AP Biology Course Syllabus
advertisement
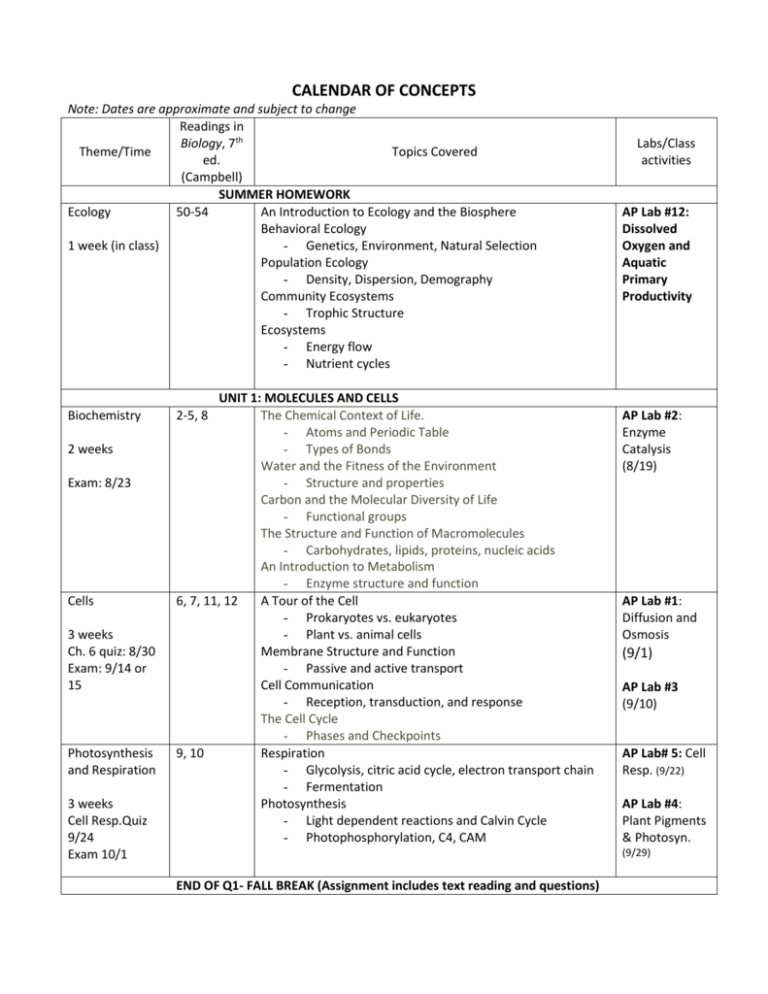
CALENDAR OF CONCEPTS Note: Dates are approximate and subject to change Readings in Biology, 7th Theme/Time Topics Covered ed. (Campbell) SUMMER HOMEWORK Ecology 50-54 An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Behavioral Ecology 1 week (in class) - Genetics, Environment, Natural Selection Population Ecology - Density, Dispersion, Demography Community Ecosystems - Trophic Structure Ecosystems - Energy flow - Nutrient cycles Biochemistry 2 weeks Exam: 8/23 Cells 3 weeks Ch. 6 quiz: 8/30 Exam: 9/14 or 15 Photosynthesis and Respiration 3 weeks Cell Resp.Quiz 9/24 Exam 10/1 UNIT 1: MOLECULES AND CELLS The Chemical Context of Life. - Atoms and Periodic Table - Types of Bonds Water and the Fitness of the Environment - Structure and properties Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life - Functional groups The Structure and Function of Macromolecules - Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids An Introduction to Metabolism - Enzyme structure and function 6, 7, 11, 12 A Tour of the Cell - Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes - Plant vs. animal cells Membrane Structure and Function - Passive and active transport Cell Communication - Reception, transduction, and response The Cell Cycle - Phases and Checkpoints 9, 10 Respiration - Glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain - Fermentation Photosynthesis - Light dependent reactions and Calvin Cycle - Photophosphorylation, C4, CAM 2-5, 8 Labs/Class activities AP Lab #12: Dissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Primary Productivity AP Lab #2: Enzyme Catalysis (8/19) AP Lab #1: Diffusion and Osmosis (9/1) AP Lab #3 (9/10) AP Lab# 5: Cell Resp. (9/22) AP Lab #4: Plant Pigments & Photosyn. (9/29) END OF Q1- FALL BREAK (Assignment includes text reading and questions) Cellular Reproduction and Mendelian Genetics 4 weeks Quiz 10/15 Exam 10/27 Molecular Genetics UNIT II: GENETICS AND EVOLUTION 13-15 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles - Stages of Meiosis Mendel and the Gene Idea - Mendel’s Laws and Punnett squares - Inheritance patterns The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - Recombination - Eukaryotic chromosomes 16-20 4 weeks Exam 11/22 Evolution 2 weeks Plants: Diversity, Anatomy, and Physiology 4 weeks The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Structure of DNA - DNA replication From Gene to Protein - Transcription, translation The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria - Viral and bacterial structure and replication - Gene regulation Eukaryotic Genomes: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution - Organization of DNA DNA Technology and Genomics - Gel electrophoresis - Restriction enzymes - Applications of nucleic acid technology AP Lab #7: Drosophila genetics (10/14) M&M’s and Chi-square Velcro DNA AP Lab #6B: Restriction Analysis of Lambda DNA and Gel Electrophoresis AP Lab #6A: Bacterial Transformation Week of 11/15 END OF Q2 – WINTER BREAK Winter break assignment will include reading Survival of the Sickest by Dr. Sharon Moalem. 22-25 Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life AP Lab #8: - Darwin’s research and principles Population - Evidence for evolution Genetics The Evolution of Populations - Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium conditions and Breeding equations (calculations practice) Bunnies Lab The Origin of Species - Convergent, divergent, parallel evolution - Directional, stabilizing, disruptive Phylogeny and Systematics UNIT III: ORGANISMSAND POPULATIONS 29, 30, 3539 How Plants Colonized Land - Mosses, Ferns - Alternation of Generation The Evolution of Seed Plants - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Plant Structure, Growth, & Development - Differentiated Plant Cells AP Lab #9: Transpiration Transport in Vascular Plants - Transpiration and Stomata Plant Nutrition - Symbiotic relationships - Soil exchange Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology - Flower Structure and Germination Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals - Hormones, tropisms & environmental stress Animals: Diversity, Anatomy, and Physiology 8 