Dipole-Dipole Interactions and H bonding TMD
advertisement

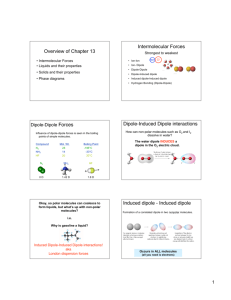
Starter • Define the groups of compounds shown by the three lines • What could you label the x-axis as? • Describe the pattern shown in the three lines and what types of bonding are present? Starter answers • • • • Red = Group 5 hydrides Green = Group 6 hydrides Blue = Group 7 hydrides or Hydrogen halides X-axis could be labelled as “Period” (2,3,4 and 5) • NH3, H2O, and HF all polar. • The rest are non-polar but b.p. increases due to increased spontaneous dipole-induced dipole (Van der Waals) bonding Dipole-Dipole Interactions & Hydrogen Bonding Objectives Be able to... • Apply knowledge of electronegativity to determine polarity of covalent bond • Describe permanent dipole-induced dipoles • Define hydrogen bonding as a special type of permanent dipole-induced dipole • Be able to recognise biochemical and material examples of hydrogen bonding Specification... Where this comes from... Intermolecular Forces • Van der Waals forces (instantaneous dipoleinduced dipole interactions) exist between all molecules whether polar or non polar • They are: ▫ Weak intermolecular forces ▫ Caused by very small or instantaneous dipoles in molecules , caused by the random movement of electrons within electron clouds Induced Dipoles • Movement of electrons produces an oscillating dipole (temporary) – this oscillating dipole induces a dipole in a neighbouring molecule which is induced onto further molecules – induced dipoles attract one another. • As electrons are constantly moving, dipoles are always being created and destroyed, however the overall effect is constant and the atoms are attracted to each other. Factors which affect the strength: • The greater the number of electrons in each molecule • The larger the oscillating and induced dipoles • The greater the attractive forces between molecules • How well the molecules fit together in 3D space... Tetris theory! Questions • Grades C-D • Grades A-B Permanent Dipole-Dipoles • What is a polar molecule? ▫ (a molecule which atoms have significant differences in their electronegativity and a dipole is created) • + and - charges on polar molecules cause weak electrostatic forces of attraction between molecules E.g. in HCl(g) H-Cl….. H-Cl….. H-Cl • Although they are weak forces they are still much greater then VdWaals Hydrogen Bonding • Special type of permanent dipole – dipole interaction • Hydrogen bonding can only occur when Hydrogen is bonded covalently to Fluorine, Nitrogen, or Oxygen. • Hydrogen has a high charge density as it is so small and F, N & O are highly electronegative. • The bond is highly polarised • Molecules which have hydrogen bonding are usually organic Examples of H-Bonding Effects of H-Bonding • Hydrogen bonding has a huge effect on the properties of substances. They are soluble in water and have higher boiling and freezing points than non-polar of similar size. • Why does ice float? ▫ (less dense than liquid water due to rigid Hydrogen bonds which are relatively long, molecules held in an open lattice structure) H-bonding and Ice • Ice has relatively high melting point, and water a relatively high boiling point • Relatively strong H-bonds between H2O molecules • Extra forces on top of VdWaals • The extra intermolecular forces from H-bonds also explains high surface tension and viscosity in water Exam Question • State and explain the overall trend in boiling points for Group 6 Hydrides. Why is water’s boiling point higher than expected comparison to the other group 6 hydrides? [Total 5 marks] in Exam Answers 1. Except for water there is an increase in boiling point going down the group 2. The increase in the size/Mr and number of electrons… 3. Leads to an increase in Van der Waals 4. More energy… 5. Is needed to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules Three types of intermolecular bonding... • Instantaneous dipole-induced dipole (otherwise known as Van der Waals) • Permanent dipole-induced dipole • Permanent dipole-Permanent dipole (of which Hydrogen bonding is an extreme example) Three types of intermolecular bonding... Home Learning • Complete worksheet on Intermolecular Bonding for next lesson. Objectives Be able to... • Apply knowledge of electronegativity to determine polarity of covalent bond • Describe permanent dipole-induced dipoles • Define hydrogen bonding as a special type of permanent dipole-induced dipole • Be able to recognise biochemical and material examples of hydrogen bonding