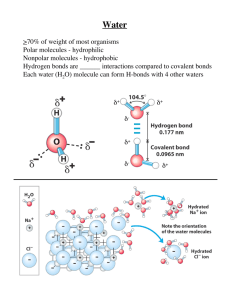
acid-base review - Southwest High School
advertisement

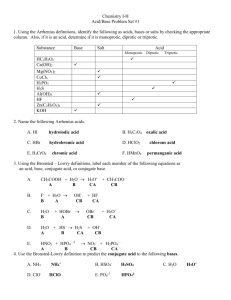
ACID-BASE REVIEW 2014 1. Define Arrhenius Acid and Base Acid: Base: 2. Define Bronsted-Lowry Acid and Base Acid: Base: 3. Define a Lewis Acid and Base Acid: Base: 4. Give some properties of an acid, and some of a base Acid: Base: 5. H3O+ is called: 6. OH- is called: 7. [OH-] = 3x10-3. Is it an acid, base or neutral solution? 8. [H]+= 6x 10-12. Is it an acid, base or neutral solution? 9. Give the pH of (use practice sheet to review; pH + pOH = 14) a. [H+] = .0001 b. [OH-] = .001 c. [H+] = 5.3 x 10-5 d. [OH-] =3 x 10-4 10. Give an example of a monoprotic acid, diprotic acid and triprotic acid. (practice nomenclature of acids & bases) 11. What does amphoprotic mean? To what type of materials does it apply? 12. Write the equation for the self-ionization of water. 13. Write the equation for the ionization of HCl in water. 14. Label conjugate acid-base pairs. NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH15. Write the dissociation equation for KOH in water.(what ions form? Is the solution acidic or basic (alkaline)) 16. Which is the strongest acid (same Molarity)? Oxalic acid [H+] = 9.5 x 10-3 Carbonic acid [H+] = 2.24 x 10-6 17. Which is the strongest base (same Molarity)? Ammonia [H+] = 2.0 x 10-12 Ethylamine [H+] = 4.47 x 10-13 18. Which is the color you would expect litmus paper to turn when exposed to an acid like orange juice? 19. In the following equation which is the conjugate base? C2H3O2-1 + H2S HC2H3O2 + HS-1 20. What role does H2O play in the following reaction? H2O + H3PO4 H2PO4-1 + H3O+1 21. In the following equation which is the conjugate acid? HNO3 + NH3 NH4+ + NO3-1 22. Underline the acids and cross out the bases: NaCl CH4 H3PO4 LiOH H2O HI Cu(OH)2 LiBr NH4NO3 Mg(OH)2 H2S AgCl ACID-BASE REVIEW 2014 1. Define Arrhenius Acid and Base Acid: formula begins with “H” and produce hydrogen ions in solution Base: formula ends with “OH” and produce hydroxide ions in solution 2. Define Bronsted-Lowry Acid and Base Acid: proton donor Base: proton acceptor 3. Define a Lewis acid and base: Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor, Lewis base an electron pair donor 4. Give some properties of an acid, and some of a base Acid: turn litmus red, taste sour, low pH, neutralize bases, react with metals to make H2 gas, react with carbonates to produce carbon dioxide, a metal salt and water Base: turn litmus blue, taste bitter, high pH, neutralize acids, turn phenolphthalein from clear to pink 5. H3O is called: hydromium ion or a hydrated hydrogen ion 6. OH- is called: hydroxide ion 7. (OH-) = 3x10-3. Is it an acid, base or neutral solution? pOH about 3; pH about 11 so … BASIC 8. (H)+= 6x 10-12. Is it an acid, base or neutral solution? pH about 12; pH = 11.22 so … BASIC 9. Give the pH of (use practice sheet to review; pH + pOH = 14) a. [H+] = .0001 pH = 4 b. [OH ] = .001 pH = 11 pOH = 3 c. [H+] = 5.3 x 10-5 pH = 2.28 pOH = 3.52 d. [OH-] =3 x 10-4 pH = 10.48 10. Give example of monoprotic acid, diprotic acid. (practice nomemclature of acids & b ases) Monoprotic = HCl, HNO3, Diprotic = H2SO4, H2CO3 11. What does amphoprotic mean? Can act as both a proton donor and a proton acceptor (L-B Theory) ex: HS-, H2O, H2PO412. Write the equation for the ionization of water. HOH(l) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) 13. Write the equation for the ionization of HCl in water. HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) 14. Label conjugate acid-base pairs. NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OHbase acid C acid C base 15. Write the dissociation equation for KOH in water. KOH(s) K+(aq) + OH-(aq) ; the solution is basic since there are more hydroxide ions 16. Which is the strongest acid (same Molarity)? Oxalic acid [H+] = 9.5 x 10-3 Carbonic acid [H+] = 2.24 x 10-6 Oxalic it has the lower pH 23. Which is the strongest base (same Molarity)? Ammonia [H+] = 2.0 x 10-12 Ethylamine [H+] = 4.47 x 10-13 Ethylamine since it has the lower pH 24. Which is the color you would expect litmus paper to turn when exposed to an acid like orange juice? Red 25. In the following equation which is the conjugate base? C2H3O2-1 + H2S HC2H3O2 + HS-1 HS-1 is the conjugate base 26. What role does H2O play in the following reaction? H2O + H3PO4 H2PO4-1 + H3O+1 H2O acts as the base; H3O+ is the conjugate acid 27. In the following equation which is the conjugate acid? HNO3 + NH3 NH4+ + NO3-1 NH4+ is the conjugate acid 28. Underline the acids and cross out the bases: NaCl CH4 H3PO4 LiOH H2O HI Cu(OH)2 LiBr NH4NO3 Mg(OH)2 H2S AgCl