Second exam study questions
advertisement

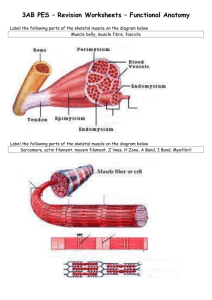
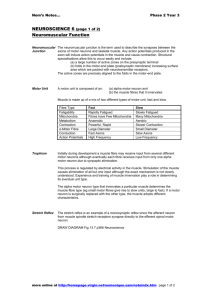
Vertebrate Physiology Study questions-2nd exam 1. What is sensory transduction? How is intensity of a stimulus coded? How is duration of a stimulus coded? (What is the difference between a tonic and phasic receptor?) How is the location of a stimulus coded? ( eg a particular place on the skin?) . How does lateral inhibition improve detection of a skin stimulus’ location? 2.What is the general anatomy of a somatic ( skin ) receptor? What are the different types of skin receptor cells and what they respond to( including subtypes of touch receptors)? 3. What are the general pathways by which input from skin receptors gets carried to the cerebral cortex? What are dorsal root ganglia? How is skin sensory input organized in the cerebral cortex? 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? How do taste cells stimulate sensory neurons and how is taste information carried to and within the brain? 6. What properties of sound waves are detected as volume and pitch? What are the roles of the outer, middle and inner ear in hearing? How does the Organ of Corti in the cochlea transduce sound and send action potentials to the CNS? What encodes volume and pitch? What are the auditory connections to and within the CNS? 7. What are the functions of the various vestibular organs? How does sensory transduction occur ? What are connections to and within the CNS? 8. What is the general function of various parts of the eye? What is the arrangement of cells in the retina? What is different in structure and function between rods and cones What are the three types of cones? 9. What is the mechanism of transduction of light stimuli by photoreceptor cells? . How does more light cause increased action potentials in the optic nerve? 10. What are connections from the eye to and within the CNS? What are some specific features about how visual information is processed in the brain? 11. What areas of the brain control autonomic motor output to the periphery? 12. What is the anatomy of the parasympathetic and sympathetic motor output including the location of preganglionic cell bodies, the location of ganglia and targets innervated?. Where are particular neurotransmitters and their receptors located ? 13. What is the general functional difference between sympathetic vs parasympathetic output? What are some examples of opposing effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation ? What is an example of an autonomic reflex and how does it work? 14. What are the characteristics of α motor neurons (location , pattern of connection to muscle cells, What is a motor unit ? How are motor neurons organized in the spinal cord? 15. What are the locations and roles of muscle stretch receptors and Golgi tendon organs? What are the neuronal connections and functions of the the Knee Jerk (stretch) reflex and the flexor/ cross extensor reflex ? (HANDOUT). 16. How is output from the brain to spinal motor neurons organized ? What controls postural reflexes and intended voluntary movement? What is the special role of cerebellum and basal ganglia? . 17. What is the general anatomy of the skeletal muscle fiber? What is the anatomical relationship of muscle fibers, myofibrils and sarcomeres? 18.What is the arrangement of myosin, actin, troponin and tropomyosin in the sarcomere. How does this arrangement change when Ca ++ increases and allows the sarcomere to shorten? 19. What are the events leading from the arrival of an action potential in the motor neuron terminal to the increase in Ca++ outside the sarcomeres? 20. What is the cycle of movement of the myosin head and the role of ATP in the cycle ? 21. How do the frequency of action potentials in the motor neuron and the number of motor units activated affect the extent of muscle contraction? 22. What are the characteristics of isotonic and isometric contraction? What is the optimal fiber length for isometric tension ? How does isotonic contraction velocity vary with load? 23. What are sources of energy for muscle contraction during light and heavy exercise?. What are the characteristics of different types of muscle fibers? 24. What is the anatomy of smooth muscle cells? What is the mechanism of their contraction? What distinguishes single unit and multiunit smooth muscles? 25. What are functions of the circulatory system ? 26. What are structural characteristics and general functions of arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins? What is the sequence of blood flow through these structures? What distinguishes pulmonary and systemic circulation from the heart?