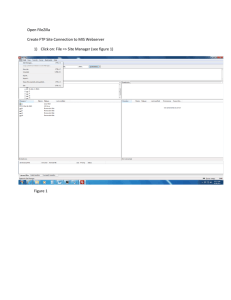
Management Information System
advertisement

Part III Management Information Systems (MIS) Lecture Note 1 BC311 ระบบสารสนเทศเพือ ่ การจ ัดการ (Management Information System) อาจารย์นา้ ทิพย์ ตระกูลเมฆี www.tapee.ac.th/numtip/course/BC311/ *** ไฟล์ *.htm (ให้ไปดูจาก net เองเนือ ่ งจาก SAVE ยาก ) อธิบายรายวิชา ศึกษาลักษณะโครงสร้างของระบบสารสนเทศ การวางแผน การจัดการและการตัดสิ นใจในการพัฒนาระบบสารสนเทศทางธุ รกิจ การบริ หารโครงการพัฒนาระบบสารสนเทศ การจัดโครงสร้างของหน่วยงานสารสนเทศ การนาระบบสารสนเทศมาใช้ในองค์กร การบริ หารงานและการประเมินผลระบบสารสนเทศ วัตถุประสงค์ ของวิชา 1.ศึกษาเกี่ยวกับโครงสร้างและการวางแผนระบบสารสนเทศเพื่อใช้ในการตัดสิ นใจ 2.เรี ยนรู ้เกี่ยวกับการสร้างและพัฒนาระบบสารสนเทศเพื่อใช้ในองค์กร 3.เรี ยนรู ้การบริ หารงานและการประเมินผลระบบสารสนเทศ หัวข้ อวิชา Week 1 - Course Syllabus Week 2 - ความรู ้เบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศ Week 3 - เทคโนโลยีคอมพิวเตอร์ฮาร์ดแวร์ Week 4 - เทคโนโลยีการสื่ อสารและการคมนาคม Week 5 - เทคโนโลยีซอฟต์แวร์ Week 6- เทคโนโลยีฐานข้อมูล Week 7- เทคโนโลยีอินเทอร์ เนต สอบกลางภาค Week 9 - ระบบสารสนเทศเพื่อการจัดการ Week 10 - ระบบสารสนเทศเพื่อการจัดการด้านต่าง ๆ Week 11 - การพัฒนาระบบสารสนเทศเพื่อการจัดการ Week 12 - เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศเพื่อการศึกษา Week 13 - การประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศในสาขาต่าง ๆ Week 14 - ผลการทบของเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศ Week 15 – เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศกับแนวโน้มในอนาคต Lecture Note 2 “MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS” http://business.alfred.edu/duserick/chapter.htm Course Objectives: 1. Build a fundamental & theoretical foundation for Management Information Systems 2. Investigate the major resources for information systems 3. Understand and use methodology for systems analysis 4. Review key factors in the management of information systems 5. Explore the impact of developing technologies on MIS 6. Recognize, evaluate & react responsibly to ethical dilemmas in the Management of Information Systems 7. Continue development of computer competency 8. Explore the Internet Lectures : CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER 1. 2. 3. 4. THE INFORMATION SYSTEMS REVOLUTION THE STRATEGIC ROLE OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS INFORMATION SYSTEMS, ORGANIZATIONS, & MANAGEMENT COMPUTERS & INFORMATION PROCESSING CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER 6. MANAGING DATA RESOURCES 7. TELECOMMUNICATIONS 8. THE INTERNET 9. REDESIGNING THE ORGANIZATION 10. APPROACHES TO SYSTEM BUILDING 11: MANAGING KNOWLEDGE 12. ENHANCING MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING 13. INFORMATION SYSTEMS & CONTROL 14. ETHICAL & SOCIAL IMPACT 15. MANAGING INTERNATIONAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS *** See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/AlfredMIS/ Lecture note 3 Slides ประกอบหนังสื อของ Laudon “Essentials of management Information Systems” http://myphlip.pearsoncmg.com/cw/mpbookhome.cfm?vbookid=349 เลือกบทแล้วกดคลิก Go จะมีไฟล์ .ppt ให้ download Lectures: CHAPTER 1. CHAPTER 2. CHAPTER 3. CHAPTER 4. CHAPTER 5. CHAPTER 6. CHAPTER 7. CHAPTER 8. CHAPTER 9. MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM * INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN THE ENTERPRISE * INFORMATION SYSTEMS, ORGANIZATIONS, MANAGEMENT, AND STRATEGY * THE DIGITAL FIRM: ELECTRONIC BUSINESS AND ELECTRONIC COMMERCE ETHICAL AND SOCIAL ISSUES IN THE DIGITAL FIRM MANAGING HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ASSETS MANAGING DATA RESOURCES TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS THE INTERNET AND THE NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE CHAPTER 10. MANAGING KNOWLEDGE FOR THE DIGITAL FIRM CHAPTER 11. ENHANCING MANAGEMENT DECISION-MAKING FOR THE DIGITAL FIRM CHAPTER 12. REDESIGNING THE ORGANIZATION WITH INFORMATION SYSTEMS CHAPTER 13. UNDERSTANDING THE BUSINESS VALUE OF SYSTEMS AND MANAGING CHANGE CHAPTER 14. INFORMATION SYSTEMS SECURITY AND CONTROL CHAPTER 15. MANAGING INTERNATIONAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS *** See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/LaudonMISBook/ Lecture Note 4 CS276 IT Management and Business Strategy , SURREY http://www.computing.surrey.ac.uk/courses/cs386/ Aim : Information Technology (IT) has been heralded as having an impact that is on a par with the industrial revolution. Within an organisation, IT can have a significant impact on productivity, from the automation of communications through to business decision support, production, sales and marketing. This module aims to relate the knowledge gained by students about IT to how it can be effectively used in Information Systems (IS), which organisations may use to improve efficiency and competitiveness. Learning Outcomes : At the end of the module students should