Cold War Vocab Packet
advertisement

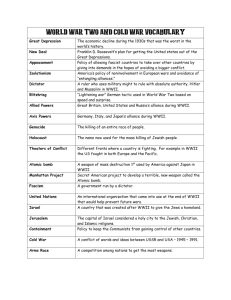
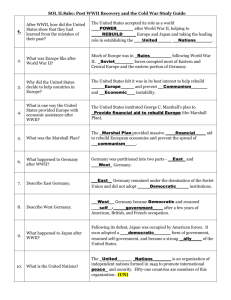
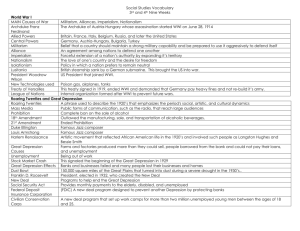
Aftermath of World War II Term/Person/Event World Bank Definition Created by US and 43 other nations to provide development and reconstruction loans Processing Why is this an important term to remember about the Aftermath of WWII? Find three additional facts about this organization. United Nations A new international peacekeeping organization formed after WWII Find three additional facts about this event. Nuremberg War Crimes Trials A series of trials in 1945 and 1946 in which former Nazi leaders were convicted of war crimes Why is this an important term to remember about the Aftermath of WWII? GI Bill of Rights Provided federal funds to help returning GIs transition to civilian life. How can you best remember the meaning of this word? Isolationism A government policy of not taking part in economic and political alliances or relations with other countries What are three examples of how the United States took an internationalist approach after WWII? Internationalism A policy of creating strong economic and diplomatic ties between nations How can you best remember the meaning of this word? Universal Declaration of Human Rights Affirmed the rights to life, liberty, and equality before the law and to freedom of religion, expression, and assembly Origins of the Cold War Term/Person/Event Cold War Definition The struggle between the Communist world led by the Soviet Union and the nonCommunist world led by the U.S. Processing How can you best remember the meaning of this term? What important decisions were made at this conference? Yalta Conference Roosevelt, Stalin, and Churchill met at this conference in the Soviet city of Yalta to plan for the end of WWII. What was important about this conference? Potsdam Conference Allied leaders met at this conference after the defeat of Germany to finalize plans for postwar Germany. Superpowers Nations that influence or control less powerful states Who were the two major superpowers during the Cold War? How can you best remember the meaning of this word? Containment The restriction of Soviet expansion Iron Curtain Symbolized the growing geographic and political divisions between Communist and Capitalist nations in Europe Truman Doctrine Policy that the US must support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures What clues does this term have in it to help you remember what it means? How can you best remember the meaning of this word? Marshall Plan Molotov Plan Offered all European nations, including the USSR, generous funding to rebuild their economies as long as the money was spent on goods made in the US A plan to aid economic recovery in Eastern Europe, encouraged member states to specialize in goods and services and trade with other states. How can you best remember the meaning of this word? How can you best remember the meaning of this word? List three examples of satellite nations during the Cold War. Satellite Nation A country dominated politically and economically by another nation What are two examples of ideologies? Ideology The set of beliefs that forms the basis of a political and economic system Communism A type of system characterized by single-party rule of politics and government control of the economy Capitalism An economic system in which individuals and private businesses make most of the economic decisions What are strengths and weaknesses of this system? What are strengths and weaknesses of this system? The Cold War Expands Term/Person/Event Berlin Blockade/Airlift Definition Processing Draw a picture or cartoon of this word to help you remember the meaning. Operation that moved supplies into West Berlin by American and British planes during a Soviet blockade in 1948-1949 North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) 1949 alliance of nations that agreed to band together in the event of war and to support and protect each nation involved What clues does this term have in it to help you remember what it means? What clues does this term have in it to help you remember what it means? Warsaw Pact Military alliance between the Soviet Union and nations of Eastern Europe, formed in 1955 Korean War Conflict over the future of How can you best remember the meaning of this term? the Korean peninsula, fought between 1950 and 1953 and ending in a stalemate Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) An area, often along the border between two military powers, that no military forces are allowed to enter Without using a dictionary, write a definition of this word. What were three examples of First World countries during the Cold War? First World Developing, capitalist countries What were three examples of Second World countries during the Cold War? Second World Communist countries Third World Covert Action Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) Poor, developing nations in Latin America, Africa, and Asia many of whom had recently gained freedom from colonial rule A secret political, economic, or military operation that aims to shape events or influence affairs in a foreign country in order to support the initiating country’s foreign policy Agency created to collect and analyze intelligence gathered by agents operating in foreign countries What were three examples of Third World countries during the Cold War? What is an example of how the US used this strategy during the Cold War? What clues does this term have in it to help you remember what it means? Why was this a significant advancement in the arms race? H-bomb A hydrogen bomb, more powerful than an atomic bomb, first tested in 1952 Arms Race A competition between nations to achieve the more powerful weapons arsenal Brinkmanship A foreign policy characterized by a willingness to push a dangerous situation to the edge of war, rather than give in to an opponent Without using a dictionary, write a definition of this word. What clues does this term have in it to help you remember what it means? Deterrence Collective Security Mutual Assured Destruction (MAD) 38th Parallel A foreign policy in which a nation develops a weapons arsenal so deadly that another nation will not dare attack A system in which a group of countries commit to jointly dealing with a nation that threatens the peace or security of any one of the countries The principle that either side would respond to a nuclear attack by launching its own missiles What is an example of how the US used this strategy during the Cold War? Why was this significant during the Cold War? The first artificial satellite to orbit Earth, launched by the Soviets in 1957 U-2 Incident What is an example of how the US used this strategy during the Cold War? The line dividing North and South Korea Sputnik Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles What clues does this term have in it to help you remember what it means? Why was this a significant event during the Cold War? What significant advancement did these make in the arms race? Long range rockets that could deliver nuclear weapons to their targets around the world A 1960 incident in which the Soviet military used a guided missile to shoot down an American U-2 spy plane over Soviet territory Why was this a significant event during the Cold War?