Year-At-A-Glance-Biology 1 Honors
advertisement
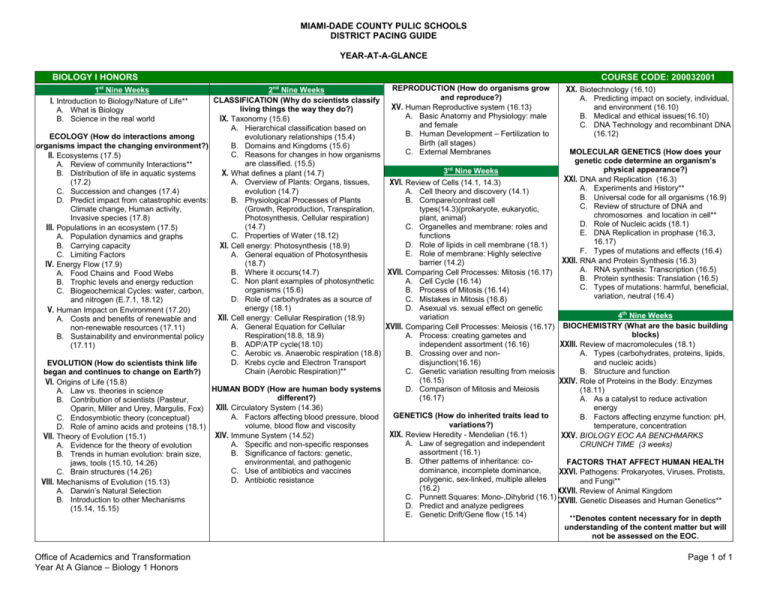
MIAMI-DADE COUNTY PULIC SCHOOLS DISTRICT PACING GUIDE YEAR-AT-A-GLANCE BIOLOGY I HONORS COURSE CODE: 200032001 REPRODUCTION (How do organisms grow XX. Biotechnology (16.10) 2nd Nine Weeks and reproduce?) A. Predicting impact on society, individual, CLASSIFICATION (Why do scientists classify and environment (16.10) XV. Human Reproductive system (16.13) living things the way they do?) A. Basic Anatomy and Physiology: male B. Medical and ethical issues(16.10) IX. Taxonomy (15.6) and female C. DNA Technology and recombinant DNA A. Hierarchical classification based on B. Human Development – Fertilization to (16.12) ECOLOGY (How do interactions among evolutionary relationships (15.4) Birth (all stages) organisms impact the changing environment?) B. Domains and Kingdoms (15.6) MOLECULAR GENETICS (How does your C. External Membranes C. Reasons for changes in how organisms II. Ecosystems (17.5) genetic code determine an organism’s are classified. (15.5) A. Review of community Interactions** physical appearance?) 3rd Nine Weeks B. Distribution of life in aquatic systems X. What defines a plant (14.7) XXI. DNA and Replication (16.3) (17.2) A. Overview of Plants: Organs, tissues, XVI. Review of Cells (14.1, 14.3) A. Experiments and History** C. Succession and changes (17.4) evolution (14.7) A. Cell theory and discovery (14.1) B. Universal code for all organisms (16.9) D. Predict impact from catastrophic events: B. Physiological Processes of Plants B. Compare/contrast cell C. Review of structure of DNA and Climate change, Human activity, (Growth, Reproduction, Transpiration, types(14.3)(prokaryote, eukaryotic, chromosomes and location in cell** Invasive species (17.8) Photosynthesis, Cellular respiration) plant, animal) D. Role of Nucleic acids (18.1) (14.7) C. Organelles and membrane: roles and III. Populations in an ecosystem (17.5) E. DNA Replication in prophase (16.3, C. Properties of Water (18.12) functions A. Population dynamics and graphs 16.17) D. Role of lipids in cell membrane (18.1) B. Carrying capacity XI. Cell energy: Photosynthesis (18.9) F. Types of mutations and effects (16.4) E. Role of membrane: Highly selective C. Limiting Factors A. General equation of Photosynthesis XXII. RNA and Protein Synthesis (16.3) barrier (14.2) (18.7) IV. Energy Flow (17.9) A. RNA synthesis: Transcription (16.5) B. Where it occurs(14.7) XVII. Comparing Cell Processes: Mitosis (16.17) A. Food Chains and Food Webs B. Protein synthesis: Translation (16.5) C. Non plant examples of photosynthetic A. Cell Cycle (16.14) B. Trophic levels and energy reduction C. Types of mutations: harmful, beneficial, organisms (15.6) B. Process of Mitosis (16.14) C. Biogeochemical Cycles: water, carbon, variation, neutral (16.4) D. Role of carbohydrates as a source of C. Mistakes in Mitosis (16.8) and nitrogen (E.7.1, 18.12) energy (18.1) D. Asexual vs. sexual