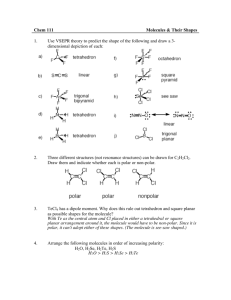
Polar Molecule
advertisement

Activity #10.5: Polarity of Molecules AP Chemistry What effect does the shape or geometry of the molecule have on molecular polarity? Why? Why are oil and water mixtures immiscible? What causes sugar to dissolve in water? The geometry of a molecule has an effect on physical properties such as solubility. How can the molecular geometry be used to predict properties? Model 1 Non Polar Molecule CH4 Polar Molecules NH3 H2O # Bonding electron pairs # Lone pairs of electrons on central atom AB designation E 1. Complete the table in Model 1. Determine the # of Bonding electron pairs and # of lone pairs of electrons for each species. Compare your answers with your team members. E 2. Identify the AB type for each molecule and check with your team members. E 3. a b. I What is the number of lone pairs of e- in the non polar molecule. What is the number of lone pairs of e- in the polar molecules 4. Write a cohesive sentence that explains the relationship between lone pairs and polarity of a molecule. 5. Draw and picture of CH2H2. Determine the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs of electrons. Is this a polar molecule? Explain. Model 2 Non Polar Molecules Polar Molecules Key = Carbon ( EN =2.5) = Chlorine (EN= 2.7) = Hydrogen (EN = 2.3) E 6. Write the formulas and names for the non-polar molecules. E 7. Write the formulas and names for the polar molecules. E 8. What do the non-polar molecules have in common? E 9. What do the polar molecules have in common? I 10. By observing Model 2, what is the main reason a non-polar molecule to exhibit polarity? Be specific. Compare your answer to your team members and reach a consensus. E 11. Determine the ΔEN for each of the bonds and write the results on the model. 12. Look at Model 2 and write down any trends in polar and non-polar molecules and ΔEN E I 13. Using Models 1 and 2. What are THREE factors that determine if a molecule is polar. a. b. c. I 14. Using Models 1 and 2. What are THREE key characteristics of a non-polar molecule? a. b. c. 15. Using the concepts developed on whether a molecule is polar or non-polar, fill in the table below. A Geometry ABE Form Non-Polar or Polar Extension Questions: 1. Write the Lewis Dot Structure for the following compounds. Predict the molecular geometry, AB form, and molecular polarity. a. NO3- b. SO2 c. SF4 d. XeF4 e. PCl5 HSPI Activity #10.5: Polarity of Molecules Teacher Guide AP Chemistry Objectives o Students will distinguish between polar bonds and polar molecules. o Students will be able to compare and contrast polar and non polar molecules by o utilizing EN differences of bonds in conjunction with molecular shape and symmetry. Students will be able to discover that lone pairs of electrons can have an effect on molecular polarity Prerequisites o o o o Students should be proficient in drawing Lewis dot structures for molecules. . Students should be able to predict molecular shape, AB form and bond angles. Students should be able to define polar and nonpolar bonds. Students need to determine EN differences of bonds and use the calculated value to predict the type of bonding. Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for SOCl2? a) d) b) e) c) 2. Which one of the following molecules is a polar molecule? a) c) b) d) 3. If a molecule has an AB3 form, draw the possible Lewis structures, identify the AB format, molecular shape and explain molecular polarities ( if all bonded atoms are the same species) Teacher Tips 1. Molecular model kits should be available for student use. The models aid in determining polarity of the molecule 2. It is recommended that students be given opportunities to practice a variety of molecules. Targeted Responses Activity #10.5: Polarity of Molecules AP Chemistry What effect does the shape or geometry of the molecule have on molecular polarity? Why? Why are oil and water mixtures immiscible? What causes sugar to dissolve in water? The geometry of a molecule has an effect on physical properties such as solubility. How can the molecular geometry be used to predict properties? Model 1 Non Polar Molecule # Bonding electron pairs # Lone pairs of electrons on central atom AB designation Polar Molecules CH4 4 NH3 3 H2O 2 0 1 2 AB4 AB3E AB2E2 E 1. Complete the table in Model 1. Determine the # of Bonding electron pairs and # of lone pairs of electrons for each species. Compare your answers with your team members. E 2. Identify the AB type for each molecule and check with your team members. E 3. a. What is the number of lone pairs of e- in the non polar molecule. 