7A Cells Crossword
advertisement

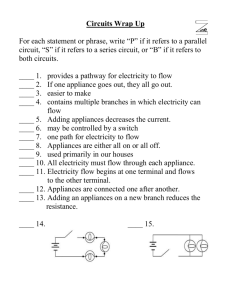
7A Cells Crossword 1 2 3 4 5 7 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Across 1 It has a large surface area to help the cell absorb water quickly. (4,4,4) 3 Small hairs on some cells. (5) 4 How much bigger a microscope makes something appear. (13) 7 Organ that pumps blood. (5) 8 Green substance found inside chloroplasts. (11) 10 Organs used to clean the blood and make urine. (7) 19 Cell that can change its length and so help us to move. (6,4) 20 Part of the microscope you look down. (8, 4) 22 Cell that carries messages around the body. (5,4) 23 Storage space in plant cells. (7) Down 2 When something has certain features to help it do a particular job. (7) 3 Jelly inside a cell where the cell’s activities happen. (9) 5 Controls what a cell does. (7) 6 Carries oxygen and food around the body. (11,6) 9 Used to magnify small things. (10) 11 What you see down a microscope. (5) 12 Part of the microscope you put slides on. (5) 13 An organ used to digest and absorb food. (9) 14 A group of the same cells all doing the same job. (6) 15 A cell used for sexual reproduction. (3,4) 16 Tough wall around plant cells, helps to support the cell. (4,4) 17 Glass sheet that a specimen is put on. (5) 18 Organ that controls what the body does. (5) 21 The basic unit which living things are made of. (4) 7B Reproduction 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Across 3 Organ in females in which a baby develops. (6) 5 A mixture of sperm cells and special fluids released by men during sexual intercourse. (5) 6 Fusing of a male sex cell with a female sex cell. (13) 8 Carries egg cells from the ovaries to the uterus in women. (7) 9 The male sex cell. (5,4) 10 When the penis becomes stiff. (8) 12 A cell used for sexual reproduction. (3,4) 15 When a woman has an embryo growing inside her uterus. (8) 19 Female reproductive organ which produces egg cells. (5) 20 Semen is pumped out of a man's penis during sexual intercourse. (11) 21 Time when physical changes happen in the body between the ages of about 11 and 15. (7) 23 Tiny new human life which grows by cell division from a fertilised egg cell. (6) 24 Monthly discharge blood and other material from the lining of the uterus (12) Down 1 All the reproductive organs. (12,6) 2 Releasing of an egg cell from an ovary in women. (9) 4 Producing new organisms by the joining of two sex cells. (6,12) 7 Male reproductive organ, produces sperm cells. (6) 11 A tube carrying semen or urine running down the centre of the penis in males (7) 13 The female sex cell. (3,4) 14 Bag of skin containing the testes in males. (7) 15 Organ which takes oxygen and food out of the mother's blood and puts waste materials into the mother's blood. (8) 16 When the placenta is pushed out through the vagina. (5, 5) 17 Tube in females where the penis is placed during sexual intercourse. (6) 18 When the ovaries in women stop releasing eggs. (9) 22 Name given to the developing embryo. (5) 7C Environment and Feeding Relationships 1 2 3 4 5 7 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Across 1 The last animal in a food chain. (3,8) 7 An animal that eats both plants and other animals. (8) 10 An organism that has to eat other organisms to stay alive. (8) 12 An animal that is caught and eaten by another animal. (4) 13 An animal that only eats plants. (9) 15 Creatures that are active at night. (9,7) 16 The place an organism lives in (e.g. woodland). (7) 17 All the plants and animals that live in a habitat. (9) Down 2 An animal that catches and eats other animals. (8) 3 The features that plants and animals have to help them live in a particular place. (11) 4 An organism that is able to make its own food. (8) 5 A way of showing what eats what in a habitat. (4,5) 6 Many food chains linked together. (4,3) 8 The conditions around a certain organism caused by physical factors. (11) 9 A stored form of energy found in food. (8,6) 11 An animal that only eats other animals. (9) 12 A small container connected to two tubes used to catch tiny animals. (6) 14 A square frame, thrown randomly on the ground, which is used to sample plants in an area. (7) 7D Variation and Classification 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Across 2 Largest groups that living things are sorted into. The two biggest are the plant and animal _________ (7) 6 Arthropod with long, thin body divided into sections. Two pairs of legs on each body section. (9) 7 Middle part of an animal's main body. In insects the legs are attached to this. (6) 8 Rear or bottom end of an animal's main body. (7) 9 Name given to any living thing. (8) 10 An animal with a backbone. (10) 15 Sorting things into