Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach
advertisement

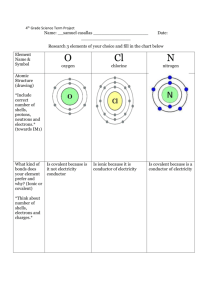
CE : 1. CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.1 Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach 93 5(b) The diagram below shows an apparatus, which, when it contains water, is part of the set-up used in the preparation of chlorine gas. (i) Label clearly (1) the level of water that should be used in the apparatus. (2) the direction of the chlorine gas passing through the apparatus. (ii) Give TWO functions of the apparatus in the preparation of chlorine gas. (iii) The chlorine gas coming out from the apparatus is not dry. Draw a diagram showing how it can be dried and collected. Specify the drying agent used. (6 marks) 2. 94 2 For each of the following experiments, decide and explain which of the experiment set-ups, X or Y, should be used. (6 marks) 3. 94 5(a) CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.2 A domestic drain cleaner named 'RAINBOW' contains concentrated sulphuric acid as the active ingredient. A student carried out the following experiment to determine the concentration of sulphuric acid in 'RAINBOW'. 1.0 cm3 of 'RAINBOW' was diluted to 500 cm3 with distilled water. 25.0 cm3 of the diluted solution were measured and transferred to a conical flask. The solution in the flask required 18.2 cm3 of 0.10 M sodium hydroxide solution for complete neutralization. (i) Name the apparatus used to measure 25.0 cm3 of the diluted solution. (ii) Calculate the molarity of sulphuric acid in 'RAINBOW'. (iii) Suggest ONE disadvantage of using 'RAINBOW' for cleaning drains. (iv) State ONE safety precaution needed when using 'RAINBOW'. Explain your answer. (v) If 'RAINBOW' is poured into drains blocked with fat, the fat can be removed. Assuming the formula of fat is . Explain how ‘RAINBOW' can remove the fat. (8 marks) 4. 95 2 In each of the following groups of substance, there is ONE substance which is different from the others in terms of their properties. In each group, identify the substance which is different from the others and explain your choice. (a) argon, fluorine, helium, neon. (b) nylon, perspex, polyethene, urea-methanal (c) milk of magnesia, soap, vinegar, window cleaner (d) carbon monoxide, hydrogen, methane, nitrogen (8 marks) 5. 95 5 Describe how large crystals of ammonium sulphate can be prepared from an aqueous solution of ammonia in a school laboratory. (6 marks + 3) 6. 95 6(a) The illustration below shows the plastic bottle of a domestic toilet cleaner and its label. (i) Explain, with the help of a chemical equation, why the toilet cleaner should not be mixed with bleaches. (ii) (1) Suggest ONE chemical, other than bleaches, that should not be mixed with the toilet cleaner. (2) If the chemical suggest in (1) and the toilet cleaner are mixed together, what change would be observed ? Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. (iii) Explain why it is necessary to handle the toilet cleaner with care. (iv) (1) Explain why plastic is used for making the bottle for the toilet cleaner. (2) Name ONE plastic material suitable for making the bottle for the toilet cleaner. CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.3 (9 marks) 7. 95 8(b) Small swimming pools usually use sodium hypochlorite solution rather than chlorine gas to sterilize the pool water. (i) Suggest ONE reason for using sodium hypochlorite solution rather than chlorine gas in small swimming pools. (ii) Suggest ONE chemical test to show the presence of hypochlorite ions in a sample of pool water. State the observable change in the test. (iii) A 100 cm3 sample of pool water contains 5.0 g of sodium hypochlorite. Calculate the concentration, in mol dm-3, of sodium hypochlorite in the sample. (iv) What would be observed if a petal of red flower was put into a sodium hypochlorite solution ? Using an equation, explain this observation. (v) Briefly describe how sodium hypochlorite solution can be produced industrially. (Relative atomic masses : O=16.0; Na=23.0; Cl=35.5) (10 marks) 8. 96 8(a) The table below lists some information about four nitrogen-containing compounds which may be used as fertilizers. Compound Solubility in water at 25oC Cost per kg of compound Cost per kg of nitrogen in / mol dm-3 / $ the compound / $ NH3 31.1 12.0 14.6 NH4NO3 26.8 20.0 x (NH4)2SO4 5.8 15.0 70.7 (NH4)2HPO4 4.4 141.0 664.7 (i) Explain why nitrogen is essential for the growth of plants. (ii) Calculate the value of x. (iii) Suggest TWO reasons why farmers do not prefer using ammonia (gas or solution) directly as a fertilizer. (iv) The growth of some plants such as turnips requires a large amount of nitrogen. Which of the four compounds is the most suitable for use as a fertilizer for these plants? Explain your answer. (Relative atomic masses : H = 1.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0) (8 marks) 9. 