OrganicQualAnalysis
advertisement

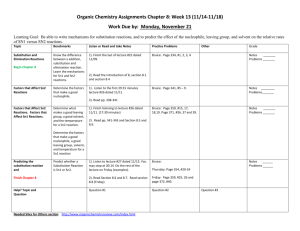
Chem 2364 Organic Qualitative Analysis SN1 and SN2 tests for alkyl halides R Cl AgNO3/EtOH SN1 Only if C+ intermediate is stable 3ry,2ry, special (resonance stabilized) It will give you a racemic mix. if the attacked C was chiral ROEt NaI/Acetone SN2 R I Only if the attacked C has room for backside attack. 1ry, 2ry Mechanisms Planar R1 R1 R2 C SN1 Cl R3 R1 C AgNO3/EtOH R2 EtO R3 R2 R1 C + R3 R2 EtO + C AgCl R3 B Racemization B: is EtOH wich then gets deprotonated it can attack from the top or the bottom R1 I R2 R3 I C Cl SN2 NaI/acetone R2 R3 + NaCl C R1 Inversion Lucas test (ZnCl2/HCl) for alcohols R OH ZnCl2/HCl R Cl aka Lucas The alkyl halide produced (R-Cl) is insoluble in the aqueous solution. Hence, a second phase or turbidity can be seen. ES Chem 2364 R1 R3 C OH R1 R1 R1 R2 HCl + ZnCl2 R2 C O C ZnCl2 R2 R3 R3 + HO-ZnCl2 R2 Cl- R3 H Jones Oxidation test, CrO3/H2SO4 A color change is seen if the test is positive O N.R. R C N.R. O H+ O R1 C R2 R2 Ag(NH3)2+ R1 COH OH aka Tollens R3 O O O CrO3/H2SO4 aka JONES O R CH2OH R CH further oxidation R C R2 R1 R3 R2 R4 O R1 C O R1 C R2 O + R2 R1 CHOH R3 C R4 Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) test for stable enols FeCl3 Stable OH Colored Fe complex ES OH C Cl Chem 2364 Br2/CHCl3 for alkenes, phenols and stable enols The red-brown Br2/CHCl3 solution becomes colorless if test is positive. If the compound is a phenol or a stable enol the positive test will also result in the production of bubbles (HBr gas is produced). OH Br R1 R2 Br R1 R3 R4 R3 OH Br R2 R4 + HBr Br2/CHCl3 Addition EAS Br O R1 Br C CH2R2 O R1 C CHBrR2 + HBr Tollens mirror test for aldehydes O R O H + 2 Ag(NH3)2+ + 2 OH- 2 Ag0 (silver mirror) + R O + NH4+ + 3 NH3 + H2O 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNP) for aldehydes and ketones R2 NHNH2 NO2 O C R1 R2 H NN C NO2 NO2 in H2SO4 aka 2,4-DNP R1 + H2O NO2 R1 & or R2 can be H ES