be able to: Explain how IT impacts upon organisations. Analyse the necessity for IS in the management of modern, and increasingly global, organisations. Recognise that IT professionals need to understand how an organisation operates in order to effectively apply technology to make the organisation more efficient and competitive. Explain how an organisation must change in order to successfully capitalise on the use of IS and the consequent impact on organisational structure and employees. Identify how the benefits of using IS may be measured and assessed, and contrast with existing practice. Produce a plan of how IS may be implemented within an organisation to provide competitive advantage. Content : The course is divided into the following areas: The IS revolution: the advent of IT, its impact on organisations and its strategic role. Information, IS, organisations and business processes: what is information and how can it be exploited? Management and decision-making: what is a manager? Managing data resources and managing knowledge: the management and exploitation of information. Redesigning the organisation with IS and enhancing management decisions: how can IT be integrated into an organisation to exploit information and improve process? Management approaches to systems-building, assessment of system success and failure: strategies for implementing IT systems and assessing their success or failure. Managing telecommunications and networks: the management of infrastructure, e-mail, Intranets, the Internet, Extranets and electronic business. IS security and control: how systems can be attacked and how systems can be designed to be secure from attack. Managing international IS, managing firm infrastructure and enterprise systems. Text Books : Campbell, Stonehouse & Houston: Business Strategy, An Introduction. Butterworth Heinemann, ISBN 07506 4207 6 Laudon, K.C. & Laudon, J.P. (2002). Management Information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm, 7th Edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall International, Inc. Hannagan Tim, Management Concepts and Practices, Third Edition, 2002. Financal Times Management/Pitman Publishing ISBN: 0-273-65189-7 IT Manager’s Guide to Business Strategy, Techrepublic, ISBN 1-931490-73-2, (www.techrepublic.com) Lecture Notes : Introduction Information Systems in Organisations Information Systems, Organisations, Management and Strategy Enhancing Management Decision Making Redesigning the Organisation with Information Systems and Managing Change Managing Data and Information Information Systems Security and Control Managing International Information Systems Case Studies: Toromont Industries University of Albion 'Healthlite Yogurt' *** See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/MISSurrey/ Lecture Note 5 Management of Information Systems http://www.ltn.lv/~apsitis/class02/mis/ Aim To give an introduction to Information Systems from a managerial perspective. The main teaching methods used will be lectures and case studies. Concrete IT knowledge and skills 1. Various computer hardware items and their main technical characteristics, human-computer interaction issues. [Oz, ch4]. 2. Concepts of computing - bits, bytes, various digital formats for documents, graphics and multimedia, the hierarchy of files and directories. [Oz, ch4, ch8]. Ability to recognize various file types and their characteristics, compute memory usage, write file paths, understand file archivation and compression. 3. Operating system concepts - resource management and sharing, multitasking. [Oz, ch5]. Ability to define heavyweight and lightweight processes, understand the behavior of multithreaded programs, daemon processes, services. 4. Software - generations/levels of programming languages, compilers and interpreters, distributed programming, types of programming errors, [Oz, ch5]. Ability to define various paradigms of programming, the notions of external libraries, object-orientation and inter-process communication techniques. 5. Networking - modes of communication (simplex/half-duplex/duplex, synchronous/asynchronous, connection/connectionless, clientserver/peer-to-peer). Network hardware issues. Communication protocols, the seven layers of the OSI model, [Oz, ch6]. 6. Network hosts, IP and DNS addresses, TCP/IP protocol, clients and servers, server ports, firewalls. Application protocols - Telnet/SSH, FTP, E-mail, Web. [Oz, ch7]. Understanding the notions of host, port, network traffic, the capabilities of various application protocols. 7. Data markup - HTML, XML, proprietary formats. Hypertext, data definition schemes, encodings, Unicode. Ability to write simple HTML/XML documents. 8. Databases - database models, RDBMS. Entity Relationship diagrams. Database administration, database scheme (ERD) modification, setting user permissions. Ability to write simple queries in SQL. 9. Representations of knowledge and metainformation. Inference engines and other "intelligent" ways to extract information. Ability to use simple and advanced search capabilities of Web search engines. 