97 6(b) In a certain country, sulphuric acid is manufactured by the Contact Process using sulphur as the raw material. The uses of sulphuric acid in this country are summarized in the following pie-chart. (i) The stages involved in the Contact Process can be represented by the following equations: S(s) + O2(g) SO2(g) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) SO3(g) + H2SO4( ) H2S2O7( ) H2S2O7( ) 2H2SO4( ) Suppose that the conversion of sulphur to sulphuric acid is 100%. (1) How many moles of sulphur are required to produce one mole of sulphuric acid? (2) If the annual production of sulphuric acid in this country is 2.6 x 10 9 kg, calculate the annual consumption of sulphur, in kg, in the Contact Process. (3) Referring to the above equations, explain why the actual annual consumption of sulphur is greater than the value calculated in (2). CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.4 (ii) Suggest ONE other method that can be used to produce sulphur dioxide required for the Contact Process. Write the chemical equation(s) involved. (iii) As we enter the twentieth century, global demand for fertilizers is increasing annually. (1) Name ONE fertilizer which can be made from sulphuric acid. (2) Explain why global demand for fertilizers is increasing annually. (iv) Sulphuric acid is also used in the paint industry. Suggest ONE paint additive that can be prepared from sulphuric acid. (v) Suggest ONE use of sulphuric acid categorized as 'Others' in the pie chart. (Relative atomic masses : H = 1.0, O = 16.0, S = 32.1) (10 marks) 10. 97 8(a) A class of students visited a chemical plant which manufactures chlorine by the electrolysis of brine. Some of the chlorine produced is used to make chlorine bleach. At the end of the visit, each student was given a bottle of chlorine bleach as a gift. (i) Explain, in terms of preferential discharge of ions, how chlorine is produced in the electrochemical process. (ii) The students found some metal cylinders containing chlorine in the chemical plant. The students were told that these cylinders would be used in water treatment plants. (1) Which one of the following hazard warning labels should be displayed on the metal cylinders? (2) Explain why chlorine is used in water treatment plants. (iii) Suggest ONE product, apart from chlorine and chlorine bleach, that is likely to be manufactured in the chemical plant. (iv) When the students returned to the school, their teacher asked them to carry out an experiment using the chlorine bleach as illustrated below. (1) Write the ionic equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with the chlorine bleach. (2) State the observable change that would occur on the filter paper. Explain whether or not the change would involve a redox reaction. (9 marks) 11. 98 6(a)(ii) Sodium nitrate is a nitrogenous fertilizer. (1) Calculate the percentage by mass of nitrogen in sodium nitrate. (Relative atomic masses : N = 14.0, O = 16.0, Na = 23.0) (2) Explain why nitrogen is essential for the growth of plants (4 marks) CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.5 12. 99 8(b) Manufacturing ammonia by the Haber process involves the following exothermic reaction: N2(g) + 3H2(g) (i) 2NH3(g) (1) Name a catalyst used in the process. (2) Suggest how the heat liberated in the reaction can be used in the process. (ii) A sufficient amount of hydrogen and 6.0 x 109 dm3 of nitrogen, measured at room temperature and pressure, are allowed to react in the reaction chamber to give ammonia. Suppose that the conversion of nitrogen to ammonia is 15%. Calculate the mass of ammonia formed. (iii) Upon reaction with a suitable chemical, ammonia gives a nitrogenous fertilizer. Write a chemical equation for such a reaction. (iv) Most window cleaners contain ammonia solution as an active ingredient. (1) Explain why ammonia solution is used in window cleaners. (2) State ONE reason for using ammonia solution instead of sodium hydroxide solution in window cleaners. (Relative atomic masses: H = 1.0, N = 14.0; molar volume of gas at room temperature and pressure = 24.0 dm3) (9 marks) 13. 99 9(a) In an experiment to prepare sulphur dioxide, a mixture of copper turnings and concentrated sulphuric acid was heated in a test tube as shown in the diagram below: (i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction that occurred in the test tube. (ii) Decide which of the following set-ups, (I), (II) or (III), should be connected to the delivery tube to collect the sulphur dioxide produced. Explain your decision. (iii) (1) State and explain the observation when a piece of wet blue litmus paper is added to a gas jar of sulphur dioxide. (2) State the observation when a few drops of bromine water are added to a gas jar of sulphur dioxide. Write a chemical equation for the reaction that occurs. (8 marks) CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.6 14. 