CHEMISTRY-CP, CHAPTER 9
advertisement

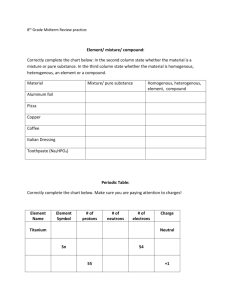
CHEMISTRY-CP, CHAPTER 9 CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND BONDING OBJECTIVES Describe the development of the periodic table Define periodic table and periodic law Identify and define groups and periods Name the groups on the periodic table Identify an element as either a solid, liquid, or gas based on the periodic table. Determine if an element is radioactive or synthetic based on its position on the periodic table Describe the following periodic properties of the periodic table: energy levels, valence electrons, and Lewis Dot Diagrams Define the octet rule Determine the oxidation numbers of the elements and describe the pattern of oxidation numbers found on the periodic table Distinguish between metals, nonmetals and metalloids State the octet rule Define ion, monatomic ion, polyatomic ion, cation and anion Name anions and cations Write ion symbols Identify and name the polyatomic ions Illustrate how ionic bonds form Define ionic and covalent bonds Define binary ionic compound & ternary ionic compound and give examples of each Name ionic compounds Determine the empirical formula of an ionic compound State the prefixes used in naming Name and write the chemical formulas for molecular compounds Define hydrate and anhydrous Name and write the chemical formulas for hydrates Describe how to tell a compound is a hydrate Name and write the chemical formulas for acids CHAPTER VOCABULARY (VOCABULARY QUIZ ON THURSDAY, OCTOBER 25) Acid Element Molecule Alkali Metal Empirical Formula Monatomic Ion Alkaline Earth Metal Formula Unit Noble Gas Anion Group Nonmetal Binary Compound Halogen Octet Rule Cation Hydrate Monatomic Ion Chemical Formula Inner Transition Metal Oxidation Number Chemical Symbol Ion Period Compound Ionic Bond Periodic Law Covalent Bond Ionic Compound Periodic Table Diatomic Molecule Metal Polyatomic Ion Electron Metalloid Precipitate Electron Dot Structure Molecular Compound Transition Metal Transuranium Element Unshared Pair Valence Electron In 1860, ___________________ elements had been discovered J.W. Dobereiner (early 1800’s): Triads had: Examples of triads: Important because: Dmitri Mendeleev (1869): Listed the elements according to __________________________________________. Important because: Periodicity: Examples of Periodicity: Allowed him to: Henry Moseley: Listed the elements according to ________________________________________. Important because: The modern periodic table is listed in order of _____________________________. Periodic Law: Periodic Table: Element Key: Groups(Families): There are _______________ groups labeled with the numbers ______________________. Group Number/Location 1 2 3-12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Atomic #57-70 Atomic #89-102 (bottom row) Group Name Periods: There are _________________ periods labeled with the numbers __________________. Practice Problems Identify the element with the following designation: a) Group 2, Period 2 ____________________ b) Group 18, Period 6 ___________ c) Group 14, Period 5 ____________________ d) Group 3, Period 6 ___________ e) Alkali Metal in Period 2 ____________________ f) Noble gas in Period 4 ___________ g) First Lanthanide ____________________ h) Halogen in Period 5 ___________ States of Matter: Solids: Liquids: Gases: Practice Problems Identify each of the following as either a solid, a liquid or a gas. a) Arsenic ___________________ b) neon c) Halogen in Period 4 ___________________ d) element in period 5, Group 12________ Types of Elements 1) Metals: Properties of Metals: Luster: _________________ Malleable: Ductile: Location of Metals: Exception: 2) Nonmetals: Properties of Nonmetals: Location of Nonmetals: Exception: 3) Metalloids: Properties of Metalloids: Location of Metalloids: Exception: Practice Problems Identify each of the following elements as a metal, a nonmetal or a metalloids. a) Potassium _______________________ b) Antimony ______________________ c) Carbon d) Boron _______________________ ______________________ Identify each of the following elements. a) An element in Period 6 that does not conduct electricity and is a gas __________________ b) An element in Group 13 that has some metallic properties & some nonmetallic properties______________ c) A liquid that conducts electricity ________________________ Radioactive Elements: Radioactivity: Elements are radioactive because they have too many or too few ____________________________. Synthetic Elements: Synthetic elements are __________________________. Electrons are located __________________________________in _______________________________. Energy Level 1 can hold a maximum of ____________ electrons Energy