0 b. What is the number of lone pairs of e- in the polar molecules. >0 1 and 2 4. Write a cohesive sentence that explains the relationship between lone pairs and polarity of a molecule. When a molecule has 1 or more lone pairs, the molecule is polar. I 5. Draw and picture of CH2H2. Determine the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs of electrons. Is this a polar molecule? Explain. Model 2 Non Polar Molecules Polar Molecules ΔEN = 0.4 C-H: ΔEN = 0.4 C-Cl: ΔEN = 0.5 ΔEN = 0.5 C-H: ΔEN = 0.4 C-Cl: ΔEN = 0.5 C-H: ΔEN = 0.4 C-Cl: ΔEN = 0.5 Key = Carbon ( EN =2.5) = Chlorine (EN= 3.0) = Hydrogen (EN = 2.1) E 6. Write the formulas and names for the non-polar molecules.CH4 CCl4 E 7. Write the formulas and names for the polar molecules. CH3Cl CH2Cl2 CHCl3 E 8. What do the non-polar molecules have in common? Same type of atoms attached to the central atom (carbon) E 9. What do the polar molecules have in common? Different types of atoms attached to the central carbon ( Cl, H) I 10. By observing Model 2, what is the main reason a non-polar molecule to exhibit polarity? Be specific. Compare your answer to your team members and reach a consensus. The main reason a non-polar molecule exhibits polarity is due to different types of atoms ( with different EN values) attached to the central atom. E 11. Determine the ΔEN for each of the bonds and write the results on the model. 12. Look at Model 2 and write down any trends in polar and non-polar molecules and ΔEN As the ΔEN increases between the central atom and the surrounding atoms, the greater the possibility the molecule is polar. E I 13. Using Models 1 and 2. What are THREE factors that determine if a molecule is polar. a. If the central atom is surrounded by different types of atoms that may have different EN values b. If the molecule is symmetrical around the central atoms c. If there are lone electron pairs I 14. Using Models 1 and 2. What are THREE key characteristics of a non-polar molecule? a. Atoms attached to the central atom are the same with the same EN values. b.The molecule is symmetrical c. There are no lone electron pairs. 15. Using the concepts developed on whether a molecule is polar or non-polar, fill in the table below. A Geometry ABE Form Non-Polar or Polar AB5 Non- Polar AB4 E Polar AB3 E2 Polar AB5 E Polar AB4 E2 Non- Polar AB2 E3 Non- Polar Extension Questions: 1. Write the Lewis Dot Structure for the following compounds. Predict the molecular geometry, AB form, and molecular polarity. a. NO3- Trigonal planar AB3 Ion Resonance Bent AB2E Polar Resonance See Saw AB4E Polar ABrE2 Non-Polar b. SO2 c. SF4 d. XeF4 Square Planar e. PCl5 Trigonal Bipyramidal AB5 Non-Polar HSPI Activity #10.5: Polarity of Molecules Teacher Guide AP Chemistry Objectives o Students will distinguish between polar bonds and polar molecules. o Students will be able to compare and contrast polar and non polar molecules by o utilizing EN differences of bonds in conjunction with molecular shape and symmetry. Students will be able to discover that lone pairs of electrons can have an effect on molecular polarity Prerequisites o o o o Students should be proficient in drawing Lewis dot structures for molecules. . Students should be able to predict molecular shape, AB form and bond angles. Students should be able to define polar and nonpolar bonds. Students need to determine EN differences of bonds and use the calculated value to predict the type of bonding. Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for SOCl2? B a) d) b) e) c) 2. Which one of the following molecules is a polar molecule? B a) c) b) d) 3. If a molecule has an AB3 form, draw the possible Lewis structures, identify the AB format, molecular shape and explain molecular polarities ( if all bonded atoms are the same species) Possible AB Forms: AB3 ( Trigonal Planar – Non-Polar- no lone pairs, symmetrical ) AB3E ( Trigonal Pyramidal – Polar- 1 lone pair, asymmetrical) AB3E2 (T-Shape- Polar- 2 lone pairs, asymmetrical) AB3E3 (T-Shape- Polar- 3 lone pairs, asymmetrical)