Fall 2009
advertisement

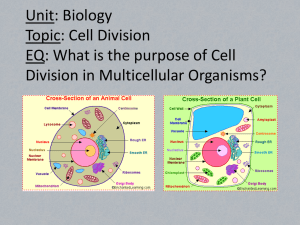
Biology 2014 - 2015 Final Exam Study Guide Outline This packet contains the concepts covered this year in the Biology classes. The concepts are based on the Georgia Performance Standards for Biology that are listed below. SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. b. Explain how enzymes function as catalysts. c. Identify the function of the four major macromolecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids). d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. a. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. b. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. c. Using Mendel’s laws, explain the role of meiosis in reproductive variability. d. Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of new traits including: Alterations during replication; Insertions, Deletions, and Substitutions; Mutagenic factors that can alter DNA - High energy radiation (xrays and ultraviolet), Chemical e. Compare the advantages of sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction in different situations. f. Examine the use of DNA technology in forensics, medicine, and agriculture. SB3. Students will derive the relationship between single-celled and multi-celled organisms and the increasing complexity of systems. a. Explain the cycling of energy through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. b. Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals). c. Examine the evolutionary basis of modern classification systems. d. Compare and contrast viruses with living organisms. SB4. Students will assess the dependence of all organisms on one another and the flow of energy and matter within their ecosystems. a. Investigate the relationships among organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes. b. Explain the flow of matter and energy through ecosystems by arranging components of a food chain according to energy flow. Comparing the quantity of energy in the steps of an energy pyramid. Explaining the need for cycling of major nutrients (C, O, H, N, P). c. Relate environmental conditions to successional changes in ecosystems. 1 d. Assess and explain human activities that influence and modify the environment such as global warming, population growth, pesticide use, and water and power consumption. e. Relate plant adaptations, including tropisms, to the ability to survive stressful environmental conditions. f. Relate animal adaptations, including behaviors, to the ability to survive stressful environmental conditions. SB5. Students will evaluate the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. d. Relate natural selection to changes in organisms. e. Recognize the role of evolution to biological resistance (pesticide and antibiotic resistance). Chapter 1: Biology in the 21st Century Define the word biodiversity. Where is it the greatest and why? 1. List the 4 characteristics shared by all living organisms (Pages 5 & 6) and briefly explain them. 2. Define the terms structure and function---How are they related? 3. Define the term homeostasis? What process is used for it to be maintained? What are some examples of how we maintain homeostasis? 4. What is the relationship between adaptation and natural selection? 5. Identify the different elements of scientific inquiry and differentiate between dependent variable, independent variable, and constant. Chapter 2: Chemistry of Life 6. Identify elements common to living things. 7. Describe how ions form and be able to compare ionic and covalent bonding. 8. Explain why many compounds dissolve in water. 9. What is the purpose of the pH scale? Be able to identify if a solution is an acid or a base. 10. Compare the 4 different macromolecules…carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. 11. Be able to identify if a chemical reaction is exothermic or endothermic. 12. Explain the effect of a catalyst. Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function 13. What are the 3 principles of the Cell Theory? 14. What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? 15. Be able to define and label what 3 organelles does a plant cell have that an animal cell does not? How does a plant cell look different than an animal cell? 16. Be able to define the functions for cell organelles. 17. The cell membrane is made up of ___layer and is said to be ____________ ______________, which means it, allows some but, not all materials to cross. Scientists have developed the _________ ___________ _________, which 2 18. 19. 20. 21. describes the arrangement of the molecules that make up the cell membrane. Each head is ________which means it ________ water. Each head has two _______ that are said to be ___________ meaning they _______ like water. Define Passive transport and define two types of passive transport? What are the 3 ways a solution can be described and define each one? What is facilitated diffusion? Define Active transport. Provide examples Chapter 4: Cells and Energy 22. Briefly explain how Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) becomes Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) and why is the process important? 23. Identify energy sources used by organisms. 24. Describe the process of photosynthesis. 25. Describe the process of Cellular respiration. 26. Compare and contrast photosynthesis to cellular respiration (hint: look at the chemical equations!!) Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 27. What are the 4 stages of the cell cycle. 28. In what stage does replication takes place in? Why must it happen before Mitosis? 29. What are the 4 major phases of mitosis and what happens in each phase? 30. When does the cytoplasm of a cell divide? 31. What is the end result of mitosis? Chapter 6: Meiosis and Mendel 32. What are the differences between somatic cells and germ cells (gametes). 33. What type of cells is involved in Meiosis? 34. What is the purpose of Meiosis and what is the end result? 35. Compare and contrast mitosis to meiosis. 36. Explain the differences between a haploid cell and a diploid. 37. Identify the steps of meiosis and what occurs in each. 38. Who is Gregor Mendel and what was his contribution to genetics? 39. Compare the following terms: A) Homozygous: Heterozygous: B) Genotype: Phenotype: C) Dominant: Recessive: 40. Create a Punnett square for the following: Brown and Blue eyes (Brown is the dominant trait) Heterozygous vs Homozygous recessive.) Chapter 7 Extending Mendelian Genetics 41. Describe patterns of inheritance in sex-linked traits. 42. Describe different types of allele interactions (Incomplete Dominance & Codominance). 3 Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins 43. What are the 3 parts that make up a nucleotide? 44. What are the 4 nitrogen bases in DNA and their base paring rules? ___________ with ___________, ____________ with ____________. 45. The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 46. What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 47. What process follows replication and what nucleic acid does it involve? 48. What 3 types of RNA does transcription make and define them? 49. The third or last step that converts an mRNA message using amino acids to make proteins. 50. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 51. Three nucleotide sequence that code for an amino acid. 52. Compare and contrast between stop, start and anticodons. 53. What are the two types of gene mutations and define them. Chapter 9 54. Type of genetic engineering where a genetically identical copy of a gene or an organism is created. 55. Define genetic engineering and how is it possible? 56. How does genetic engineering produce organisms with new traits? 57. How is genetic engineering beneficial in plants and in animals? 58. What was the purpose of the Human Genome Project? Chapter 10 59. Define evolution. How did Lamarck’s ideas about evolution differ from Darwin’s? 60. Darwin proposed that ________________________ is the mechanism for evolution. What did he use to support his ideas? 61. Evidence for evolution includes what 4 sources? (section10.4) (analogous, homologous, vestigial) Chapter 11 62. How is genetic variation beneficial in a population? 63. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium – what is required? 64. 5 factors that can lead to evolution (section 11.4) 65. Speciation may lead to isolation. What are some ways populations may become isolated? (section11.5) 66. How do convergent and divergent evolution differ? Chapter 12 67. How can the age of fossils be determined? Which method is the most accurate? Chapter 13 & 14 68. What are the levels of organization. 69. What is ecology? 70. Understand the difference between and provide examples of biotic and abiotic factors 4 71. What is biodiversity? 72. Vocabulary: producer/autotroph, consumer/heterotroph, chemosynthesis versus photosynthesis 73. How are food chains different from food webs? Explain how energy flows within a food chain or food web. 74. Be able to view an energy pyramid and decide which are producers/consumers (primary, secondary…) * Be able to explain the rule of 10% and how it pertains to trophic levels and the number of organisms at each level 75. Distinguish between habitat and niche 76. What are 3 types of symbiosis? Give examples/ be able to decide which type if given an example – know if an organism is harmed, unaffected, or benefits from a particular type of interaction. What is predation? 77. How do exponential and logistic growth differ? 78. What is succession? What is the difference between primary and secondary succession? What are pioneer species? Chapter 15 & 16 79. What are the biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and geosphere? 80. What factors that influence climate: temperature, sunlight, water and wind. How does climate differ from weather? 81. Know the 8 biomes, general locations and characteristics of each. 82. What is an estuary? What is unique about estuaries? 83. How do renewable and nonrenewable resources differ? 84. What is an ecological footprint? 85. Be describe the greenhouse effect. Understand the need for the greenhouse effect and also be able to explain how scientists think it could cause global warming. 86. What is biomagnification? Chapter 17 & 18 87. Carolus Linnaeus, binomial nomenclature, dichotomous key, cladogram 88. What are the 6 kingdoms of classification and basic characteristics of each? 89. How do viruses differ from living cells? How do we treat viral diseases? 90. What roles (beneficial and harmful) do prokaryotes carry out for organisms and in ecosystems? 91. Name the first antibiotic and the person who discovered it. Chapter 19 – 26 Review the information you have in your Kingdom Project Composition Book. Focusing on important characteristics of each kingdom. (adaptations,structure/function, response, reproduction, etc.) 5