The Design Process
advertisement

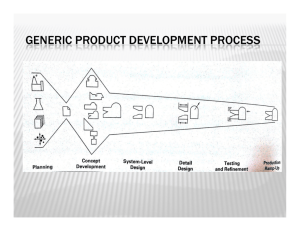
The Design Process Products of technology that moved people from the Agricultural Age to our Information Age often were the result of design. Designing is not a simple or quick task. It requires investigating, answering questions, and making decisions. We can say that designing is the step-by-step process of developing solutions to problems. This process can guide you as you create design solutions to problems presented to you. The seven-step process is: 1. Identify a need or clarify the problem 2. Research the problem 3. Develop possible solutions 4. Choose and justify the optimal design 5. Develop a prototype 6. Test and evaluate the solution 7. Refine the solution/Communicate your ideas Step 1: Identify a Need or Clarify the Problem • What are the requirements or specifications that the solution must fulfill? • What are the constraints? (Items that are available/not available, timeline, cost, materials, tools needed, energy considerations) These questions can be answered in a Design Brief A design brief states the problem and lists the specifications for a design. Lets look at an example of a design brief on the next page. Design Brief: Date: Designers: Client: Problem Statement Design Statement Requirements Constraints Step 2: Research the Problem • Through research, you can identify problems, issues, and questions that relate to the design challenge • Gather information from other people, the library, Internet. Visit stores that sell products similar to the one your designing. • Take measurements, collect data about different types of materials and the performance of those materials • Always keep the design criteria in mind Step 3: Develop Possible Solutions • BRAINSTORM (a process in which group members suggest ideas out loud as they think of them) • Look at the advantages and disadvantages of each idea • Narrow down to a few possible solutions Step 4: Choose and Justify the Optimal Design • Decide on a design that best meets the specifications, fits within the constraints, and has the least number of negative characteristics. • Good design solutions are those that work well, are inexpensive, and cause little or no harm to the environment. • They meet all of the design requirements within all of the limitations. • Once you have chosen a design, be prepared to justify your choice. -Why is it the optimal choice? -How does it meet your design specifications? Step 5: Develop a Prototype • Make either a model or a prototype of the design solution. • A scale model can be larger or smaller than the final product. A prototype is a full-scale, fully operational version of the solution When might you use a scale model instead of a prototype during the design process? Scale models or prototypes make it easier for a designer to modify and refine the design. Step 6: Test and Evaluate the Solution • Collect performance data • Analyze your product for flaws You should note each different factor that affects the performance of your design. These are called variables. Step 7: Refine the solution/Communicate your ideas After evaluating your products design, you may want to refine your solution. Don’t be afraid to consider new ideas at this stage. You may need to adjust items like cost, weight, materials etc. Communicate your ideas is the final step. This is your chance to “show off” or sell the your design. Your design maybe the best, but how you communicate it to the public means a great deal.