Ligaments and tendon..
advertisement

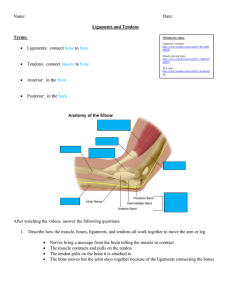
Ligaments: Strong band of white fibrous connective tissue (fibrous connective tissue which attaches bone to bone Joins bones to other bones Joins bones to fibrocartilage Bundles of collagenous fibers Provide stability of joints during motion In 2 or 3D ??? serves to hold structures together and keep them stable during motion Pliable but not elastic Limit freedom of movement Hold the attached bones in place Forms fibrous sheet - Support internal organs Kidneys spleen Load transmission from where to where? Help determine motions between opposing fibro-cartilage surfaces http://adam.about.com/encyclopedia/19089.htm also slides on stabilizing role (chart?) and degrees of freedom Tendons: Interposed between muscles and bones Muscles attach to bones via tendons Transmit the force created in the muscle to bone Make joint movement possible A tendon is a fibrous connective tissue which attaches muscle to bone. Tendons may also attach muscles to structures such as the eyeball. A tendon serves to move the bone or structure. http://adam.about.com/encyclopedia/19089.htm Long cylindrical structures Tightly packed longitudinally running collagen fibers Nuclei and sparse cytoplasm of fibrocytes compressed almost flat between them. Relatively avascular Slow to heal from trauma injuries Basically each muscle has two tendons: Proximal Distal The attachment of the proximal tendon - muscle origin The attachment of the distal tendon - insertion The myotendinous junction ( MTJ) The point of union with a muscle The osteotendinous junction (OTJ) The point of union with a bone Force transmission Sustain high tensile stresses Saves substantial muscular energy during locomotion Energy storage capacity Enables the muscle belly to be at a convenient distance from joint Satisfies kinematic and damping requirements Also slides on mechanical properties