58 Cl 3.16 K 0.82 Ca 1.0 Ga 1.81 Ge 2.01 As 2.18 Se 2.55 Br 2.96 Rb 0.82 Sr 0.95 In 1.78 Sn 1.96 Sb 2.05 Te 2.1 I 2.66 Cs 0.79 Ba 0.89 Tl 2.33 Pb 2.02 Bi 2.0 Po 2.2 Substance battery acid benzene, C6H6 blood (whole) bromine, Br2 chocolate copper, Cu chromium(III) oxide, Cr2O3 gasoline gold, Au iron, Fe magnesium, Mg nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2 oleic acid phosphorus oxychloride, POCl3 sulfuric acid (concentrated) water at 20 °C Density in g/mL 1.29 0.879 1.05 3.12 1.75 8.94 5.2 0.7025 19.0 7.87 1.74 1.20 0.895 1.675 1.84 0.997 1 Xe 2.6 Answer the following by writing the word, words, letter, letters or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (2 points each unless stated otherwise) 1. The evaporation of ethyl alcohol is a physical (chemical or physical) change. 2. A(n) heterogeneous mixture is a mixture with two or more phases. 3. Metalloids or semimetals are the elements that have some but not all of the characteristics of metals. 4. A substance that is malleable is capable of being extended or shaped by the blows of a hammer. 5. The symbol for the element gold is Au, for cadmium is Cd, and for tin is Sn. (1 point each) 6. The name of the element with the symbol Pt is platinum, F is fluorine, and Mn is manganese. (1 point each) 7. The name of the group on the periodic table to which strontium belongs is alkaline earth metals. 8. The element iron is in the 4th period on the periodic table. 9. The accepted SI unit for energy is the joule and its abbreviation is J. 10. The metric prefix nano means 10−9, and its abbreviation is n. 11. A(n) cation is an ion formed from an atom that has lost one or more electrons and thus has become positively charged. 12. Precision describes the closeness in value of a series of measurements of the same entity. The closer the values of the measurements, the more precise they are. Accuracy describes how closely a measured value approaches the true value of a property. 13. A(n) empirical formula is a chemical formula that includes positive integers that describe the simplest ratio of the atoms of each element in a compound. 14. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. 15. Alcohols are compounds that contain a hydrocarbon group with one or more -OH groups attached. 2 16. Draw a reasonable Lewis structure for CH3COF. (4 points) 17. Write the name of the substance below. (3 points) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane 18. Identify each of the following as a binary covalent compound, a binary ionic compound, a binary acid, an ionic compound with a polyatomic ion, an oxyacid, an alcohol, or a sugar. Write name for each. (9 points) Chemical Formula Type of Substance Name Sr(H2PO3)2 ionic with polyatomic ion strontium dihydrogen phosphite HF(aq) binary acid hydrofluoric acid C2H5OH alcohol ethanol Ni(C2H3O2)3 ionic with polyatomic ion nickel(II) acetate H2SO3 oxyacid sulfurous acid SO2 binary covalent sulfur dioxide 3 19. Identify each of the following as a binary covalent compound, a binary ionic compound, a binary acid, an ionic compound with a polyatomic ion, an oxyacid, an alcohol, or a sugar. Write formula for each.) (9 points) Chemical Formula Type of Substance Formula hydrobromic acid binary acid HBr(aq) chromium(III) sulfide binary ionic Cr2S3 calcium bicarbonate ionic with polyatomic ion Ca(HCO3)2 perchloric acid oxyacid HClO4 glucose sugar C6H12O6 aluminum hypochlorite ionic with polyatomic ion KClO4 20. Complete the following table by (1) writing the name for the type of particle viewed as forming the basic structure of each of the following substances and (2) writing the name of the type of attraction the is broken when these substances are melted or boiled, e.g. covalent bonds, dipole-dipole attractions, etc. (14 points) Substance Particles to Visualize Type of Attraction carbon in the diamond form atoms covalent bonds CH3NH2 molecules hydrogen bonds and London forces scandium sulfite Sc3+ cations and SO32− anions ionic bonds phosphorus molecules London forces zinc cations in a sea of electrons metallic bonds hydrogen chloride molecules dipole-dipole attractions and London forces methylbutane molecules London forces 4 For the following numerical problems, be sure to carefully show your work and round your answer using the appropriate guidelines. NOTE: Remember that there is part credit for each problem. Even if you cannot do all of a problem, be sure to set up as much of it as you can. (8 points each) 21. You fill your tank with gasoline that is 4.2% by mass hexane, C6H14. If the tank contains 2.44 lb hexane, what volume in gallons of gasoline did you add? ⎛ 453.6 g ⎞ ⎛ 100 g gas. ⎞ ⎛ 1 mL gas. ⎞ ⎛ 1 L ⎞ ⎛ 1 gal ⎞ ? gal gas. = 2.44 lb hex. ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟⎜ 3 ⎟⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ = 9.9 gal gas. ⎝ 1 lb ⎠ ⎝ 4.2 g hex. ⎠ ⎝ 0.7025 g gas. ⎠ ⎝ 10 mL ⎠ ⎝ 3.785 L ⎠ 22. Chromium metal is used in metal alloys and as a surface plating on other metals to minimize corrosion. It can be obtained by reducing the chromium(III) in chromium(III) oxide, Cr2O3, to the uncharged metal with finely divided aluminum. What mass of Cr2O3, in megagrams, must be used to make 897 kg chromium, Cr? ⎛ 103 g ⎞⎛ 1 mol Cr ⎞ ⎛ 1 mol Cr2O3 ⎞ ⎛ 151.990 g Cr2O3 ⎞ ⎛ 1 Mg ⎞ ? Mg Cr2O3 = 897 kg Cr ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ ⎜ 6 ⎟ = 1.31 Mg Cr2O3 ⎟⎜ ⎝ 1 kg ⎠⎝ 51.9961 g Cr ⎠ ⎝ 2 mol Cr ⎠ ⎝ 1 mol Cr2 O3 ⎠ ⎝ 10 g ⎠ 5 Answer the following in short answer form. 23. Write an explanation for why electrons affect the chemical characteristics of an atom, write an explanation for why protons affect the chemical characteristics of an atom, and write an explanation for why neutrons do not affect the chemical characteristics of an atom. (6 points) Electrons can be lost, gained and shared, so they are actively involved in chemical changes. Their negative charge is felt by surrounding atoms, also affecting chemical changes. Although protons remain in the nucleus of atoms in chemical changes, their positive charge is felt by surrounding atoms. The number of protons also determines the number of electrons in uncharged atoms. Neutrons stay in the nucleus and have no charge. 24. Write a description of the element bromine as it is found at room temperature and pressure. Your description should include mention of the particles that form its structure, whether it’s a gas, liquid, or solid, how the particles are moving, how much space they occupy, and the strengths of attractions between the particles. (8 points) Bromine is composed of diatomic molecules, Br2, with 35 protons and a +35 charge in each of the two nuclei surrounded by a −70 electron-charge cloud. Bromine is a liquid at room temperature and pressure so the particles occupy about 70% of the volume of the liquid. Attractions are strong but not strong enough to keep particles from moving throughout the liquid. Constant collisions lead to changes in direction and velocity. 6