sightP
advertisement

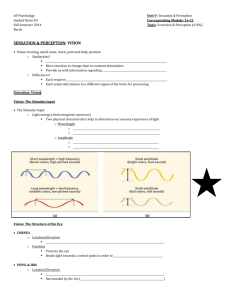
NAME & section #: SENSES - SIGHT PRELAB EXERCISE (2003/2004) (Martini p. 569-589) TO BE COMPLETED BEFORE COMING TO THE LAB. I. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES OF THE EYE. (Martini p. 569-571) List them: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define conjunctiva? What are its functions? What are the functions of the extrinsic eye muscles? Where are they located? How many of them are there (do not learn their names)? 1 II. STRUCTURE OF THE EYE. (Martini p. 571-577) 1. Briefly describe the functions of the following structures: - fibrous tunic: cornea: sclera: - vascular tunic: choroid: ciliary muscles: ciliary processes: suspensory ligaments: iris: radial and circular smooth muscles fibers in the iris: - nervous tunic (= retina): pigmented layer: sensory layer: 2 - lens: - vitreous humor (give the composition and functions): - aqueous humor (give the composition and functions): - scleral venous sinus (= canal of Schlemm): 2. What is the optic disc? Why is it called the blind spot? 3. What are the macula lutea and fovea centralis? 3 4. Define accommodation? (Martini p. 578-579) Does a normal person need to accommodate in order to look at a distant object? Why? Will she accommodate when she reads her newspaper? Why? What are the 2 other active adjustments made by the eyes? 5: Using Figure 17.6 in Martini p. 575, draw a diagram of a close-up of the retina on a separate page. Indicate in brackets the function of these 8 types of cells composing the retina. Indicate on your diagram the passage of the light through the retina and the direction that electrical signals flow. Indicate also the pigmented layer and the sensory layer of the retina. 6: On a separate page, make a table and list all the difference between rods and cones (sensitivity to light; wavelength absorbed; pigments; color perceived; nerve pathways connecting them to the brain; their significance; overall functions) 4