Vision
advertisement

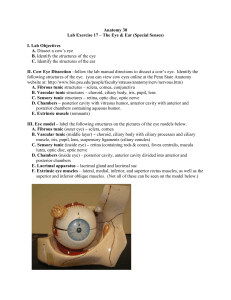
Vision 1 Slide 1 Segments Chambers Humors 2 Tunics Slide 2 1. Fibrous Tunic Cornea Sclera 2. Vascular Tunic Choroid Ciliary body iris 3 3. Sensory Tunic Retina Pigmented layer Slide 3 Nervous layer Rods Cones Bipolar Horizontal Amacrine Ganglion 4 • Light refraction Slide 4 • Lens Accommodation Disorders: Myopia Hyperopia Presbyopia Astigmatism 5 Excitation of photoreceptors Slide 5 Photoreception Photopigments Opsins and Retinal Rods Cones (b,r,g) 6 Slide 6 How photopigments respond to light. 7 Slide 7 Release of neurotransmitter by photoreceptors 8 Pathway to the brain Slide 8 Ganglia Optic Nerve Optic Chiasma Optic Tracts Optic Radiation 9 16.14 What is lacrimal fluid and what are its functions? 16.15 Why does your nose run when you cry? 16.16 What are the components of the fibrous tunic and vascular tunic? 16.19 Which part of the retina produces the sharpest vision when light falls on it? 16.20 What is the function of the aqueous humor? The vitreous body/humor? 16.22 What is refraction? Which components of the eye are primarily responsible for refracting light? 16.23 If you look at the horizon to determine where you are, then look down to read a map, what process must your eyes accomplish to keep your vision focused? 16.29 How do photopigments respond to light and recover in the dark? 16.30 Why does a decreased release of glutamate by photoreceptors generate a receptor potential in bipolar cells? 10