Ionic Bonding Lab: Modeling Compounds & Electron Transfer
advertisement

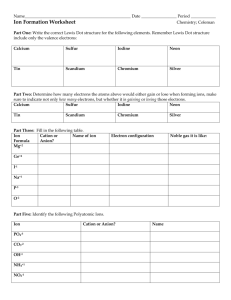
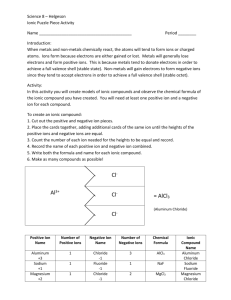
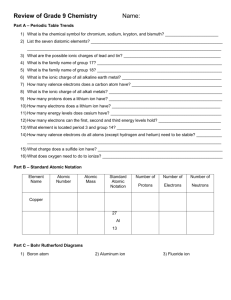
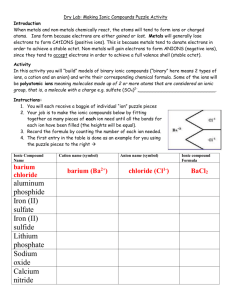
Student page IPC Paper Ions Enduring Understandings All matter in the universe is composed of the same basic building blocks. Specific properties determine the behavior of matter. Concepts Important to Know and Understand chemical reactions, atomic structure EQ: Can I eat off the periodic table? How do chemical reactions keep me alive? ? Targeted Skills Using the periodic table Using a model Broad Brush Knowledge Bonding, chemical formulas and equations, valence electrons Core Objectives 1. Demonstrate the proper use and care of laboratory equipment and supplies. 6. Predict an element’s behavior based on its location on the periodic table. 7. a) Differentiate between ionic and covalent bonding. Purpose Construct models of compounds forming between two ions. Materials Set of Ion cards Scissors Glue Construction paper Markers Lab Preview 1. How many electrons must be in the outer shell for an element to be chemically stable? 2. How do the electrons behave during ionic bonding? 3. What types of elements do we expect to join together with ionic bonds? Procedure 1. Before you begin, place the valence electrons in their proper place using E-dot diagram structures on each “ion”. 2. Cut the ions apart from one another. 3. In the data chart below, are + ions and – ions that will bond to form a compound. Your job is to find how many of each you need to form a stable compound. 4. Glue each model onto the construction paper with the + ion(s) on the left and the – ion(s) to the right. 5. Draw arrows showing the path of electrons moving. 6. Write the formula for the compound formed under the model and also in your data chart. updated 6/11/2003 1 Student page Positive ion Negative ion Al Br Na O Na I K S Li Cl Al O Na P Formula Data Analysis 1. List the similarities between lithium chloride and sodium iodide. 2. Why might lithium lose one electron rather than gain 7 electrons? 3. When electrons leave aluminum, what happens to the balance of positive and negative charges? What is aluminum’s oxidation number? 4. What happens to oxygen’s charge when it gains the electrons from the aluminum atom? What is oxygen’s oxidation number? 5. When sodium and chlorine form a chemical bond, what is the overall charge of the molecule? Why do you think sodium and chlorine combine in a 1:1 ratio? updated 6/11/2003 2 Student page Br Br P O O O S Cl Br I O Al Na K K Na Al Al Na Li Na Na Na updated 6/11/2003 3