00-6 (a) The flow diagram below shows the stage involved in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende, ZnS. (i) The reaction in Stage I gives apart from zinc oxide, a gaseous product. (1) Write the chemical equation for the reaction. (2) Give ONE industrial use of the gaseous product. (ii) Suggest how zinc oxide can be converted to zinc sulphate solution in Stage II. (iii) The zinc sulphate solution obtained contains ions of other metals. During the electrolysis in Stage III, zinc metal is liberated at one of the electrodes. (1) Suggest ONE way to remove ions of metals which are less reactive than zinc from the zinc sulphate solution before electrolysis. (2) Why is it not necessary to remove ions of metals which are more reactive than zinc from the solution? (3) Write half equations for the reactions occurring at the anode and cathode during the electrolysis. (iv) Give ONE use of zinc in daily life. (8 marks) (b) In Hong Kong, the supply of fresh water mainly comes from Dong Jiang ( 東 江 ). After some preliminary treatment of the river water in the water treatment plants, chlorine and calcium hydroxide are successively added. (i) Why are the following substances added to the river water? (1) chlorine? (2) calcium hydroxide (ii) Chlorine can react with organic matter present in the river water to give trichloromethane which is harmful to human beings. (1) Draw the structure of trichloromethane (2) Why is trichloromethane harmful to human beings? (3) Suggest ONE preventive measure to reduce the amount of organic matter in the river water. (5 marks) 15. 00-9 (c) Nitrogen constitutes about 78% of the atmosphere. The flow diagram below shows the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to plant proteins. (i) Draw the electronic diagram for a molecule of nitrogen, showing electrons in the outermost shells only. (ii) Describe ONE process by which atmospheric nitrogen can be converted to nitrates in soil. (iii) When plants are eaten by animals, the plant proteins are transformed into animal proteins. State ONE way by which the nitrogen in animal proteins can return to soil. (4 marks) CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.7 (d) Fritz Haber, a German chemist, discovered the transformation of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which can be used to produce nitrogeneous fertilizers and explosives. He also managed to successfully use chlorine and mustard gas as chemical weapons. In 1919, when he was awarded the Nobal Prize for chemistry, several other Nobel Prize winners refused to accept their awards because of Haber's involvement. State whether or not you agree that Haber's inventions contributed to the well-being of the world. Explain your answer. (2 marks) 16. 01-8(b) The flow diagram below shows the four key stages in the production of ammonium nitrate from ammonia. (i) (1) Give the name of X. (2) Write a chemical equation for the reaction in Stage I. (ii) Is the reaction in Stage II a redox reaction? Explain your answer in terms of oxidation number. (iii) Suggest how nitrogen dioxide can be converted to nitric acid in Stage III. (iv) Suggest ONE use of ammonium nitrate in daily life. (v) Ammonium nitrate can be prepared by reacting ammonia with nitric acid. Calculate the theoretical volume of ammonia gas, measured at room temperature and pressure, required to produce 5.0 g of solid ammonium nitrate. (Relative atomic masses: H = 1.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0; molar volume of gas at room temperature and pressure = 24 dm3) (9 marks) 17. 01 9(d) Both chlorine and sulphur dioxide are industrial bleaching agents. For each of these bleaching agents, state ONE advantage. (2 marks) 18. 02-1 Both ammonium dihydrogenphosphate and ammonium sulphate are nitrogenous fertilizers. (a) Why is nitrogen essential for plant growth? (b) List all the elements in ammonium dihydrogenphosphate. (c) (i) Calculate the percentage by mass of nitrogen in ammonium sulphate. (ii) The use of ammonium sulphate as a fertilizer adds acidity to the soil. If the soil is too acidic, it is not suitable for plant growth. Suggest ONE substance that is commonly used by farmers to reduce soil acidity. Explain your answer. (Relative atomic masses: H = 1.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0, S = 32.0) (6 marks) 19. 02-7 (b) Chlorine bleach can be made by reacting chlorine with sodium hydroxide solution. (i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction. (ii) The reaction is known to be a redox. State whether chlorine acts as an oxidizing agent, a reducing agent or both. Explain your answer in terms of the change in oxidation number. (iii) Apart from being used as a bleach, suggest ONE other use of chlorine. (5 marks) CE : Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Bleach LQ P.8 (c) Ammonia was once used to detect the leakage of chlorine in chemical plants. If there was a leakage, white fumes would be observed. The word equation below represents the reaction of chlorine with ammonia: chlorine + ammonia ammonium chloride + nitrogen (i) Transcribe the word equation into a chemical equation. (ii) Suggest what the white fumes might have been. (3 marks)