Nomenclatura Chimica: Foglio di Lavoro Sistema Prefissi Greci
advertisement

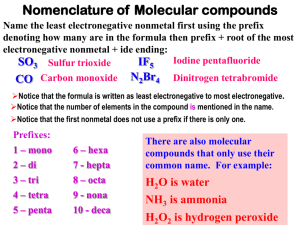
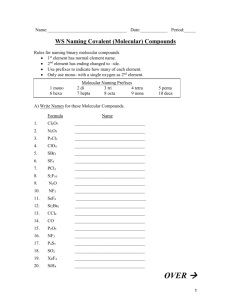
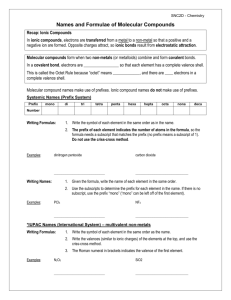
Chemical Nomenclature: The Greek Prefix System Rev. 021712 Part three - Binary compounds of two nonmetals Simple binary compounds composed of two nonmetals do not use the Stock system. Instead, Greek prefixes are used to indicate the number of each element. To use the Greek prefix system… 1. Write the name of the first element and include a Greek prefix to indicate the number of atoms of that element. 2. Write the name of the second element with the name modified to end in "-ide", and include a Greek prefix to indicate the number of atoms of that element. Greek prefixes mono 1 di 2 tri 3 tetra 4 penta 5 hexa hepta octa nona deca 6 7 8 9 10 Examples Write the name, given the formula: CO2 → carbon dioxide SO3 → sulfur trioxide CCl4 → carbon tetrachloride N2O3 → dinitrogen trioxide P4O10 → tetraphosphorous decoxide Write the formula, given the name: silicon dioxide → SiO2 dichlorine oxide → Cl2O phosphorous pentachloride → PCl5 dinitrogen pentoxide → N2O5 arsenic tribromide → AsBr3 Note: When a prefix ending in "a" or "o" precedes a vowel, the final "a" or "o" is dropped. For example, drop the "o" in mono in "carbon monoxide". Drop the "a" in tetra in "dinitrogen tetroxide". Write the name of each compound. 1. PCl3 2. CO 3. BF3 4. SCl6 5. XeF4 6. AsBr5 7. N2O5 8. SO2 9. N2O 10. KrF2 Write the formula of each compound. 1. sulfur trioxide 2. Iodine heptafluoride 3. dichloroine trioxide 4. arsenic triiodide 5. diphosphorous trioxide 6. nitrogen trichloride 7. selenium monoxide 8. silicon tetrafluoride 9. chlorine pentafluoride 10. xenon hexafluoride Review: Balance the following chemical equations O2(g) → SO3(g) 1. S(s) + 2. PH3(g) + 3. C2H6(g) + O2(g) → 4. Cl2O(g) + HF(g) → ClF(g) + H2O(l) 5. As2O5(s) + H2O(l) → H3AsO4(aq) O2(g) → H3PO4(l) CO2(g) + H2O(l) Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. PCl3 → phosphorous trichloride CO → carbon monoxide BF3 → boron trifluoride SCl6 → sulfur hexachloride XeF4 → xenon tetrafluoride AsBr5 → arsenic pentabromide N2O5 → dinitrogen pentoxide SO2 → sulfur dioxide N2O → dinitrogen oxide KrF2 → krypton difluoride 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. sulfur trioxide → SO3 Iodine heptafluoride → IF7 dichloroine trioxide → Cl2O3 arsenic triiodide → AsI3 diphosphorous trioxide → P2O3 nitrogen trichloride → NCl3 selenium monoxide → SeO silicon tetrafluoride → SiF4 chlorine pentafluoride → ClF5 xenon hexafluoride → XeF6 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2S(s) + 3O2(g) → 2SO3(g) PH3(g) + 2O2(g) → H3PO4(l) 2C2H6(g) + 5O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) Cl2O(g) + 2HF(g) → 2ClF(g) + H2O(l) As2O5(s) + 3H2O(l) → 2H3AsO4(aq)