10. IS modeling techniques. Use-case models, static modeling (object diagrams), dynamic modeling (sequence/collaboration diagrams). Ability to design and to analyze simple UML diagrams. 11. Computer security. Various risks and addressing them. Security policies. Cryptography and its application to various communication protocols. Understanding of symmetric/asymmetric cryptography, public/private keys, certification authorities, digital signatures and encryption procedures. Credit for the class Your grade will be the total of the following: Quizzes - 20% (about 10 quizzes costing about 2% each) Group Case presentation - 10% (just one) Group Project milestone discussions - 20% (every group participates in discussions covering all three milestones) Group Project and its ultimate presentation - 20% Final exam - 30% Groups organize by themselves or with a help of instructor, there are 2-3 students in each group. Each group is responsible for one "Case study" and the Group Project and its 3 milestones (see below). For any of these things all members of the same group get equal grades. Quizzes Each quiz lasts 5-8 minutes, they contain multiple-choice questions or other questions prompting short answers. If students miss the class, or if they arrive too late to take a quiz, they do not get any credit. Grade is proportional to the # of questions you got right. Group "Case studies" A group studies relevant literature about an IT topic (databases, accounting, etc.) which is relevant for their project, they tell about it in class and hand in 35 page long report about the topic and also the printout of the presentation slides. Grade depends on the quality and relevance of the case study itself (it affects 50% of the "case study" grade) and the quality of the presentation (also 50% of the grade, it is lowered ). Case study should be handed in and ready to present by the deadline. You lose 25% of the grade, if complete submission is no more than one week late; and further 25% for every subsequent week. Project milestones A group gives a short presentation of the milestone and submits its project directory by e-mail to kalvis@datapro.lv or uploads through the Web (this will be indicated by the instructor). Grade depends on the quality of the project description (50%), and the quality of the presentation (50%). Group project (ultimate presentation) Unlike the mostly "technical" talks of milestone presentations, the ultimate presentation is "client-oriented". It is evaluated by the panel of all the people which are present in the class. Certain evaluation criteria (to be announced) account for 50% of the grade. Panel members also vote for the project as a whole (every panel member has number of votes which is 1/2 of the total number of projects being presented). Those who get maximum number of votes, get another 50% of the grade for this item, others get proportionally less than that. Course Outline This schedule is tentative and can be changed. Class Date Topics Readings 1 2002- Course outline. Strategic role of IS. The notion of IS, 09-06 energy and information, data and information, synergy, transformational effects of IS in organizations. [Oz, ch12] 2 2002- Types of IS. Relating IS with different levels in an 09-13 organization. [Oz, ch3] 3 (TBA) IS and processes in organizations. Final decisions on [Oz, ch3] group membership; each group chooses an alias (short name of the group), and describes in 20 word abstract the subject area of their project. Late submissions of aliases and project abstracts will result in lowered grade for the 1st milestone. 4 2002- Ethical, legal and social issues of IS. Privacy for 09-27 individuals, consumers, employees. Freedom of speech. Intellectual property rights. Quality enforcement for ISs and responsibility of IS workers. Security concerns and cybercrimes. "Digital divide". 5 2002- Data processing hardware and operating systems. Parts of [Oz, ch4] 10-04 a PC, peripheral devices, wireless gadgets, various OSs, compatibility issues. Human-computer interface. The deadline of the first milestone. 6 2002- Software. Programming languages and IT development. [Oz, ch5] 10-11 Compilers, interpreters, API libraries, software applications and tools. Interfaces of an application - CUI, [Oz, all] GUI, component approach. Software reusability. 7 2002- Data resources. File system, databases, data structures and [Oz, ch8] 10-18 their algorithms, time and storage requirements of various data processing tasks. 8 2002- Telecommunications and Networks. Networking hardware, [Oz, ch6] 10-25 network protocols, IP addresses and DNS, email/FTP/Telnet etc., URLs, the HTTP protocol. 9 2002- Web technologies. Document markup, Web design, client- [Oz, ch7] 11-01 side/server-side technologies. Data representation through XML. Web applications, e-commerce, data search and metadata in Internet. 