Earth`s Changing Surface Test: Friday, February 13, 2015
advertisement

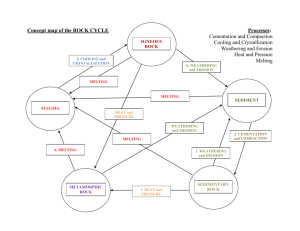
Earth’s Changing Surface Test: Friday, February 13, 2015 Weathering (mechanical vs. chemical), Erosion, Deposition Agents (wind, running water, waves, glaciers, gravity, animals) Which are constructive (building) vs. destructive (destroying) processes? Examples (study that sorting chart and the online practice quiz!) Types of sediments based on size (charts from lab) o Conclusion: larger sediment is harder to erode, but deposits more easily Special features: the Great Lakes, the Grand Canyon, sinkholes, delta formation Topographic Maps Features (mountains/hills, rivers and direction of water flow, cliffs, valleys, etc.) Determining the contour interval or elevation based on a map Types of Rock. How does each form? o Sedimentary: erosion/weathering/deposition of sediment, add water & pressure, (compaction, water evaporates, cementation), often have visible layers o Igneous: cooling & hardening of lava or magma o Metamorphic: an existing rock undergoes a change by heat and pressure and turns into a new rock Fossils (“Getting Into the Fossil Record” online activity info) Formed in what type of rock? Who studies them? Fossil record- How do we use it? What does it tell us? Relative age of rocks/fossils based on layers Difference between relative age and absolute age Pictures with: igneous intrusions, faulting, folding, tilting, erosion, o Put in order from oldest to youngest Earth’s Changing Surface Test: Friday, February 13, 2015 Weathering (mechanical vs. chemical), Erosion, Deposition Agents (wind, running water, waves, glaciers, gravity, animals) Which are constructive (building) vs. destructive (destroying) processes? Examples (study that sorting chart and the online practice quiz!) Types of sediments based on size (charts from lab) o Conclusion: larger sediment is harder to erode, but deposits more easily Special features: the Great Lakes, the Grand Canyon, sinkholes, delta formation Topographic Maps Features (mountains/hills, rivers and direction of water flow, cliffs, valleys, etc.) Determining the contour interval or elevation based on a map Types of Rock. How does each form? o Sedimentary: erosion/weathering/deposition of sediment, add water & pressure, (compaction, water evaporates, cementation), often have visible layers o Igneous: cooling & hardening of lava or magma o Metamorphic: an existing rock undergoes a change by heat and pressure and turns into a new rock Fossils (“Getting Into the Fossil Record” online activity info) Formed in what type of rock? Who studies them? Fossil record- How do we use it? What does it tell us? Relative age of rocks/fossils based on layers Difference between relative age and absolute age Pictures with: igneous intrusions, faulting, folding, tilting, erosion, o Put in order from oldest to youngest