weeks 41-49 Animal Nutrition - Ingestion & Digestion Circulation and Gas Exchange - Open vs closed systems - Vertebrate Circulatory Systems - Respiratory The Immune System - Immunity Osmoregulation and Excretion - Fresh vs Marine Animals - Kidney structure & function Hormones and the Endocrine System - Major Endocrine Glands - Invertebrate Hormones Animal Reproduction - Asexual reproduction - Reproductive organs - Gametogenesis Animal Development - Fertilization, cleavage, gastrulation - Organogenesis Nervous Systems - Neuron structure and function - Neurotransmitters - Brain structure and function Sensory and Motor Mechanisms - Types and functions of sensory receptors - Taste vs smell - Vertebrate vision - Skeletons and muscle movement AP Lab #11: Animal Behavior AP Lab # 10: Physiology of the Circulatory System Thematic Approach: All of the concepts covered in this class are related to one of the following AP themes. Science as a Process: Science is a way of knowing. It can involve a discovery process using inductive reasoning, or it can be a process of hypothesis testing. - All labs give students this practice as they clearly define a problem of study, form a hypothesis, collect data, analyze and interpret data, and form conclusions. In some of the labs, the students will design their own experiments, including a fieldbased research project. - Evolution Biological change of organisms that occur over time is driven by the process of natural selection. Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth. - Aerobic and anaerobic cell respiration Discussion of introns Endosymbiotic theory Diversity of life and evolutionary trends Reproductive methods Animal embryonic development Energy Transfer Energy is the capacity to do work. All living organisms are active (living) because of their abilities to link energy reactions to the biochemical reactions that take place within their cell. - Population dynamics Cell respiration and fermentation Photosynthesis Continuity and Change All species tend to maintain themselves from generation to generation using the same genetic code. However, there are genetic mechanisms that lead to change over time, or evolution. - Mitosis and Meiosis Asexual and sexual reproduction Alternation of generations in plants Crossing over Independent assortment and segregation Mutations Cloning Transformation and transduction Relationship of Structure and Function The structural levels from molecules to organisms ensure successful functioning in all living organisms and living systems. - Structure of water related to its properties - Discussion of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids - Relationship of membrane structure to neuron transmission and muscle contraction - Discussion of cells, tissues, organs in association with any plant or animal system - Structure of DNA related to replication - Structure of tRNA - Protein conformation and function - Homologous structures - Structure of a stomata Primary productivity – Dissolved oxygen lab Cell respiration lab Regulation Everything from cells to organisms to ecosystems is in a state of dynamic balance that must be controlled by positive or negative feedback mechanisms. - Discussion of what regulates enzyme activity by various inhibitors, product concentration, positive and negative feedback - Regulation of cell respiration - Regulation of photosynthesis - Regulation of the cell cycle - Regulation of gene expression by the promoter, operator, - Transcription factors, inducers, repressors and methylation - Regulation of stomatal closure in a plant - Regulation of alternation of generations Interdependence in Nature Living organisms rarely exist or thrive alone in nature. - Science, Technology and Society Scientific research often leads to technological advances that can have positive and/or negative impacts upon society as a whole. - Biotechnology - Genetically modified plant has environmental consequences of toxic wastes and global warming - Discussing pros and cons to gene therapy - Discussion of stem cell research Requirement for nutrients Symbiotic, parasitic, and mutualistic relationships Cell respiration and photosynthesis Dissolved oxygen lab carried out in several aquatic environments over time