groups. (14) 19 Vertebrate with moist skin, e.g. a frog. (9) 21 A group of organisms that can reproduce with each other to produce offspring that will also be able to reproduce. (7) 22 Type of arthropod with long thin body divided into sections. One pair of legs on each body section. (9) 23 Front or top end of an animal's body. (4) 25 Thick outer covering found on arthropods. (11) 26 Invertebrate with jointed legs, e.g. a fly or spider. (9) Down 1 Invertebrate with a body in five parts, e.g. a starfish. (10) 3 Vertebrate with hair, which also produces milk, e.g. a human. (6) 4 Vertebrate with feathers, e.g. an eagle. (4) 5 Type of arthropod with a chalky shell and 5-7 pairs of legs, e.g. a lobster. (10) 8 Something sticking out of an animal's head which is used to sense things. (7) 11 The differences between things. (9) 12 The surroundings of an organism. (11) 13 Animal with no backbone. (12) 14 Invertebrate that crawls on a fleshy pad, e.g. a snail. (7) 16 Vertebrate with dry scales, e.g. a snake. (7) 17 Any plant or animal formed by reproduction. Offspring are produced by their parents. (9) 18 Type of arthropod with three pairs of legs, e.g. a fly. (6) 19 Type of arthropod with four pairs of legs, e.g. a spider. (8) 20 Some animals have bodies that are divided into obvious sections called _____________ . (7) 24 Vertebrate with wet scales, fins and gills. (4) 7E Acids and Alkalis 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Across 1 6 8 10 12 14 16 17 18 19 Something made of particles that are very spread out and have no bonds between them. (3) The acid in vinegar. (8,4) Substance that is not an acid or an alkali. Has a pH of 7. (7) The old name for ethanoic acid. It is the acid in vinegar. (6,4) A common acid containing nitrogen. (6,4) Something that causes inflammation to the skin and eyes. (8) The acid in citrus fruits. (6,4) Substance that turns litmus blue. Has a pH of more than 7. (6) A simple kind of indicator. It turns red in acids and blue in alkalis. (6) We __________ a solution by adding more of the solvent to it. (6) Down 2 A substance that makes things taste sweeter. (9) 3 A common acid that is also found in your stomach. (12,4) 4 A mixture of indicators giving a different colour depending on how weak or strong an acid or alkali is. (9,9) 5 A common acid used in car batteries. (9,4) 7 Substances that attack metals, stonework and skin. (9) 9 A numbered scale from 1-14 showing the strengths of acids and alkalis. (2,5) 10 Chemical name for vitamin C. (8,4) 11 A dye that will change colour in acids and alkalis. (9) 13 Another word for irritant. (7) 15 A substance that turns litmus red. It has a pH of less than 7. (4) 7F Simple Chemical Reactions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Across 1 The scientific word for burning. (10) 6 The kind of energy stored in chemicals. (8,6) 7 A chemical that goes cloudy when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it. (9) 8 A change in which what you end up with can easily be turned back into what you started with. (10,6) 9 Substance formed when iron or steel reacts with oxygen and water. (4) 10 A chemical that can release energy when it reacts. (4) 11 A change where no new substances are formed. (8,6) 12 Chemicals that join together to form a new substance. (9) 14 A gas which will put out a lighted splint and turn limewater milky. (6,7) Down 2 A reaction in which what you end up with cannot be turned back into what you started with. (12,6) 3 Rain containing sulphuric and nitric acid. (4,4) 4 A gas which is given off when metals react with acids. It burns with a squeaky pop. (8) 5 A chemical compound containing only hydrogen and carbon. (11) 6 A change where new substances are formed. (8,8) 11 New chemical formed in a chemical reaction. (7) 13 A compound that includes oxygen. (5) 7G Particle Model of Solids, Liquids and Gasses 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Across 1 Something with a fixed shape and volume. (5) 6 An idea about why things work the way they do. (6) 7 When particles mix with each other without anything moving them. (9) 9 A description of how a material behaves and what it is like. (8) 11 Move backwards and forwards. (7) 12 Forces holding particles together. (5) 14 The tiny pieces that everything is made out of. (9) Down 1 The term given to the three different forms which a substance can be in; solid, liquid or gas. (6,2,6) 2 Something with a fixed volume but no fixed shape. (6) 3 Numbers which are the results of an experiment. (4) 4 The force caused by particles hitting a certain area. (8) 5 What you think will happen in an experiment. (10) 8 Move steadily in a constant stream or current. (4) 10 Something that does not have a fixed shape