Level 2 can hold a maximum of ____________ electrons Energy Level 3 can hold a maximum of ____________ electrons Energy Level 4 can hold a maximum of ____________ electrons Valence Electrons: o Pattern for the # of valence electrons within the representative elements Group 1 2 13 14 15 16 17 18 o Transition Metals: Exceptions Silver is always _________________ Zinc is always __________________ o Inner Transition Metals: Practice Problems How many valence electrons does each of the following elements have? a) phosphorus____________________ b) calcium _____________________ c) zinc d) fluorine _____________________ ____________________ e) uranium ____________________ Lewis Dot Diagrams: f) germanium _____________________ Practice Problems Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram for each of the following elements. a) Iodine __________________________ b) Aluminum ________________________ c) Xenon __________________________ d) Silver ________________________ Oxidation Number: o Ion: o Octet Rule: If an element loses electrons, its oxidation # is a ___________________ number because: Cation: o Elements with 1-3 valence electrons: If an element gains electrons, its oxidation # is a __________________ number because: Anion: o Elements with 5-8 valence electrons: o Elements with 4 valence electrons: Pattern for the oxidation #s of elements within the representative elements: Group 1 2 13 14 15 16 17 18 o Transition Metals: Exceptions Zinc is always _________________ Silver is always ________________ o Inner Transition Metals: Monatomic Ions: Cation: o To Name a Cation: Transition Metals: o To Name a Transition Metal: Except: Anion: o To Name: Ion Symbol: Example: Write the ion symbol for the ions formed from the following elements. a) Lithium b) Aluminum c) Silver d) Phosphorus e) Selenium g) Bromine Example: Name the following ions. a) Fe2+ b) Cl- c) N3- d) K+ f) P3- e) Zn2+ Polyatomic Ions: -Names typically end in: -The only positively charged polyatomic ion is: -Where should you look to find the polyatomic ions? Example: Name the following ions. a) PO4 3- b) O2- Example: Write the symbols for the following ions. a) nitride b) nitrate Ionic Compound: o Binary Ionic Compound: c) NH4+ c) nitrite o Ternary Ionic Compound: o Ionic Bond: An ionic bond is formed between an ______________________ and a __________________________ because: Therefore, ionic bonds form between ___________________ and ______________________________ because: Electrons are ________________________________ in an ionic bond because: Empirical Formula: o Subscripts: Shows: Three different ways to determine the empirical formula (all get the same result): To illustrate an ionic bond to determine the empirical formula: Examples: a) Show how an ionic bond forms between sodium and iodine. b) Show how an ionic bond forms between calcium and chlorine. c) Show how an ionic bond forms between aluminum and oxygen. To use charges to determine the empirical formula: Examples: Write the chemical formulas for the compounds formed from the following two ions. a) Potassium and chloride b) Ammonium and sulfide The Crisscross method of determining the Empirical Formula Example: Use the crisscross method to determine the empirical formulas for the compounds formed from the following two ions. a) zinc and oxide b) Sodium and hydroxide To Name an Ionic Compound 1) Ex. 1—CaCl2 Ex. 2—Fe2O3 Ex. 3--NaOH 2) 3) Ionic Compound Examples: 1) Name the following compounds: a) MgS b) CaSO4 2) Write the chemical formulas for the following compounds. Cobalt(II) chloride b. potassium bromide c) Cu(C2H3O2)2 c. manganese(IV) oxide Covalent Compound (Molecular Compound): Covalent Bond: A covalent bond is formed between 2 or more __________________ Electrons are ________________________________ in a covalent bond because: Molecule: 1. Diatomic Molecules: a. The 7 Diatomic Molecules: Molecular Substance: Naming Molecular Compounds -Numerical Prefixes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 -To Name a Molecular Compound: Examples--Name the following molecular compounds: a) N2O4 b) PCl5 c) NO2 -To Write the Chemical Formula of a Molecular Compound: Example—Write the chemical formulas for the following molecular compounds. a) nitrogen trifluoride b) diphosphorus pentoxide c) carbon tetrachloride Other Types of Compounds: -Hydrates: -Anhydrous: -To Name a Hydrate: Example: Name the hydrate MgSO4 2H2O. -To Write the Chemical Formula of a Hydrate: Example: Write the chemical formula for copper(II) pentahydrate. -Acid: -start with: -To Name a Binary Acid: Example: HCl To name a ternary acid: Example: Name HNO3 Other Common Acids: HNO3 = nitric acid H2CO3 = carbonic acid H2SO4 = sulfuric acid H3PO4 = phosphoric acid HC2H3O2 = acetic acid