10 2002- Interorganizational and international IS. Web services. EDI [Oz, ch11] 11-08 and customized data exchange protocols. Deadline of the group "Case study". 11 2002- Knowledge management. Artificial intelligence, data 11-15 mining, expert systems, metainformation and its models, Semantic Web. [Oz, ch8,ch13] 12 2002- IS for managers. Decision support systems and like. The 11-22 deadline of the second milestone. [Oz, ch9,ch1213] 13 2002- IS planning and its development. Modeling a new IS. 11-29 Software development phases, waterfall model. Unified Process and other methodologies of IS planning and implementation. [Oz, ch1415] 14 2002- IS acquisition and introducing into an organization. 12-06 Managerial issues when switching to a new IS. The [Oz, ch16] deadline of the third milestone. 15 2002- IS security. Security risks, guarding against data loss, [Oz, ch17] 12-13 types of attacks, secure channels, cryptography, hash functions, digital signatures, certification authorities and certificates. The project presentation - tell about your project 16 2002- Managing IS, quality control Organizing IS maintenance, [Oz, ch10] 12-20 process quality and product quality, ISO certification, IS auditing. About the Group Project Ideas for this are taken, among other sources, from http://socrates.berkeley.edu/~americ/c111/projects/overview.html and Rational Unified Process (see http://www.rational.com/products/rup/index.jsp). Literature [Oz] Effy Oz. Management Information Systems, 2nd edition. Course technology. 2000. *** See files *.htm in htr directory /MIS/ITN/ Lecture Note 6 : Management Information System mis.ucd.ie/courses/misp914/ Lectures: Chapter 1 Business Information Systems: An Overview Chapter 2 First Mover/Follower Chapter 3 Enterprise Resource Planning Chapter 4 Information Technology in Business Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Organising Information Systems and External Information Systems Chapter 7 Organisation & Information Chapter 8 Decesion Support Systems Chapter 9 Planning IS Chapter 10 System Development Chapter 11 Buying Solutions Chapter 12 Security and Control - Some current major issues *** See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/UCDMIS/ Lecture Note 7 Management Information System www.ru.ac.th Lectures: Module I Module 2 Module 3 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Module 8 Fundamental of Information Systems System Concepts Information Systems in Organizations Hardware: Input Processing, Output, and Storage Devices Overview of Software Starting Along the Information Highway Organizing Data and Information Information System in Business *** See files *.pdf in the directory /MIS/MISRamkumhang/ Lecture Note 8 Management Information System http://www.course.com/downloads/mis/oz/powerpoint_pres.cfm Lectures: Chapter 1 Business Information Systems: An Overview Learning Objectives : • Explain why information systems are essential to business • Describe how computers process data into useful information for problem solving and decision making • Identify the functions of different types of information systems • Describe how different information systems serve different levels within an organization • Evaluate how telecommunications and database technology can help implement the goals of information systems • Recognize the role of information technology in e-commerce • List major factors to consider when evaluating information systems and their roles in organizations • Identify major ethical and societal conflicts created by widespread use of information systems Chapter 2 Strategic Uses of Information Systems Learning Objectives : • Explain what business strategy and strategic moves are • Illustrate how information systems can give businesses a competitive advantage • Identify basic initiatives for gaining a competitive advantage • Explain what makes an information system a strategic information system • Identify fundamental requirements for developing strategic information systems • Explain circumstances and initiatives that make one SIS succeed and another fail Chapter 3 Information Systems in Business Learning Objectives : • Identify various business functions and the role of ISs in these functions • Explain how ISs in the basic business functions relate to each other • Show how ISs of different business functions support each other • Explain how information technology is used in the most common business functions to make business processes more effective and more efficient • Explain the notion of enterprise resource planning systems • Identify business areas where information technology facilitates the work of managers and knowledge workers Chapter 4 Information Technology in Business: Hardware Learning Objectives : • List major components of a computer and explain their functions • Explain how computers communicate • Classify computers into major categories, and identify their strengths and weaknesses • Describe how computers have affected the development of business • Define the most commonly used hardware terminology • Identify and evaluate key criteria when deciding what computers or related devices to purchase • Explain the controversy regarding the health hazards of computers • Evaluate hardware so that you can harness it to improve managerial processes Chapter 5 Information Systems in Business: Software Learning Objectives : • Explain why professionals must keep abreast of software developments • Enumerate the different generations of programming languages and explain how they differ • Explain the difference between application software and system software • Compare the strengths and weaknesses of tailored software versus off-the shelf software • Cite the latest major developments in application and system software • List characteristics that are important in evaluating packaged software applications for business use Chapter 6 Information Technology in Business: Telecommunications and Networks Learning Objectives : • Explain why successful managers must be familiar with telecommunications concepts and terminology • Describe the principles of communication within a computer system and among computers • Identify the major media and devices used in telecommunications • List and explain the functions of different network layouts and the concept of protocols • Explain how telecommunications can improve operations in organizations • Cite the latest developments in telecommunications media and transmission speed Chapter 7 E-Commerce: The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets Learning Objectives : • Explain how the Internet functions • List the features for information exchange that can be conducted over the World Wide Web • Explain how the Web facilitates electronic commerce • Explain basic business models on the Web • Chapter 8 Data and Knowledge Management Learning Objectives : • Explain the difference between traditional file organization methods and the database approach • Explain how database management systems are used to construct databases, populate them with data, and manipulate the data to produce information • Describe the different database models and the advantages and disadvantages of each model • Enumerate the most important features and operations of a relational database, the most popular database model • Illustrate how databases are changing business operations across industries and what impact they might have on our personal lives • Explain the concepts of data warehousing and data mining and their use in business and give examples of their use • Identify needs for knowledge storage and management in organizations • Give examples of the ways in which knowledge is managed in organizations Chapter 9 Managers and Their Information Needs Learning Objectives : • Explain the link between an organization’s structure and information flow • List the main functions and information needs at different managerial levels • Identify the characteristics of information needed by different managerial levels • Recognize the influence of politics on the design of, and accessibility to, information systems Chapter 10 Organizing Information Technology Resources Learning Objectives : • Describe the ways in which information technology personnel are deployed in organizations • List and explain the advantages and disadvantages of various personnel deployments • Explain the importance of collaboration between IS managers and business managers, and describe the relationships between the two groups • Contrast the advantages and disadvantages of charge-back methods for IS services • Describe career paths and responsibilities in the IS field Chapter 11 Supply Chain Management and Global Information Systems Learning Objectives : • Explain the difference between vertical and horizontal markets • Describe vertical and horizontal information integration among companies • Articulate the differences between traditional and Web-based EDI • Recognize the benefits of supply chain management systems • Explain the role of global information systems • Cite the legal, cultural, and other challenges to implementing international information systems Chapter 12 Decision Support Systems Learning Objectives : • List and explain the steps in decision making • Articulate the difference between structured and unstructured decision making • Describe the typical software components that decision support systems comprise • Describe the typical elements of geographic information systems • Identify business situations in which decisions can be supported by geographic information systems Case Studies: Case1.pdf (bad file) Case2.pdf Case3.pdf Case4.pdf *** See *.ppt and *.pdf files in the directory /MIS/MISozBook/ Lecture Note 9 : School of Business BSAD 556 TOPICS: MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS http://dheise.andrews.edu/courses/MIS/laudon/index.htm Instructor: David Heise The textbook: Laudon, Kenneth C. and Laudon, Jane Price. Management Information Systems: The Digital Firm, 7th ed List of Chapters Chapter 1: The Information Systems Revolution: Transforming Business and Management 1.1 Why Information Systems? 