Nursing Care Plan: Activity Intolerance & Fluid Volume
advertisement

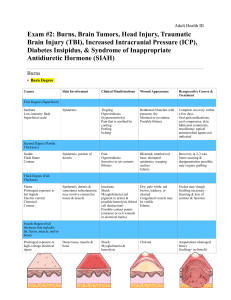
Nursing Care Plan 1 Lethbridge University, NESA program Nursing Care Plan Assessment Subjective: Complaining of SOB, especially at night and when walking, fatigue, and swelling in his ankles and feet. Stated, did not take his “water pill” for the last 5 days because his wife’s ankles were swollen so he gave the pill to her. Admitted to being “out of them heart pills” but cannot remember which ones. Nursing Diagnosis Activity intolerance r/t weakness, fatigue Expected outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Patient will participate in physical activity with appropriate changes in heart rate, blood pressure and breathing rate by the end of the month. Allow for periods of rest before and after planned exertion periods such as meals, baths, treatments, and physical activity. Patient will have both emotional and physical rest which will help lower arterial pressure and reduce workload of the myocardium Client will have increased activity tolerance by the end of the month. Slow the pace of care. Allow the client extra time to carry out activities Patient will improve the time it takes to do daily activities. Refer to heart failure program or cardiac rehabilitation program for education, evaluation, and guided support to increase activity and rebuild like. Patient will improved exercise capacity and quality of life in mild to moderate heart failure. Patient will be able to verbalize an understanding of the need to gradually increase activity based on teaching and symptoms by the end of the week. Patient will have reduced number of cardiac deaths, also decreasing cholesterol levels, and blood pressure. Client will verbalize understandin g of gradually increasing activity by the end of the week. Nursing Care Plan States is on several heart medications. Objective: -69 year old male. Allergic to penicillins, cephalosporin s, and midazelam. Physical exam revealed mild respiratory distress and 2+ dependent pitting edema. Serum creatine level was 88.4 umol/L 12 lead ECG revealed sinus tachycardia without ectopy. Chest radiography showed cardiomegaly Excess fluid volume r/t impaired excretion of sodium and water. 2 Patient will remain free of edema, effusion,and anasarca; and maintain stable weight by the end of two weeks. Monitor location and extent of edema; use a millimetre tape in the same area at the same time each say to measure edema in extremities. Patient will maintain clear lung sounds no evidence of dyspnea or orthopnea by the end of the month. Monitor lung sounds for crackles, monitor respirations for effort, and determine the presence and severity of orthopnea. Patient will maintain clear air ways and have adequate oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange at the alveolar-capillary membrane. Patient will maintain clear lung sounds by the end of the month. Patient will be able to explain measures that can be taken to treat or prevent excess fluid volume, especially fluid and dietary restrictions and medications by Monitor for side effects of diuretic therapy, orthostatic hypotension, hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalances. Fluid restrictions may decrease intravascular volume and myocardial workload Patient will verbally explain different measures that can be taken to prevent Monitor daily weights for sudden increases; use same scale and type of clothing at same time each day, preferably before breakfast to asses hydration status, and fluid overload Patient will have decrease in edema and swelling in extremities Patient will remain stable when it comes to their fluid volume by Patient will maintain a the end of stable weight. two weeks. Nursing Care Plan with lung filtrates. ABG results are pending. Swelling in ankles and feet. the end of the week. Implement fluid restriction as ordered , especially when serum sodium is low; include all routes of intake. A cognitivebehavioural group effectively helps Calculate an appropriate daily clients adhere to fluid fluid intake amount and work restrictions. with client to establish a fluid intake goal. 3 excess fluid volume. Provide scheduled rest periods. Bed rest can induce diuresis related to diminished peripheral venous pooling, resulting in intravascular volume and glomerular filtration rate. Care plan to be reassessed in 3 months with health care team



![Lymphatic problems in Noonan syndrome Q[...]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006913457_1-60bd539d3597312e3d11abf0a582d069-300x300.png)