2010 - Louisiana Tech University
advertisement

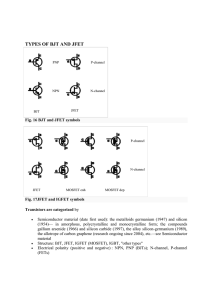
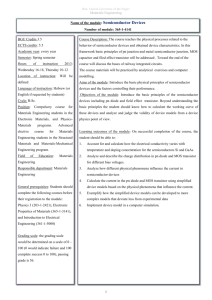
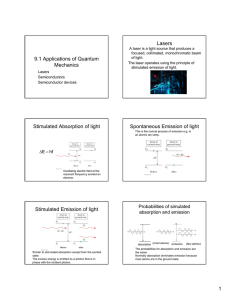
ELEN 334 SYLLABUS FALL 2010 Solid State Electronics, Dr. Sandra Zivanovic Course Description: In this undergraduate course students will familiarize with the physical properties of semiconductor materials and methods of growing semiconductor crystals. We will investigate the electronic structure of atoms and the interaction of atoms and electrons. We shall give a brief introduction to quantum mechanics. The specific mechanisms by which current flows in a solid will be addressed and fundamental concepts of charge transport explained. We will study the mechanism of electron-hole pair recombination, the diffusion of excess carriers and the mechanism of the drift in an electric field. Then we will learn about p-n junctions, the equilibrium state of the junction, the flow of electrons and holes across a junction. Most important, students will gain the knowledge about the operations, and applications of a field-effect transistor (FET) and bipolar junction transistor (BJT). If time permits, students will be introduced to photodiodes, solar cells, light emitting diodes, and lasers. Goal: Students successfully completing the course will understand how p-n junction devices work from first principles. Prerequisites: ENGR221, PHYS 202, and MATH244. Cumulative GPA≥2.0 for MATH240 through MATH244. Textbook: Semiconductor Physics and Devices, Basic Principles, Donald Neamen, Third Edition, 2003. Reference Books: Solid State Electronic Devices, B. G. Streetman and S. Banerjee, Prentice Hall. Introduction to Electronic Circuit Design, Richard Spencer, Mohammed Ghausi, Prentice Hall, 2003. Chapter 2. Introduction to Semiconductor Devices, Donald Neamen, First Edition, 2006. Class: Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 9:30-10.45am, Nethken Hall Room 140 Consultations: After the class. Grading: Exam1 30%, Exam2 30%, Final 30%, Homework 10%. Scale Used: A = 100-90%, B = 89-80%, C = 79-70%, D = 69-60%, F = below 60%. Exams: For exams students must work independently. Homework: Completed assignements should be turned in by the beginning of class on the due date either in class or in the box in IfM in front of my office #219. Unless the assignment specifies otherwise, you can work individually or in a team of two, handing one team solution per assignment. Strong suggestion: Each member team should set up each problem individually (define unknowns, outline the solution procedure), then get together to work out details. Computer Account: Each student must have his/her user account on the university computer network (i.e. userid@coes.latech.edu). 1 Blackboard Account: The students in this class should use the course material, syllabus, homework and exam solutions, discussion boards, announcements, etc. available at http://blackboard.latech.edu. To login for the first time, please use your LaTech username and your initial password is your SSN# (or PIN). If you have a problem to login, send me an e-mail. Attendance: Class attendance is governed by university regulations published each year in the university bulletin. Class attendance is regarded as an obligation as well as a privilege, and all students are expected to attend regularly and punctually all classes in which they are enrolled. Failure to do so may jeopardize a student’s scholastic standing and may lead to suspension from the college or university. Accommodations for Students with Disabilities: Students needing testing or classroom accommodations based on a disability are encouraged to discuss those needs with me as soon as possible. Academic Honor Code: In accordance with the Academic Honor Code, students pledge the following: Being a student of higher standards, I pledge to embody the principles of academic integrity. http://www.latech.edu/documents/honor-code.pdf Misconduct: Academic misconduct is governed by university regulations published each year in the university bulletin. Academic misconduct at the University is determined by the faculty member under whom such misconduct occurs. The penalty for cheating and other forms of misconduct is also determined by the faculty member. The penalty may be an “F” in the course. Emergency Notification System (ENS): All Louisiana Tech students are strongly encouraged to enroll and update their contact information in the Emergency Notification System. It takes just a few seconds to ensure you’re able to receive important text and voice alerts in the event of a campus emergency. For more information, please visit: http://www.latech.edu/administration/ens.shtml. Contact Information: Sandra Zivanovic, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering Institute for Micromanufacturing (IfM) Office: 911 Hergot Avenue, office #219 Tel. 318 257 5145 E-mail: sz@latech.edu Important Dates: First day of class: Friday, September 10 Exam 1: Friday, October 1 Exam 2: Friday, October 22 Final Exam: Monday, November 15 Last day of class: Wednesday, November 17 The Semiconductor Applet Service: http://jas.eng.buffalo.edu/ Summary of Basic Properties of Semiconductors: http://www.elec.gla.ac.uk/groups/sim_centre/courses/basic/basic_1.html 2 Tentative Course Schedule: Week 1 2 2 2 3 Date 09/10 09/13 09/15 09/17 09/20 3 09/22 3 09/24 4 09/27 4 4 5 09/29 10/01 10/04 5 5 6 6 10/06 10/08 10/11 10/13 6 10/15 7 7 7 8 8 10/18 10/20 10/22 10/25 10/27 8 9 9 10/29 11/01 11/03 9 10 10 10 11 11 11/05 11/08 11/10 11/12 11/15 11/17 Course Topics Chapter 1: Crystal Properties of Semiconductors Chapter 2: Short course in Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2: Atom and Potential Well Problem Chapter 2: Atom and Potential Well Problem Chapter 3: Bonding, Energy Gap, Electrons, Holes, Effective Mass, Intrinsic&Extrinsic Semiconductors Chapter 3: Bonding, Energy Gap, Electrons, Holes, Effective Mass, Intrinsic&Extrinsic SemiconductorsContinued Chapter 3: Fermi Level, Electron and Hole Concentration in Equilibrium Chapter 3: Fermi Level, Electron and Hole Concentration in Equilibrium Review Review/Questions Exam 1 Chapter 4: Temperature Dependence of Carrier Concentration Chapter 5: Drift and Diffusion Chapter 5: Conductivity, Resistivity, Mobility Chapter 5: Conductivity, Resistivity, Mobility Chapter Chapter 6: Nonequilibrium Excess Carriers in Semiconductors 7: P-N Junction, Contact Potential Chapter Problem Session 7: Space Charge, Current Flow Review/Questions Exam 2 Chapter 8: Current Flow, Forward and Reverse Bias Chapter 8: Reverse Bias, Zener and Avalanche Breakdown Chapter 10: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Chapter 10: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Cont. Chapter 11/12: Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET ( MOSFET) Chapter 13: Field Effect Transistor FET Video: Silicon Run I and II Review/Questions Review/Questions Final Exam Consultations 3