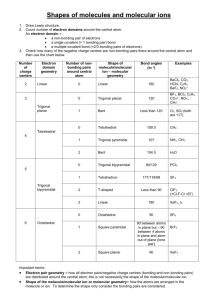
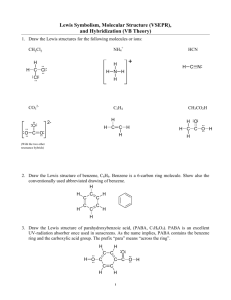
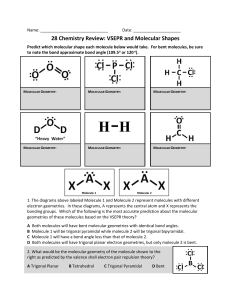
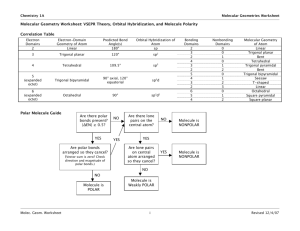
Solutions to Molecular Geometry & Bonding
advertisement

Solutions to Molecular Geometry & Bonding GEOMETRY EXERCISES 1. Determine the molecular shape and polarity of each of the following common substances. CCl4 PF3 H2S Lewis structure 4 4 4 e-pair geometry Tetrahedral Tetrahedral Tetrahedral Molecular shape Tetrahedral Trigonal Pyramid Bent (109.5) NO YES YES Steric number Sketch w/ Bond angles (incl. deviations) & bond polarities Polar Molecule? (Yes or No) 2. Chloramine (NH2Cl) is often used as a substitute for chlorine (Cl2) to disinfect municipal water systems. Determine the molecular shape, bond angles, and polarity of chloramine. Based upon polarity considerations, which do you think is more soluble in water, chloramine or chlorine? Chem 131 Solutions to Molecular Geometry Page 1 3. In last week’s discussion handout, you determined the Lewis structures of sulfur dioxide SO2, nitrate ion NO3−, and chlorine trifluoride ClF3. Determine the molecular shapes and polarities of each of these substances. SO2 NO3− ClF3 3 3 5 e-pair geometry Trigonal planar Trigonal planar Trigonal bipyramidal Molecular shape Bent (120) Trigonal planar T-shaped YES NO (ion) YES Lewis structure Steric number Sketch w/ Bond angles (incl. deviations) & bond polarities Polar Molecule? (Yes or No) 4. Methanol (CH3OH), also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is toxic and hence is often used to “denature” ethanol (drinking alcohol) so that industrial users of ethanol can avoid paying high liquor alcohol taxes. Draw the Lewis structure of methanol, and determine the bond angles around each of the “inner atoms” (C & O) in this molecule. Chem 131 Solutions to Molecular Geometry Page 2 BONDING EXERCISES 5. Analyze the bonding in each of the substances whose geometries were determined in problem 1 earlier. CCl4 has been done for you as an example. Perspective drawing CCl4 PF3 Cl F C Cl Cl ↑↓ Non-bonded e-configuration Cl ↑ ↑ Bonded econfiguration P 2p ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ 3s F ↑↓ ↑ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ P F ↑↓ Chem 131 ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑↓ 3p H ↑ S ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 3sp3 H P Cl 4 σ bonds ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 3s 2p : F Cl .. sp3 F Cl H 1s 2s 3p C S 2p 3sp3 ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ S 1s ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ Cl Balloon drawing H sp3 ↑ ↑ 3s ↑ ↑ 3p 2 sp3 Cl ↑ 2s 3p ↑ : 3s sp3 C : F 2s Hybridization of central atom H P F Cl C H2S F 3 σ bonds Solutions to Molecular Geometry : S H .. 2 σ bonds Page 3 6. Formaldehyde, also known as methanal, has the formula H2CO. Do a complete analysis of this molecule, including drawing a Lewis structure, determining the geometry and polarity of the molecule, and analyzing the bonding configuration. 7. Phosgene, a chemical warfare agent with the formula COCl2, has a very similar structure to formaldehyde above. What are some of the key differences? One difference is that while formaldehyde is very polar (dipole moment of 2.33D), the phosgene molecule is much less polar (1.17D), because the highly electronegative Cl atoms partially offset the polarity caused by the O atom, resulting in a lower net molecular polarity than that of formaldehyde. Also, the C-Cl bonds in phosgene are longer and weaker (and therefore more reactive) than the C-H bonds in formaldehyde. Chem 131 Solutions to Molecular Geometry Page 4