1.2 Contemporary Approaches to Information Systems 1.3 The New Role of Information Systems in Organizations 1.4 Learning to Use Information Systems: New Opportunities with Technology Discussion Questions Chapter 2: The Strategic Role of Information Systems 2.1 Key System Application in the Organization 2.2 Information Systems and Business Strategy 2.3 Using Systems for Competitive Advantage: Management Issues Discussion Questions Chapter 3: Information Systems, Organizations, and Business Processes 3.1 The Relationship Between Organizations and Information Systems 3.2 Salient Features of Information Systems 3.3 How Organizations Affect Information Systems 3.4 How Information Systems Affect Organizations Discussion Questions Chapter 4: Information, Management, and Decision Making 4.1 What Managers Do 4.2 Introduction to Decision Making 4.3 Individual Models of Decision Making 4.4 Organizational Models of Decision Making 4.5 How Information Technology Has Changed the Management Process Discussion Questions Chapter 5: Ethical and Social Impact of Information Systems 5.1 Understanding Ethical & Social Issues Related To Systems 5.2 Ethics in an Information Society 5.3 The Moral Dimensions of Information Systems Discussion Questions Chapter 6: Computers and Information Processing 6.1 What is a Computer System? 6.2 The CPU & Primary Storage 6.3 Computers & Computer Processing 6.4 Secondary Storage 6.5 Input and Output Devices 6.6 Information Technology Trends Discussion Questions Chapter 7: Information Systems Software 7.1 What Is Software? 7.2 System Software 7.3 Application Software 7.4 New Software Tools and Approaches 7.5 Managing Software Assets Discussion Questions Chapter 8: Managing Data Resources 8.1 Organizing Data in a Traditional File Environment 8.2 The Database Environment 8.3 Designing Databases 8.4 Database Trends 8.5 Management Requirements Discussion Questions Chapter 9: Telecommunications and Networks 9.1 The Telecommunications Revolution 9.2 Components and Functions of a Telecommunications System 9.3 Communications Networks 9.4 Electronic Commerce and Electronic Business Technologies 9.5 Management Issues and Decisions Discussion Questions Chapter 10: The Internet: Electronic Commerce and Electronic Business 10.1 The Internet: Electronic Commerce and Electronic Business 10.2 The Internet and Electronic Commerce 10.3 Intranets and Electronic Business 10.4 Management Challenges and Opportunities Discussion Questions Chapter 11: Redesigning the Organization with Information Systems 11.1 Systems as Planned Organizational Change 11.2 Systems Development and Organizational Change 11.3 Overview of Systems Development 11.4 Understanding the Business Value of Information Systems Discussion Questions Chapter 12: Approaches to Systems Building 12.1 The Traditional Systems Lifecycle 12.2 Alternative System-Building Approaches 12.3 System-Building Methodologies and Tools Discussion Questions Chapter 13: Systems Success and Failure: Implementation 13.1 Information System Failure 13.2 Causes of Information System Success and Failure 13.3 Managing Implementation Discussion Questions Chapter 14: Managing Knowledge 14.1 Knowledge Management in the Organization 14.2 Information and Knowledge Work Systems 14.3 Artificial Intelligence 14.4 Other Intelligent Techniques Discussion Questions Chapter 15: Enhancing Management Decision Making 15.1 DSS - Decision-Support Systems 15.2 GDSS - Group Decision-Support Systems 15.3 ESS - Executive Support Systems Discussion Questions Chapter 16: Information Systems Security and Control 16.1 System Vulnerability and Abuse 16.2 Creating a Control Environment 16.3 Ensuring System Quality Discussion Questions Chapter 17: Managing International Information Systems 17.1 The Growth of International Information Systems 17.2 Organizing International Information Systems 17.3 Managing Global Systems 17.4 Technology Issues and Opportunities Discussion Questions Chapter 18: Managing Firm Infrastructure and Enterprise Systems 18.1 Managing IT Infrastructure and Architecture: Enterprise Computing 18.2 Managing the New IT Infrastructure 18.3 Enterprise Systems 18.4 Industrial Networks and Extended Enterprise Systems Discussion Questions See files *.htm in the directory /MIS/Andrews/ Lecture Note 10: MIS 2403: INTRODUCTION TO DATA BASE MANAGEMENT – Spring 2004 http://www.clt.astate.edu/rsegall/lecture_notes61121.htm Instructor: Dr. Richard Steven Segall Required Texts: 1.) Hoffer, Prescott, & McFadden: MODERN DATABASE MANAGEMENT, Oracle Edition, Sixth Edition, Prentice-Hall, 2002. (ISBN: 0-13-061183-2) [Comes with Oracle 9i CD-ROM Package in Brown Box that: Includes set of 5 CD-ROMS: Oracle 9i Personal Edition Release 2 for Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP Professional (3 CDs) & Oracle 9i Developer Suite Release 2 for Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP Professional (2 CDs includes Forms Developer 9.0.2, Reports Developer 9.0.2, and Designer 9.02).] 