VSEPR Theory & Molecular Shapes Chemistry Worksheet
advertisement

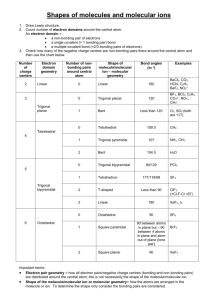
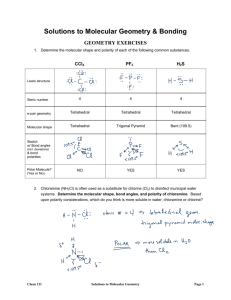
Name: ______________________________ Date: _____________________ 28 Chemistry Review: VSEPR and Molecular Shapes Predict which molecular shape each molecule below would take. For bent molecules, be sure to note the bond approximate bond angle (109.5o or 120 o). MOLECULAR GEOMETRY: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY: 1. The diagrams above labeled Molecule 1 and Molecule 2 represent molecules with different electron geometries. In these diagrams, A represents the central atom and X represents the bonding groups. Which of the following is the most accurate prediction about the molecular geometries of these molecules based on the VSEPR theory? A B C D Both molecules will have bent molecular geometries with identical bond angles. Molecule 1 will be trigonal pyramidal while molecule 2 will be trigonal bipyramidal. Molecule 1 will have a bond angle less than that of molecule 2. Both molecules will have trigonal planar electron geometries, but only molecule 2 is bent. 2. What would be the molecular geometry of the molecule shown to the right as predicted by the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory? A Trigonal Planar B Tetrahedral C Trigonal Pyramidal D Bent 3. What molecular geometry would be predicted for the compound shown above according to the VSEPR theory? A Bent B Trigonal planar C Trigonal pyramidal D Tetrahedral 4. According to the VSEPR theory, the molecule shown above will have which of the following molecular geometries? 5. What would be the molecular geometry predicted by the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory for the molecule shown above? A Linear B Octahedral C Trigonal pyramidal D Bent A Bent (120 o) B Tetrahedral (109.5 o) C Trigonal planar (120 o) D Bent (109.5 o) 6. Xenon trioxide is an incredibly unstable molecule that serves as a very potent oxidizer in chemical reactions. Based on the Lewis structure shown to the right, what molecular shape would be predicted for xenon trioxide by the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory? A Tetrahedral B Trigonal Pyramidal C Trigonal Planar D Octahedral 7. The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is used to predict the molecular shapes of compounds. What would be the shape of the molecule in the box to the right according to this theory? A Trigonal Pyramidal B Tetrahedral C Bent NCl3 D Trigonal Planar 8. Which of the following molecules would not be predicted to have a linear molecular geometry according to the VSEPR theory? A B C D 9. What would be the molecular geometry of the molecule shown to the right as predicted by the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory? A Bent B Trigonal Pyramidal C Tetrahedral D Trigonal Planar 10. The hydroxide ion (OH-) shown to the left has a tetrahedral electron geometry with respect to oxygen. What would its molecular geometry be? A Tetrahedral B Trigonal Pyramidal C Bent 11. Iodate is a polyatomic ion composed of iodine and oxygen. According to the VSEPR theory, what would be the predicted molecular geometry of iodate? A Trigonal planar B Bent C Trigonal pyramidal D Tetrahedral D Linear