Ineffective Health Maintenance Nursing Care Plan
advertisement
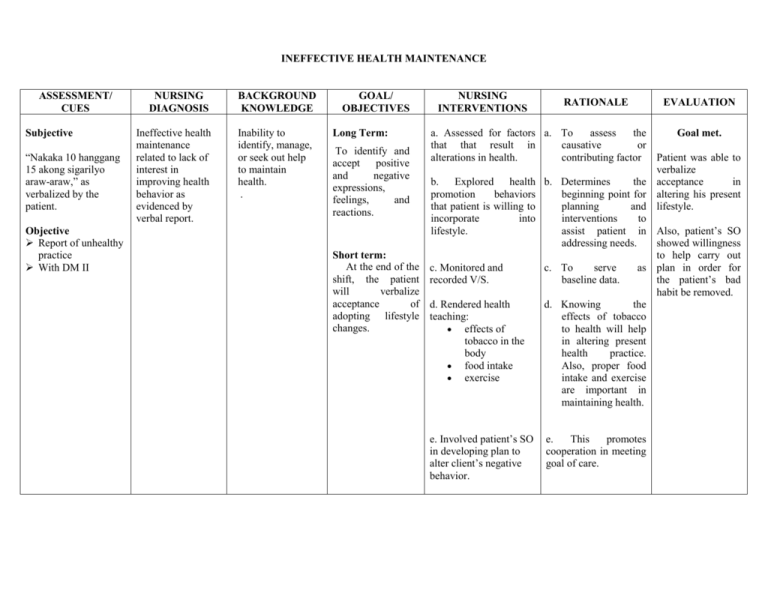
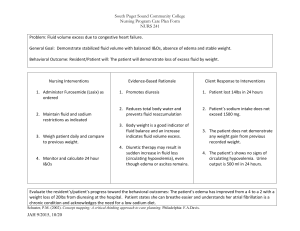
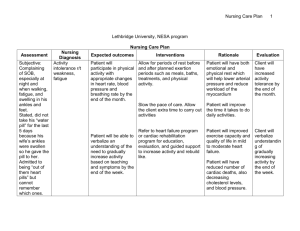
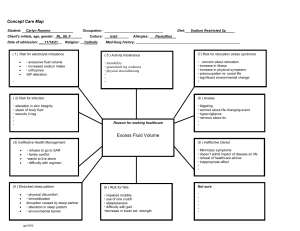
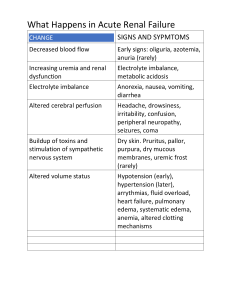
INEFFECTIVE HEALTH MAINTENANCE ASSESSMENT/ CUES Subjective “Nakaka 10 hanggang 15 akong sigarilyo araw-araw,” as verbalized by the patient. Objective Report of unhealthy practice With DM II NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective health maintenance related to lack of interest in improving health behavior as evidenced by verbal report. BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Inability to identify, manage, or seek out help to maintain health. . GOAL/ OBJECTIVES Long Term: To identify and accept positive and negative expressions, feelings, and reactions. Short term: At the end of the shift, the patient will verbalize acceptance of adopting lifestyle changes. NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION a. Assessed for factors a. To assess the Goal met. that that result in causative or alterations in health. contributing factor Patient was able to verbalize b. Explored health b. Determines the acceptance in promotion behaviors beginning point for altering his present that patient is willing to planning and lifestyle. incorporate into interventions to lifestyle. assist patient in Also, patient’s SO addressing needs. showed willingness to help carry out c. Monitored and c. To serve as plan in order for recorded V/S. baseline data. the patient’s bad habit be removed. d. Rendered health d. Knowing the teaching: effects of tobacco effects of to health will help tobacco in the in altering present body health practice. food intake Also, proper food exercise intake and exercise are important in maintaining health. e. Involved patient’s SO in developing plan to alter client’s negative behavior. e. This promotes cooperation in meeting goal of care. Name of Drug Generic name: Mannitol Brand name: Classification: Osmotic diuretic Dosage: 75 cc Form: IV solution Frequency: q8 Route: IV Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Mannitol elevates blood plasma osmolality, resulting in enhanced flow of water from tissues, including the brain and cerebrospinal fluid, into interstitial fluid and plasma. As a result, cerebral edema, elevated intracranial pressure, and cerebrospinal fluid volume and pressure may be reduced Reduction of intracranial pressure and brain mass; Cerebral edema Pulmonary congestion or edema CHF Metabolic edema with abnormal capillary fragility Anuria due to severe renal disease Severe dehydration Fluid and electrolyte imbalance; Acidosis (with high doses) Nausea and vomiting Headache, dizziness, chills, fever Tachycardia, chest pain Blurred vision; Hypotension or hypertension; Acute renal failure; Skin necrosis; Thrombophlebitis. Nursing Responsibilities 1. Note reason for therapy, characteristic S&S, underlying cause. 2. List other medications prescribed to ensure none alter drug effects. 3. Document findings, circulatory functions. neurologic evaluate and renal 4. Asses for S&S of fluid and electrolyte imbalances. 5. Monitor V/S and IO. 6. Report any S&S of pulmonary edema manifested by dyspnea, cyanosis, rales, and/or frothy sputum.