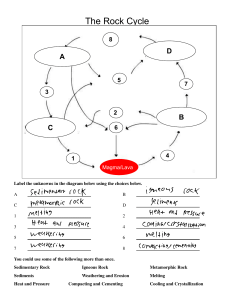
Rock Cycle Concept Map: Processes & Rock Types
advertisement
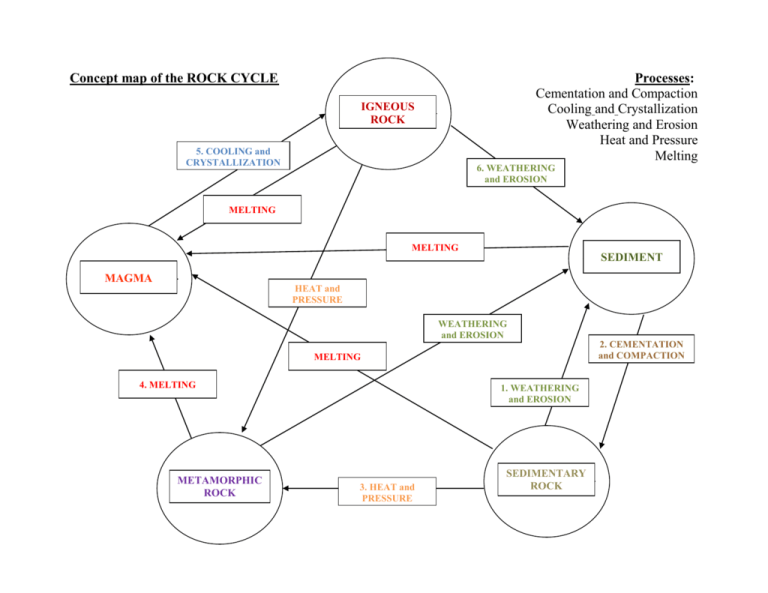
Concept map of the ROCK CYCLE Processes: Cementation and Compaction Cooling and Crystallization Weathering and Erosion Heat and Pressure Melting IGNEOUS ROCK 5. COOLING and CRYSTALLIZATION 6. WEATHERING and EROSION MELTING MELTING SEDIMENT MAGMA HEAT and PRESSURE WEATHERING and EROSION 2. CEMENTATION and COMPACTION MELTING 4. MELTING METAMORPHIC ROCK 1. WEATHERING and EROSION 3. HEAT and PRESSURE SEDIMENTARY ROCK Instructions: Fill in the boxes containing connecting words between the rocks: i.e. how you can make one into another following the arrow. Words you might use are melting, cooling and crystallization, compaction and cementation, weathering and erosion, heat and pressure. You can either supply this word list or have them think on their own depending on the class. Educator Notes: To introduce this concept map, use the powerpoint. Start with the students remembering the three different rock types. Then ask how you would go about changing an igneous rock into a sedimentary rock. This should get them to think of the need to make a sediment first (the sediment circle will appear next on the powerpoint). Next, they should determine that a melt (magma) needs to form first before an igneous rock can be formed so the magma circle needs to be added into our cycle. Once you have the five main rocks and their products, have them discuss what they learned in the sugar cycle activity. What processes are needed to change each rock into the next product. It may be easiest to work in a clockwise manner around the outside of the cycle starting from igneous rock as this way all the processes are covered.