2.) Pratt, Philip J.: A GUIDE TO SQL, Sixth Edition, Course Technologies, copyright 2003, ISBN 0-619-15957-X. Catalogue Description of Course: This course introduces the fundamental concepts and implementation of the relational database system. The student will be exposed to SQL methodology and Entity-Relationship (E-R) models. Overview of Course: This is an introductory course on database management and its system implementation techniques. It covers the structure of database management systems, relational database theory, the structural query language (SQL), and database system development and management using the industrial database system ORACLE 9i. Outline of Lecture Topics: Readings to be assigned from Hoffer, Prescott & McFadden (HPM): Modern Database Management and Pratt: A GUIDE TO SQL, Sixth Edition include: HPM Chapter 1: The Database Environment HPM Chapter 2: Database Development Process HPM Chapter 3: Modeling Data in the Organization HPM Chapter 4: The Enhanced E-R Model and Business Rules HPM Chapter 14: Object-Oriented Data Modeling HPM Chapter 5: Logical Database Design and the Relational Model HPM Chapter 6: Physical Database Design and Performance HPM Chapter 7: SQL HPM Chapter 8: Advanced SQL Pratt Chapter 1: Introduction to Database Management Pratt Chapter 2: Introduction to SQL Pratt Chapter 3: Single-Table Queries Pratt Chapter 4: Multiple-Table Queries See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/AstateDBMgmt/ และ student presentations ในไฟล์ *.ppt Lecture Note 11 : MIS 3413: ADVANCED DATA BASE CONCEPTS – SPRING 2004 http://www.clt.astate.edu/rsegall/lecture_notes611211.htm Texts: 1.) Hoffer, Prescott, & McFadden: MODERN DATABASE MANAGEMENT, Oracle Edition, Sixth Edition, Prentice-Hall, 2002. (ISBN: 0-13-061183-2) [Comes with Oracle 9i CD-ROM Package in Brown Box that: Includes set of 5 CD-ROMS: Oracle 9i Personal Edition Release 2 for Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP Professional (3 CDs) & Oracle 9i Developer Suite Release 2 for Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP Professional (2 CDs includes Forms Developer 9.0.2, Reports Developer 9.0.2, and Designer 9.02).] 2.) Pratt, Philip J.: A GUIDE TO SQL, Sixth Edition, Course Technologies, copyright 2003, ISBN 0-619-15957-X. Catalogue Description of Course: Continuation of MIS 2403 and extends the coverage of SQL using a popular DBMS. Topics include client applications, object-oriented database development, and data security. Prerequisite: MIS 2403 or equivalent. Overview of Course: This is an advanced course on database management and its system implementation techniques. It covers the implementation of databases and data administration using advanced concepts in structural query language (SQL), and other database software. Outline of Topics: Readings to be assigned from Hoffer, Prescott & McFadden (HPM): Modern Database Management and Pratt: A GUIDE TO SQL, sixth Edition, 2003 include: HPM Chapter 9: The Client/Server Database Environment HPM Chapter 8: Advanced SQL (More in-depth coverage) HPM Chapter 10: The Internet Database Environment HPM Chapter 11: Data Warehousing HPM Chapter 12: Data and Database Administration HPM Chapter 13: Distributed Databases HPM Chapter 14: Object-Oriented Data Modeling (was covered in MIS 2403!) HPM Chapter 15: Object-Oriented Database Development Pratt Chapter 4: Multiple-Table Queries Pratt Chapter 5: Updating Data Pratt Chapter 6: Database Administration Pratt Chapter 7: Reports Other topics as time permits. Grading Policy: The course grade will be determined by the following: Exam #1 (In-class & Take-Home): 15% Exam #2 (In-class & No Take-Home): 10% Exam #3 (In-class & Take-Home): 15% Homework: 23% (Any Optional Class Presentations Scores from MVCH will be added to Homework) Semester Team Project (All Phases & Final Written Report & Team Presentation): 22% Final (In-class & Take-Home): 15% See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/AdvDBMgmt/ และ student presentations ในไฟล์ *.ppt Lecture Note 12 : BARUC COLLEGE – CUNY ZICLIN SCHOOL OF BUSINESS Spring 2002, Dr. Abdullah Uz Tansel CIS 9000: Information Systems for Managers http://cisnet.baruch.cuny.edu/tansel/cis9000.html Textbook: Text (required): Laudon and Laudon: Management Information Systems (7th edition), Prentice Hall, 2001. Course Outline: Session Topic Chapter Jan. 28 Course Introduction. Formation of Project Teams Introduction to Information Systems, lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 1 Jan. 30 Finalization of Project