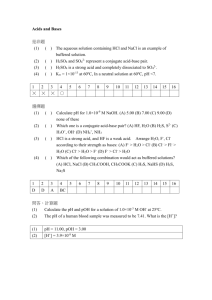
Acid-Base Problem Set #1
advertisement
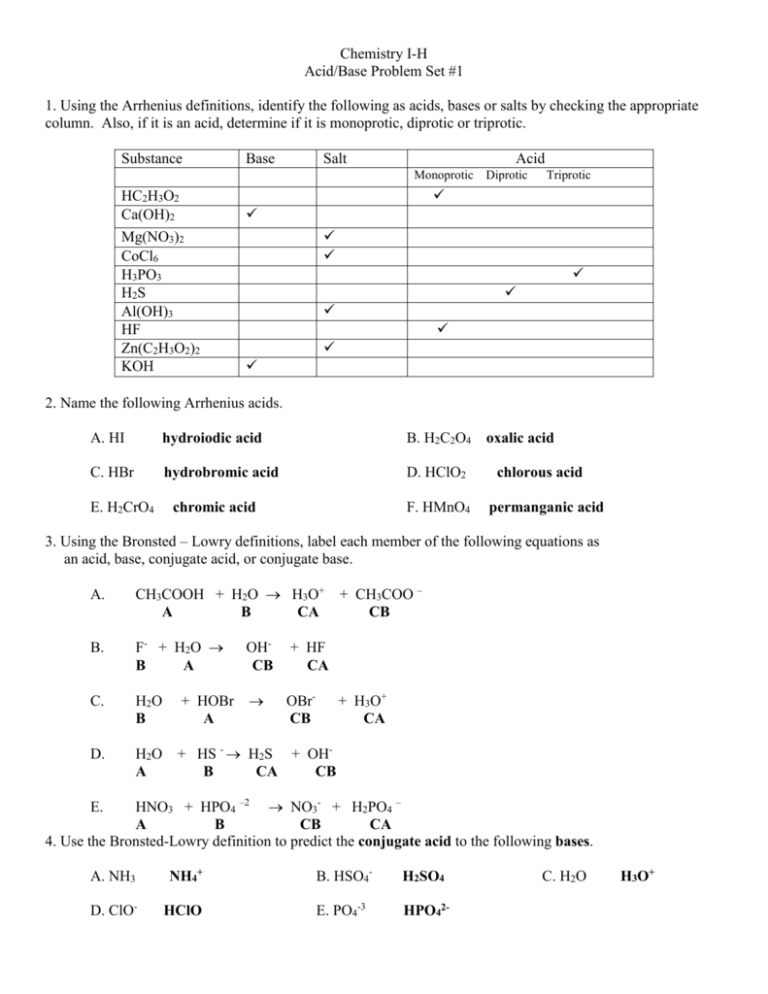
Chemistry I-H Acid/Base Problem Set #1 1. Using the Arrhenius definitions, identify the following as acids, bases or salts by checking the appropriate column. Also, if it is an acid, determine if it is monoprotic, diprotic or triprotic. Substance Base Salt Acid Monoprotic HC2H3O2 Ca(OH)2 Mg(NO3)2 CoCl6 H3PO3 H2S Al(OH)3 HF Zn(C2H3O2)2 KOH Diprotic Triprotic 2. Name the following Arrhenius acids. A. HI hydroiodic acid B. H2C2O4 C. HBr hydrobromic acid D. HClO2 E. H2CrO4 chromic acid F. HMnO4 oxalic acid chlorous acid permanganic acid 3. Using the Bronsted – Lowry definitions, label each member of the following equations as an acid, base, conjugate acid, or conjugate base. A. CH3COOH + H2O H3O+ A B CA B. F- + H2O B A OHCB + HF CA C. H2O B + HOBr A OBrCB D. H2O A + HS - H2S + OHB CA CB + CH3COO – CB + H3O+ CA HNO3 + HPO4 –2 NO3- + H2PO4 – A B CB CA 4. Use the Bronsted-Lowry definition to predict the conjugate acid to the following bases. E. A. NH3 NH4+ B. HSO4- H2SO4 D. ClO- HClO E. PO4-3 HPO42- C. H2O H3O+ 5. Use the Bronsted - lowry definitions to predict the conjugate base to the following acids. A. NH4+ NH3 B. H2O OH- D. HCO3- CO32- E. H2C2O4 HC2O4- C. HClO4 ClO4- 6. Predict the products of the following double replacement reactions, which are the neutralization of an Arrhenius acid and base. These equations have not been balanced. A. Ca(OH)2 + HNO3 Ca(NO3)2 + B. H2SO4 C. HClO3 + LiOH LiClO3 D. Al(OH)3 + H2S Al2S3 + + Mg(OH)2 MgSO4 H2O + H2O + H2 O H2O 7. Determine the pH and pOH of the following substances. FIRST determine the [H+] or [OH-] depending on whether you are working with an Arrhenius acid or base. Remember pH + pOH = 14 ex. 0.0045 M NaOH NaOH is a base. It releases OH- into solution. Therefore From the [OH-], the pOH may be calculated using the formula pOH = -log [OH-]. Knowing that pH and pOH = 14 we can determine the pH A. 0.0020 M HNO3 [ H+ ] = 0.0020 pH = 2.70 pOH = 11.3 B. 0.00035 M HCl [ H+ ] = 0.00035 pH = 3.46 pOH = 10.5 C. 0.0782 M LiOH [ OH-] = 0.0782 pH = 12.9 pOH = 1.11 D. 1.2 x 10 –5 HClO4 [ H+ ] = 1.2x10-5 pH = 4.92 pOH = 9.10 E. 3.7 x 10 –3 Ba(OH)2 [ OH- ] = 0.0074 pH = 11.7 pOH = 2.13