A roller coaster ride is a thrilling experience which involves a wealth
advertisement

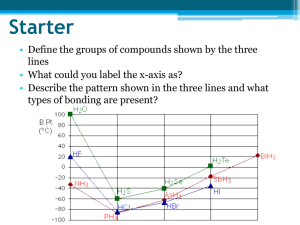
Do Now Clicker # Name ……………………………………………. Team ………………………. Title: Types of bonding Date ……………………… Describe each of the following types of bonding as fully as you can Metallic bonds Ionic bonds Pure covalent bonds Polar covalent bonds Lecture note taking More explaining What are the quantum numbers associated with the most outer electron of carbon Lecture continued CFU Lecture 1 Arrange the following in order of strength strongest first Dipole Dipole Covalent Hydrogen bonding Dipole Dipole interactions can only occur in: Polar molecules Nonpolar molecules Gases Explain what properties of oxygen allow Hydrogen bonding to occur between water molecules Independent practice Name ……………………………………………. Team ……………………… Title:intermolecular forces Date …………………… 1) Using your knowledge of molecular structure, identify the main intermolecular force in the following compounds. You may find it useful to draw Lewis structures to find your answer. a) PF3 _____________________________ b) H2CO _____________________________ c) HF _____________________________ 2) Explain how dipole-dipole forces cause molecules to be attracted to one another. 3) Rank the following compounds from lowest to highest boiling point: calcium carbonate, methane, water 4) Explain why nonpolar molecules usually have much lower surface tension than polar ones. For each of the following compounds, determine the main intermolecular force. You may find it useful to draw Lewis structures for some of these molecules: 1) nitrogen ________________________________ 2) carbon tetrachloride ________________________________ 3) H2S ________________________________ 4) sulfur monoxide ________________________________ 5) N2H2 ________________________________ 6) boron trihydride ________________________________ 7) CH4O ________________________________ 8) SiH2O ________________________________ Exit Ticket ** Clicker # Name ……………………………………………. Team ……………………… Title: Intermolecular bonding Date ……………………… 1 Place the following in order of increasing strength: 1. hydrogen bonding 2. covalent bonding 3. London dispersion forces A. B. C. D. E. ** 2, 1, 3 1, 2, 3 1, 3, 2 3, 1, 2 3, 2, 1 2a)The correct order for increasing boiling point among the noble gases is: A. B. C. D. E. * He Ne Ar Kr Xe 2 b) This phenomenon is best explained in terms of: A. B. C. D. E. hydrogen bonding dipole-dipole interaction Hund's rule London dispersion forces covalent bonding * 3) Which of the following 4 statements are false? 1. Liquids with large intermolecular forces tend to have very low boiling points 2. Liquids with large intermolecular forces tend to have considerable surface tension 3. When a substance changes from a solid to a liquid, the molecules remain intact 4. The hardness of diamond is due to strong dipole-dipole attraction A. B. C. D. E. * 1 and 3 2 and 3 2 and 4 1 and 4 3 and 4 b) Explain your answer choice 4) State which type of interaction (dipole-dipole forces or London forces) exists between molecules in the following: * N2 CO2 * CH3Cl HBr HWK Name ………………………………………… Clicker # Team ………………………. Title: intermolecular force Date ……………………… For each of the following molecules draw the Lewis dot diagram and decide the most significant type of intermolecular bonding ** 1) water H2O ** 2) carbon tetrachloride CCl4 ** 3) ammonia NH3 4) carbon dioxide CO2 * 5) phosphorus trichloride PCl3 * 6) F2 and Br2 both have London Dispersion Forces. Explain which would have the most significant amount of LDF and how effects the molecules physical state at room temperature.