Cells and Organelles - Highline School District
advertisement
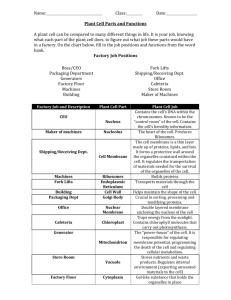
Cells and Organelles The building blocks of Life Mrs. Dignan’s Science Class The Cell Theory All living things are made of cells. New cells are only produced from existing cells. Cells are made of chemical compounds and run on chemical reactions. All Cells contain DNA. A Cell The 2 Basic Types of Cells Prokaryotes (prokaryotic cells) Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Examples: bacteria Eukaryotes (eukaryotic cells) Cells that DO have a nucleus and other organelles Examples: plant cells, fungi cells, and animal cells Cell Organelle Specialized structures that perform specific functions in the cell are called organelles. Organelle means “little organ”. Organelle Name Physical Description: What the organelle looks like Function: What the organelle DOES for the cell Type of Cell: Which type of cell contains this organelle? Analogy: If the cell were a factory, what would this cell organelle be and why? Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Cell Wall Physical Description: Thick, strong barrier around the cell made of indigestible carbohydrates (cellulose in plants). Function: supports and protects the cell Type of Cell: found in plant, bacteria, and fungi cells. NOT in animal cells. Analogy: it is like the walls, ceiling, and floor of a factory because they protect the factory and support the structure. Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Cell Membrane Physical Description: thin, flexible barrier made of phospholipids around the cell (just inside the cell wall OR the outside border of animal cells) Function: controls what enters and leaves the cell; support and protection Type of Cell: found in all cells Analogy: it is like the security guard of a factory because it controls what enters and leaves the cell Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Cytoplasm Physical Description: the fluid-like material inside the cell membrane that fills up the cell In latin, Cyto=cell Function: all cell organelles float around in the cytoplasm; “cell jelly” Site for chemical reactions Type of Cell: found in all cells Analogy: it is like the air of a factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell DNA Physical Description: The nucleic acid found inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or floating freely in prokaryotic cells. Function: controls the cells activities by controlling the making of proteins (protein synthesis). Type of Cell: found inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or floating freely in prokaryotic cells. Analogy: it is like the boss of a factory because she controls the factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Nucleus Physical Description: large round organelle that is usually near the center; contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) Function: Protects the DNA Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes Analogy:it is like the office of a factory because that is where the boss is kept Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Nuclear Membrane (aka Nuclear Envelope) Physical Description: double layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus; has pores Function: Protects the DNA; pores allow RNA to move in and out of the nucleus. Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes Analogy: it is like the office door of a factory because it lets things into and out of the office. Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) Physical Description: internal membrane system covered in ribosomes (so that it looks rough) Function: assembles and modifies proteins made in the ribosomes Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes Analogy: it is like the assembly line of a factory because it is where the proteins are assembled and finished Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Ribosomes Physical Description: very small, round structures either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or free (floating in the cytoplasm) Function: makes proteins Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes AND prokaryotes Analogy: they are like the workers in a factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Body Physical Description: stack of flattened membranes in the cytoplasm Function: attaches carbohydrates and lipids to proteins; send proteins to their final destination Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes Analogy: it is like the shipping department of a factory because it packages and moves proteins Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Lysosome Physical Description: small, round sacks in the cytoplasm Function: breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into useable molecules; break down old or damaged organelles Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes BUT are very rare in plant cells Analogy: it is like the janitor of a factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Vacuole Physical Description: large, spacious sack in the cytoplasm Function: stores materials for the cell (water, food, waste, etc…) Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes (usually one large vacuole in plants and many small vacuoles in animals) Analogy: it is like the storage warehouse of a factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Mitochondria Physical Description: “bean-shaped” organelle that has a folded inner membrane (called cristae) Function: use FOOD and Oxygen to make ATP (ENERGY) compounds for use by the cell Type of Cell: found in all eukaryotes Analogy: it is like the power plant or coalburning furnace of a factory because it makes the energy for the cell Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Chloroplast Physical Description: flattened discs that contains chlorophyll (a green pigment). Looks like a stack of green pancakes. Function: use energy from SUNLIGHT to MAKE sugar molecules through photosynthesis Type of Cell: found in plant/algae cells Analogy: it is like the solar panels of a factory because they trap the sun’s light and turn it into useful sugars for the cell. Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Cytoskeleton Physical Description: a network of protein filaments in the cytoplasm; made of microtubules (microscopic beams) Function: helps support the cell and maintain its shape; moves organelles within the cell; aids in cell movement Type of Cell: found in all cells Analogy: it is like the support beams and cranes of a factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Cillia and Flagella Physical Description: Long “tail-like” protrusions used to move the cell through water. (for transportation) Function: Aids in cell movement Type of Cell: found in bacterial cells and SOME specialized eukaryotic cells (like sperm cells) Analogy: it is like wheels on a mobile factory Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacterial Cell Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells Cell Wall Are angular Chloroplasts No Centrioles Lysosomes are rare 1 Large Vacuole No Cell Wall Are roundish No Chloroplasts Centrioles Lysosomes are common Several Small Vacuoles Job of Cells The main job of all cells is to make proteins, grow, and eventually reproduce. Different cell types do different things Protein production: Ribosome Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Final Destination of the Protein (may be outside of the cell)