File - AP Human Geo
advertisement

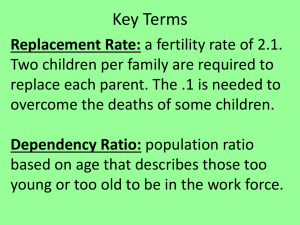
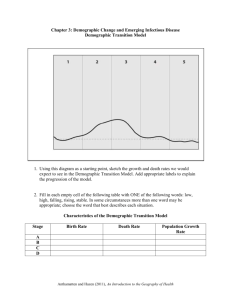
Know and be able to POPULATION GEOGRAPHY KNOW age-sex distribution: K2 demography: K1 natalism (pro- and anti-): K3 agricultural density: K1 dependency ratio: K2 natural increase rate (NIR, RNI): K2 arithmetic density: K1 diffusion of fertility control: K3 Neomalthusians: K3 baby boom: K2 disease diffusion: K4 overpopulation: K1 baby bust: K2 doubling time: K2 physiological density: K1 Cairo Conference: K3 ecumene: K1 population agglomerations: K1 carrying capacity: K1 epidemiological transition: K4 population explosion: K3 census: K1 exponential growth: K3 population projection: K3 census tract: K1 gendered space: K2 population pyramid: K2 child mortality rate: K2 Generation X: K3 replacement fertility: K2 cohort: K3 geodemography (population Rust belt: K1 contraception: K3 geography) - K1 sex ratio: K2 Cornucopians: K3 infant mortality rate (IMR): K2 standard of living: K1 Cotton Belt: K1 J-curve: K3 Sun Belt: K1 crude birth rate (CBR): K2 life expectancy (longevity rate): K4 sustainability: K3 crude death rate (CDR): K2 maladaptation: K3 S-curve: K3 demographic accounting equation: K3 Malthus, Thomas: K3 sex ratio: K2 demographic momentum: K3 maternal mortality rate: K2 total fertility rate (TFR): K2 demographic regions: K3 mortality: K2 underpopulation: K2 demographic transition model: K3 natality: K2 zero population growth: K3 BE ABLE TO map major and emerging population concentrations and describe demographic characteristics of each. calculate arithmetic, agricultural, and physiological densities, and describe the strengths and weaknesses of each for demographic analysis. calculate doubling time and dependency ratios and describe how dependency ratios are interpreted. explain the elements of a population pyramid and distinguish between characteristic shapes. explain the demographic transition model: What are its components? What are some example countries that it describes in each phase? Why might it NOT predict the future for developing countries today? explain changes: or potential changes: and the implications of each for a country’s population: changes in epidemiology changes and age distributions and gender ratios issues of overpopulation give examples of pro- and anti-natalist policies and their effects in example countries. define key demographic terms and identify regions in which high and low extreme examples of each can be found. discuss natural disasters in terms of their locations, causes, and impacts on populations.