Teams. "How to Approach a Case Study" An Epistemology of Information Systems: TPS/ MIS / DSS Case discussion: Modern Living (Available at the end of this document) Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 2 Feb. 5 Continue with chapter 2 Feb. 7 The Strategic Role of Information Systems (A Firm-Wide View of Systems) Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 3 Feb. 12 College closed Feb. 14 The digital firm: Electronic commerce and 4 Electronic business Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation Feb. 19 Computer Hardware Resources - Computer Systems Architecture. General Components, Multitasking, Multiprogramming, Multiprocessing. Downsizing and the Organization, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 5 Feb. 21 ** Case - Sun Life's Maestro Feb. 26 Software-- Machine Language Through 4GL. Trade-Offs and Programmer Productivity. Systems Software - General Functions. Offthe-Shelf (vendor) versus Custom Software, HTML, XML, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation Feb. 28 ** Case - Electronic Commerce at Air Products March 5 Database Management Systems A Advantages over 3GL Environment and traditional file processing, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 7 March 7 Database Management Systems B Comparison of DBMS Models - Costs / Considerations for DBMS Implementation 7 6 March 12 **Case: BroadVision (Written report submission) March 14 Telecommunications - LANs; Network Design, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 8 March 19 Mid term exam March 21 Telecommunications - Selection Criteria / Organizational Impacts March 26, 28 Spring recess April 2 EDI and Connectivity, Electronic Commerce, Transition to the Web, - April 4 **Case: HE Butt Grocery Company (A) April 9 Systems Analysis and Design, Structured Analysis and Design, Representation Methodologies, Alternative system building methodologies, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 9 10 April 11 ** Case: Providian Trust: Tradition and Technology (Written report submission) April 16 IT Feasibility Analysis – Tangible versus Less 11 Tangible. Impacts; Organizational, Technological and Cost Feasibility, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation April 18 Systems Analysis and Design B - Interface Issues, Implementation Design, MIS -Challenges and Issues. Organizational Resistance to IS Change April 23 ** Case: Sothebys.com April 25 Managing Knowledge, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation April 30 ** Case: BAE Automated Systems (A) Denver International Airport May 2 Decision Support Systems / Artificial 13 Intelligence. Business Applications of Expert Systems & Data Mining, Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation **Case: - How ECommerce will Trump Brand Management May 7 Contemporary Issues: Look and Feel; Security, 14 Privacy; Contractual Compliance, Restraint of Trade, Globalization and Information 17 Technology May 9 ** Case: Rich-Con Steel May 14 Social and Ethical Concerns Lecture notes in PowerPoint presentation 11 12 **Case: - The New Meaning of Quality in the Information Age See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/CunyISForManagers/ Lecture Note 13 : University of Surrey CS386 Managing Information Systems http://www.computing.surrey.ac.uk/courses/cs386/ Content The course is divided into the following areas: The IS revolution: the advent of IT, its impact on organisations and its strategic role. Information, IS, organisations and business processes: what is information and how can it be exploited? Management and decision-making: what is a manager? Managing data resources and managing knowledge: the management and exploitation of information. Redesigning the organisation with IS and enhancing management decisions: how can IT be integrated into an organisation to exploit information and improve process? Management approaches to systems-building, assessment of system success and failure: strategies for implementing IT systems and assessing their success or failure. Managing telecommunications and networks: the management of infrastructure, e-mail, Intranets, the Internet, Extranets and electronic business. IS security and control: how systems can be attacked and how systems can be designed to be secure from attack. Managing international IS, managing firm infrastructure and enterprise systems. Lecture Notes Notes divided by topic (when available): Introduction: Information Systems in Organisations: Information Systems, Organisations, Management and Strategy: Enhancing Management Decision Making: Redesigning the Organisation with Information Systems and Managing Change: Managing Data and Information: Information Systems Security and Control: Managing International Information Systems: Case Studies: Toromont Industries University of Albion 'Healthlite Yogurt' See files *.ppt in the directory /MIS/MISSurrey/ ----------------------------------