Arterial Gas Embolism
advertisement

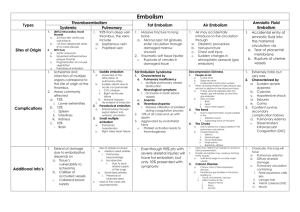
Arterial Gas Embolism 28/2/11 FANZCA Notes PY Mindmaps = ingress of gas into the arterial circulation -> embolism into distal capillary beds -> ischaemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (1) Paradoxical embolism - entrainment into the venous circulation -> enters arterial circulation causing end-artery obstruction. - patent foramen ovale (2) Overwhelming venous embolism - in the lungs with subsequent arterial embolism (3) Overexpansion of the lung through decompression barotraumas in diving, pulmonary barotraumas in ventilated and paradoxical embolism. (4) All bypass patients AETIOLOGY - entry of gas into aorta with distribution to organs - small emboli to skeletal muscle and viscera tolerated well - cerebral and coronary embolisation can result in severe morbidity CLINICAL FEATURES - cerebral: delayed recovery from anaesthesia - other end organ dysfunction INVESTIGATIONS - as indicated MANAGEMENT Jeremy Fernando (2011) - resuscitate: intubate, ventilate, CPR may be required identify and disable entry of gas hyperbaric oxygen high flow O2 volume expansion anti-epileptics (barbiturates) Jeremy Fernando (2011)