effect on genetic V. Human Impact on Environment (17.20) 4th Nine Weeks variation XII. Cell energy: Cellular Respiration (18.9) A. Costs and benefits of renewable and BIOCHEMISTRY (What are the basic building A. General Equation for Cellular XVIII. Comparing Cell Processes: Meiosis (16.17) non-renewable resources (17.11) blocks) Respiration(18.8, 18.9) A. Process: creating gametes and B. Sustainability and environmental policy B. ADP/ATP cycle(18.10) independent assortment (16.16) XXIII. Review of macromolecules (18.1) (17.11) C. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic respiration (18.8) B. Crossing over and nonA. Types (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, D. Krebs cycle and Electron Transport disjunction(16.16) and nucleic acids) EVOLUTION (How do scientists think life Chain (Aerobic Respiration)** C. Genetic variation resulting from meiosis B. Structure and function began and continues to change on Earth?) (16.15) XXIV. Role of Proteins in the Body: Enzymes VI. Origins of Life (15.8) HUMAN BODY (How are human body systems D. Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis (18.11) A. Law vs. theories in science different?) (16.17) A. As a catalyst to reduce activation B. Contribution of scientists (Pasteur, XIII. Circulatory System (14.36) energy Oparin, Miller and Urey, Margulis, Fox) GENETICS (How do inherited traits lead to A. Factors affecting blood pressure, blood B. Factors affecting enzyme function: pH, C. Endosymbiotic theory (conceptual) variations?) volume, blood flow and viscosity temperature, concentration D. Role of amino acids and proteins (18.1) XIX. Review Heredity - Mendelian (16.1) XIV. Immune System (14.52) XXV. BIOLOGY EOC AA BENCHMARKS VII. Theory of Evolution (15.1) A. Law of segregation and independent A. Specific and non-specific responses CRUNCH TIME (3 weeks) A. Evidence for the theory of evolution assortment (16.1) B. Significance of factors: genetic, B. Trends in human evolution: brain size, B. Other patterns of inheritance: coFACTORS THAT AFFECT HUMAN HEALTH environmental, and pathogenic jaws, tools (15.10, 14.26) dominance, incomplete dominance, C. Use of antibiotics and vaccines C. Brain structures (14.26) XXVI. Pathogens: Prokaryotes, Viruses, Protists, polygenic, sex-linked, multiple alleles D. Antibiotic resistance and Fungi** VIII. Mechanisms of Evolution (15.13) (16.2) A. Darwin’s Natural Selection XXVII. Review of Animal Kingdom C. Punnett Squares: Mono-,Dihybrid (16.1)XXVIII. Genetic Diseases and Human Genetics** B. Introduction to other Mechanisms D. Predict and analyze pedigrees (15.14, 15.15) E. Genetic Drift/Gene flow (15.14) **Denotes content necessary for in depth 1st Nine Weeks I. Introduction to Biology/Nature of Life** A. What is Biology B. Science in the real world understanding of the content matter but will not be assessed on the EOC. Office of Academics and Transformation Year At A Glance – Biology 1 Honors Page 1 of 1