joint name
advertisement

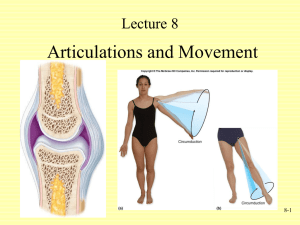
GCSE PE. YR10. 1. UNIT C4. JOINTS, TENDONS AND LIGAMENTS. Definition of Joint. “A joint is where two or more bones meet. As bones are rigid and do not bend, joints allow our muscles to create movement.” 2. 3 Types of Joint. 1. Fixed or Immoveable Joints. According to amount of movement allowed. Cannot move at all. Interlock or overlap. 3. E.g. between plates of the cranium. Slightly Moveable Joints. Move a little. Held together by ligaments and joined by cartilage. 4. E.g. between vertebrae. Freely Moveable Joints or Synovial Joints. Moves quite freely. All synovial joints have common features (see later). 3. E.g Knee Joint. Synovial Joints. A Synovial Joint has the following structures: JOINT CAPSULE SYNOVIAL MEMBRANE SYNOVIAL FLUID JOINT CAVITY CARTILAGE LIGAMENTS - 4. Outer sleeve. Holds bones together and protects the joint. Lines the capsule. Produces synovial fluid. Helps lubricate the joint. Small gap between the bones. Contains synovial fluid. Protects bones and stops them knocking together. Smooth, slippery covering on the ends of bones. Tough fibrous tissue which hold the bones together and keep the joint in place. Allow some movement. Prevent dislocation. Types of Synovial Joint. 1. Hinge Joint E.g. Knee, Elbow. Allows FLEXION and EXTENSION. 2. Ball and Socket Joint. E.g. Shoulder, Hip Allows FLEXION, EXTENSION, ABDUCTION ADDUCTION and ROTATION and CIRCUMDUCTION 3. Pivot Joint E.g. Atlas & Axis. Radius & Ulna. Allows ROTATION 4. Saddle Joint E.g. Base of Thumb, metacarpal & carpal. Allows FLEXION, EXTENSION ABDUCTION and ADDUCTION. 5. Condyloid Joint E.g. Wrist – Radius & Carpals Base of Skull & Atlas Allows FLEXION, EXTENSION ABDUCTION and ADDUCTION. 6. Gliding Joint E.g. Between Carpals. Between Tarsals. Allows a little GLIDING in all directions. 5. Diagram of the Knee Joint. Joints 3 worksheet. Teacher drawn. 6. Tendons and Ligaments. Tendons – Attach muscles to bones and allow us to move and apply power. As tendons are pull on hard by muscles, sports requiring explosive movements may damage tendons. E.g. Tendonitis at the elbow from tennis service. Ligaments – Ligaments join bone to bone and prevent joints from dislocating. As ligaments hold the joint in place, if there is too much movement at the joint it is often ligaments which are torn. This can be a very serious injury. E.g Football – Cruciate Ligament tears are quite common. 7. Ranges of Movement. FLEXION The action of bending a joint. EXTENSION Straightening a joint to it’s normal position. HYPEREXTENSION - Moving part of body / joint past it’s normal extension position. ABDUCTION ADDUCTION - Sideways movement of a limb away from the centre line of the body. Sideways movement of a limb towards or across the centre line of the body. ROTATION CIRCUMDUCTION - Turning movement around the axis of a bone. The end of a bone draws a circle. Homework. 1. 2. Complete Joints 3 sheet from EDEXCEL Teachers Resource Pack. Complete teacher planned table & question sheet. Resources. 1. 2. 3. GCSE PE for EDEXCEL 114-119 PE to 16. 20 –25 EDEXCEL Teachers Resource Pack. Joints 3 worksheet. JOINTS AND MOVEMENT. JOINT NAME JOINT TYPE BONES AT JOINT MOVEMENT ALLOWED SHOULDER ELBOW FEMUR & TIBIA BALL & SOCKET ATLAS & AXIS QUESTIONS. – Answer on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Sit straight in your chair, arms by your sides, hands flat on your knees, feet flat on the floor. A) Which Joints are flexed? B) Name two joints that are extended. 2. What movements are occurring at the following joints for these actions. a) Press up (low position) - Shoulder, Elbow & Wrist b) Preparation for kicking football - Hip, Knee & Ankle c) Finishing position for kicking a football - Hip, Knee & Ankle 3. Find a basic definition for FLEXIBILITY. 4. Why do you think FLEXIBILITY is important for performance of sports. Give examples from two different sports. 5. What is Arthritis? How is it caused? EXTENSION. - How might tendons and ligaments be affected by participation in sport. - What is Arthritis? How is it caused?