or volume, and is easy to squash. (3) 11 A completely empty space. (6) 13 Something which is heavy for its volume. (5) 7H Solutions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Across 2 Separating dissolved solids from one another. The solids are usually coloured. (14) 5 Separating things that have not dissolved from a liquid by passing the liquid through paper. (9) 6 When a solid splits up and mixes with a liquid to make a solution. (10) 9 A solid that will not dissolve. (9) 11 A solution of common salt and water. (5) 12 The solid that has dissolved in a liquid to make a solution. (6) 14 A substance that does not have anything else in it. (4) 16 A solid that can dissolve in a liquid. (7) 17 Another word for see-through. (11) 19 Another name for sodium chloride. (6,4) 20 A gas turning into a liquid. (10) Down 1 Chemicals from rocks that have dissolved in water. (5) 3 A lot of different things jumbled up together. (7) 4 A factor in an experiment that can change. (8) 6 The process of separating a liquid from a solution by evaporating the liquid and then condensing it. (12) 7 The liquid that has dissolved a solid to make a solution. (7) 8 The amount of a solid that will dissolve in 100g of a liquid. (10) 10 A liquid turning into a gas. (11) 13 Water as a gas. Also called steam. (5,6) 15 A solution that contains as much dissolved solid as it possibly can. (9) 16 When a solid has dissolved in a liquid. (8) 18 Water as a gas. Also called water vapour. (5) 7I Energy Resources 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 7I Energy Resources Across 3 1000 joules. (9) 4 The kind of energy given out by light bulbs, candles, etc. (5,6) 7 Anything that stores energy that can be converted into heat energy - includes fossil fuels and nuclear fuel. (4) 8 Making electricity by letting falling water (usually from a reservoir) turn turbines and generators. (13,5) 11 The idea that energy can never be created or destroyed, only changed from one form into another. (12,2,6) 13 Coal, oil and natural gas formed from the remains of dead plants and animals. (6,5) 16 Dangerous particles and energy given off by uranium and other radioactive materials. (9) 17 Fossil fuel formed from the remains of dead plants and animals that lived in the sea. (7,3) 19 Making electricity using the moving (kinetic) energy from the tides. (5,5) 20 Make electricity by turning a magnet inside coils of wire. (8) 22 The kind of energy made by anything that is making a noise. (5,6) 23 Fossil fuel formed from the remains of dead plants and animals that lived in the sea. (3) 24 The kind of energy stored in chemicals, food, fuels and cells (batteries). (8) 25 A fuel used in nuclear power stations. (7) 26 Any fuel that comes from plants, animals, or their wastes. (7) 27 The kind of energy in moving things. (7,6) 28 The unit for measuring energy. (5) 29 The kind of energy carried by electricity. (10,6) Down 1 Energy stored inside the particles that things are made out of. (7,6) 2 Process that plants use to make their own food. (14) 5 Any energy resource that will run out and we cannot renew our supplies of it (e.g. oil). (3-9,6,8) 6 An energy resource that will never run out (e.g. solar power). (9,6,8) 9 The machine in a power station that is pushed round by water or steam and turns the generator. (7) 10 Flat plates that convert light energy into electrical energy. (5,5) 11 A flow of liquid or gas caused by part of it being heated or cooled more than the rest. (10,7) 12 Making electricity using heat from hot rocks underground. (10,5) 14 Flat plates that use the Sun's energy to heat water. (5,6) 15 A fossil fuel made from the remains of plants. (4) 18 A kind of windmill that generates electricity using energy from the wind. (4,7) 21 Making electricity by using light or heat energy from the Sun. (5,5) 7J Electrical Circuits 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 17 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Across 1 Another name for a battery. (4) 4 Measures how much electricity is flowing around a circuit. (7) 5 A component that makes it difficult for electricity to flow. (8) 7 The brown wire in a cable or plug. (4,4) 10 Turns electricity on or off, by closing or opening a gap in a circuit. (6) 11 A piece of wire that melts if too much electricity flows through it. (4) 14 The smallest part of an element. (4) 17 The unit for current. (3) 18 Tiny particle that flows around a circuit. (8) 20 The flow of electrons around a circuit. (7) 21 A resistor that can be adjusted to change the amount of resistance it has. (8,8) 23 Electrical signal carried by a nerve cell. (7) 25 A circuit where there is only one loop of wire. (6,7) Down 1 A complete loop that electricity flows