The Cell
advertisement

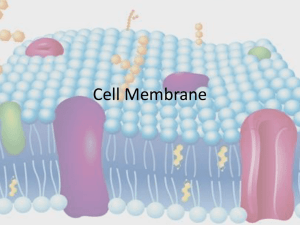
The Cell Cells vary in size, shape, content, and function. Composite Cell 3 main parts 1.nucleus 2.cell membrane 3.cytoplasm includes protein rods and tubules that form a framework called cytoskeleton Organelles within the cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum – transportation system for lipids and proteins Ribosomes – protein synthesis Golgi apparatus – packages glycoproteins (sugar attached to protein) for secretion Mitochondria – “powerhouse” of the cell – releases energy from food Lysosomes – produces digestive enzymes to decompose waste Peroxisomes – catalyze reactions, make bile, decompose hydrogen peroxide (a by product of metabolism), decompose lipids, and detoxifies alcohol Microfilaments (made up of the protein actin) and microtubules (made up of the protein tubulin) – cell movement and support and stabilization of organelles Centrosomes – contain centrioles that distribute chromosomes during mitosis Vesicles (Vacuoles) – contain substances that have entered the cell or are to be secreted Nucleus – Control center of the cell o Enclosed in a double layered envelope o Contains nucleolus – makes ribosomes o Contains chromatin The Cell Membrane Semi-permeable – Allows some substances through, but not others Composed of a Phospholipid bilayer (phospholipid – lipid made of a phosphate group and two fatty acids) The head of the phospholipid is polar and is attracted to water (hydrophilic) The tail of the phospholipid is non polar and repel water (hydrophobic) Integral proteins – proteins that extend through the lipid bilayer Peripheral proteins – proteins that are attached to the external surface of the bilayer Some proteins transport ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride Defective ion channels Cystic Fibrosis Abnormal chloride channels Symptoms – difficulty breathing, frequent respiratory infections, clogged pancreas (disrupts digestion) Caused by a buildup of thick mucous secretions from salt that gets trapped inside cells that draws moisture inside. Movement through the Cell Membrane Diffusion – movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (example – oxygen/carbon dioxide) Facilitated Diffusion – Special carrier molecule moves substances (glucose and amino acids enter this way) Hormone insulin promotes facilitated diffusion of glucose Moves only from high to low concentration Rate is limited by the number of carrier molecules Osmosis – Diffusion of water from high concentration to low concentration Isotonic solution – the solution has the same osmotic pressure inside and outside the cell Hypertonic solution – the solution has a lower water concentration than the cell Hypotonic solution – the solution has a higher water concentration than the cell Active Transport – molecules or ions move from low concentration to high concentration Requires energy from ATP and carrier molecules in the cell membrane Exocytosis – transportation of large molecules outside the cell Endocytosis – transportation of large molecules into the cell Pinocytosis – membrane engulfs droplets of liquid Phagocytosis – membrane engulfs solid particles Mitosis – cell division Stages 1.interphase 2.prophase 3.metaphase 4.anaphase 5.telophase cytokinesis - ring of microfilaments form and constrict to pinch in cell membrane Cancer Hyperplasia – uncontrolled cell division Dedifferentiation – lose specialization – develop into disorganized mass Invasiveness – break through boundaries between organs Angiogenesis – form blood vessels to nourish themselves and remove waste Cell differentiation – the development of specialized structures and functions Stem Cells – undifferentiated and remain that way until acted upon A cell that does not divide or differentiate may undergo apoptosis (a form of cell death that is a normal part of development)