10_Nomenclature molecular compounds
advertisement
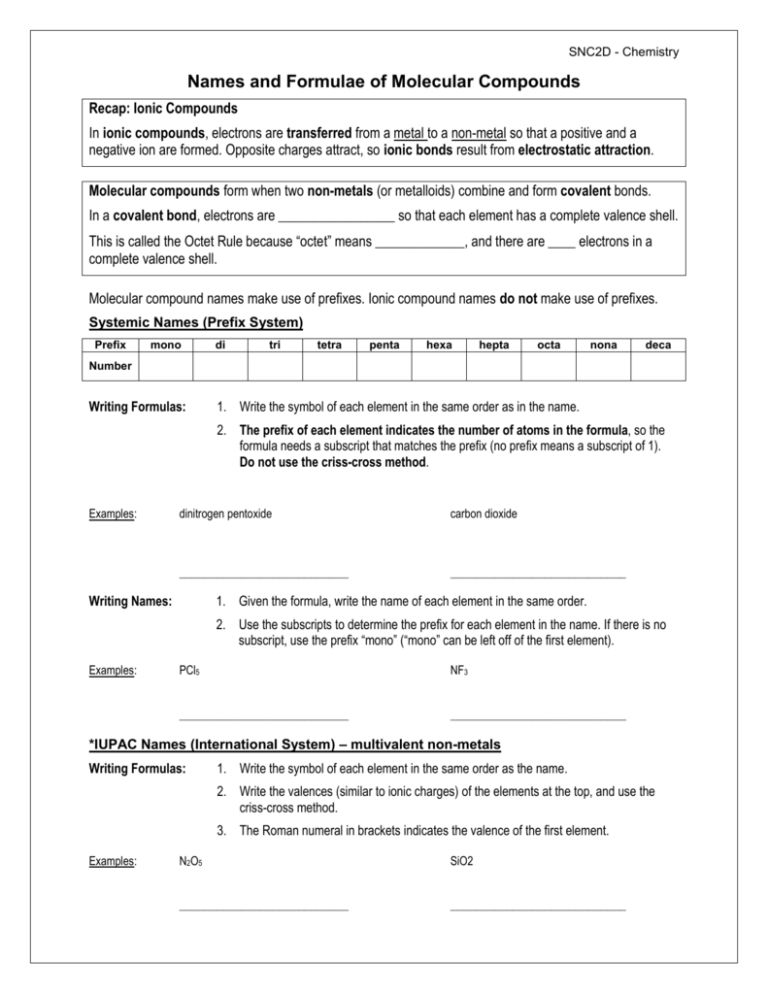
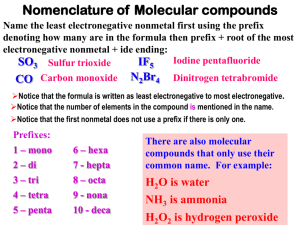
SNC2D - Chemistry Names and Formulae of Molecular Compounds Recap: Ionic Compounds In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred from a metal to a non-metal so that a positive and a negative ion are formed. Opposite charges attract, so ionic bonds result from electrostatic attraction. Molecular compounds form when two non-metals (or metalloids) combine and form covalent bonds. In a covalent bond, electrons are _________________ so that each element has a complete valence shell. This is called the Octet Rule because “octet” means _____________, and there are ____ electrons in a complete valence shell. Molecular compound names make use of prefixes. Ionic compound names do not make use of prefixes. Systemic Names (Prefix System) Prefix mono di tri tetra penta hexa hepta octa nona deca Number Writing Formulas: 1. Write the symbol of each element in the same order as in the name. 2. The prefix of each element indicates the number of atoms in the formula, so the formula needs a subscript that matches the prefix (no prefix means a subscript of 1). Do not use the criss-cross method. Examples: dinitrogen pentoxide carbon dioxide ___________________________ ____________________________ Writing Names: 1. Given the formula, write the name of each element in the same order. 2. Use the subscripts to determine the prefix for each element in the name. If there is no subscript, use the prefix “mono” (“mono” can be left off of the first element). Examples: PCl5 NF3 ___________________________ ____________________________ *IUPAC Names (International System) – multivalent non-metals Writing Formulas: 1. Write the symbol of each element in the same order as the name. 2. Write the valences (similar to ionic charges) of the elements at the top, and use the criss-cross method. 3. The Roman numeral in brackets indicates the valence of the first element. Examples: N2O5 SiO2 ___________________________ ____________________________ SNC2D - Chemistry Practice I. Write the correct formulae for the following: 1. nitrogen pentachloride 2. silicon tetrabromide 3. arsenic trioxide 4. diarsenic trisulfide 5. carbon monoxide 6. dihydrogen monoxide 7. *carbon (II) sulfide 8. *carbon (IV) chloride 9. *silicon (II) chloride 10. *nitrogen (V) sulfide Practice II. Write the names of the following, using the prefix system 1. AsI3 2. CCl4 3. NH3 4. CS 5. P2S5 6. SiBr4 7. N2S3 8. SiO2 SNC2D - Chemistry