around. (7) 2 A circuit with two or more wires running next to each other. (8,7) 3 A material that lets electricity flow through it. (9) 6 A material that does not let electricity flow through it. (9) 8 A way of saying how difficult it is for electricity to flow through something. (10) 9 Thin piece of wire inside a light bulb that glows when electricity is flowing through it. (8) 12 Something in a circuit, like a bulb, switch or motor. (9) 13 Part of a plug that holds the cable, and stops the wires being pulled out of the pins. (5,4) 15 The blue wire in a cable or plug. (7,4) 16 Carries messages around the body. (5) 19 The green and yellow wire in a cable or plug. (5,4) 22 A way of saying how much energy is transferred by electricity. (7) 24 A scientific way of thinking about how things happen. (5) 7K Forces and their Effects 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 7K Forces and their Effects Across 3 When two forces working in opposite directions are not the same strength. (10,6) 6 The amount of matter that something is made of. (4) 7 The force of attraction between any two objects. (7) 9 The amount of force with which gravity pulls, measured in newtons (N). (6) 10 A force that can affect something from a distance (e.g. gravity). (3-7,5) 11 A force that pushes things up. (8) 13 A unit for measuring mass (g). (4) 15 Not moving. (10) 22 Any substance that will return to its original shape and size after it has been stretched or squashed. (7) 23 The distance a car travels while the brakes are trying to stop it. (7,8) 24 The distance a car travels while the driver is deciding to press the brake pedal. (8,8) 25 A force that tries to slow things down when two things rub against each other. (8) 26 How fast something is moving. Often measured in metres per second (m/s). (5) 27 A force that tries to slow things down that are moving through air. It is a type of friction. (3,10) 28 The volume of water pushed out of the way by an object. (12) Down 1 A substance (normally a liquid) used to reduce friction. (9) 2 The amount of mass that 1cm3 of a substance has. Measured in g/cm3. (7) 4 A push or a pull. (5) 5 Piece of equipment containing a spring, used to measure forces. (5,5) 6 A force that attracts objects made out of iron. (9) 8 A unit for measuring mass equal to 1000 g. (8) 12 A force which attracts things with extra electrical charges on them. (6,11) 14 A force that tries to slow things down that are moving through water. It is a type of friction. (5,10) 15 Equal to the thinking distance and the braking distance added together. (8,8) 16 When two forces are the same strength, but working in opposite directions. (8,6) 17 A force that needs to touch an object before it can affect it (e.g. friction). (7,5) 18 Adding a lubricant to something. (11) 19 Another name for a force meter. (6,5) 20 What air and water resistance are both sometimes called. (4) 21 The unit of force. (6) 7L Solar System 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 28 Across 3 Once every 4 years, a period of 366 days. (4,4) 6 All the galaxies and the space between them make up the Universe. (8) 8 The path that a planet takes around the Sun. (5) 11 When the Moon moves into the shadow of the Earth. (5,7) 12 Millions of stars grouped together. (6) 17 Gives out light. (8) 20 A star with planets and other objects orbiting it. (5,6) 23 Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars make up these. (5,7) 24 The half of the Earth with the North Pole in it. (8,10) 27 A small lump of rock orbiting around the Sun (8) 28 The phase of the Moon when we cannot see the lit-up side. (3,4) 29 A shape like a ball. (6) 30 The planet we live on. (5) 27 29 30 Down 1 When the Moon completely blocks out light from the Sun. (5,7) 2 The two halves of a sphere - the shape you would get if you cut a solid ball in half. (11) 4 When the Moon only covers part of the Sun. (7,7) 5 The different shapes the Moon seems to have at different times. (6) 7 A pattern of stars. (13) 9 The galaxy that our Solar System is in. (5,3) 10 24 hours, the time it takes the Earth to spin once on its axis. (3) 13 A large lump of rock orbiting around a planet. (4) 14 The phase of the Moon when it looks like a bright, full circle. (4,4) 15 From pole to pole, an imaginary line that the Earth spins around. (4) 16 A huge ball of gas that gives out heat and light energy. (4) 18 What we call Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. (5,7) 19 28 days - the time it takes the Moon to orbit around the Earth once. (5) 21 The distance that light travels in one year. (5,4) 22 Anything that orbits a planet. (9) 25 An imaginary line around the middle of the Earth. (7) 26 The star that the Earth orbits around. (3)