Biochemistry Study Guide Answers 2014
advertisement

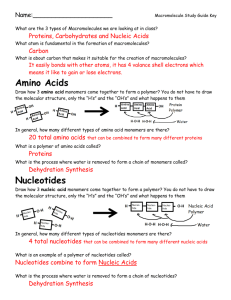
Name__________________________ Period:_________ Date:______ Biochemistry Study Guide 1. What is a macromolecule? Large organic molecules that are necessary for life. There are four major macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. 2. What is an organic molecule? Any molecule that at least contains the elements carbon (C) and hydrogen (H). 3. What is a monomer? Monomers are the building blocks or small subunits of large macromolecules. At least two Monomers put together make a Polymer. 4. What is a polymer? A polymer is many subunits, or monomers, put together to form a macromolecule. 5. Name AND draw the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates. + Monosaccharide (Monomer) + + Polysaccharide (polymer) + Disaccharide (polymer) 6. Name AND draw the monomers and polymers of proteins. AA Amino Acid (monomer) AA AA AA Polypeptide Chain (polymer) 7. Name AND draw the monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotide (Monomer) 8. Name AND draw the monomers of lipids. glycerol 3 fatty acids 9. Name and explain the reaction? This is Dehydration Synthesis We have two monomers on the reactants side (two amino acids=monomers for proteins). On the products side after the yield sign, we have a large polymer or protein and water. Water is therefore leaving the reaction so we are dehydrating. We are also building or synthesizing, going from small to large. 10. Name and explain the reaction? This is Hydrolysis (water breaking) We have a large Protein (CHON) and water on the reactants side meaning that water is being added to the protein. On the products side we have two monomers with the HO attached. We are going from large (polymer) to small (monomers) 11. What are the functions of lipids? To provide the body with long term energy, make up the cell membrane which allows it to be selectively permeable, Insulates the body. 12. What are the functions of carbohydrates? Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for all living things. 13. What are the functions of proteins? Help fight disease (white blood cells), control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes (Enzymes), used to form body tissues. 14. What are the functions of nucleic acids? Store and transmit heredity 15. What were Miller and Urey trying to prove? Simple organic molecules in the early Earth’s atmosphere can form complex organic molecules. 16. What type of biomolecule is an enzyme and what do they do? Enzymes are special proteins that increase the speed of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. Enzymes are especially important in processes such as digestion. 17. If Enzyme 3 is destroyed, what molecule will build up in the body? Galactose 1 phosphate will increase because Enzyme 3 is not there to help it break down quickly. 18. Label each part of the diagram with the appropriate term: a. Enzyme Structure Y b. Substrate Structure X c. Active Site Structure W d. Product Structure Z Structure W