Pulmonary Embolism - Wellington Intensive Care Unit
advertisement

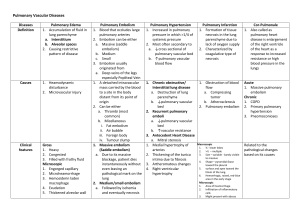
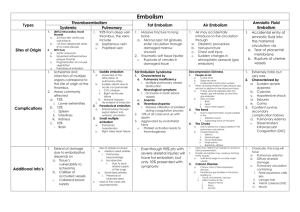
Pulmonary Embolism 16/8/10 PY Mind Maps OH Data Interpretation - Venkatesh Sinclair, D (2007) “ICU management of Pulmonary Embolism” Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 8:12 pages 534-536 British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Committee Pulmonary Embolism Development Group (2003) “The British Thoracic Society Guidelines for the management of acute pulmonary embolism” Thorax, 58:470-484 Agnelli, G et al (2010) “Acute Pulmonary Embolism” New England Journal of Medicine, 363(3):266-74, Jul 15. - effects are proportional to the time frame and degree of obstruction - increased PVR -> RVF -> obstructive shock - increased alveolar dead space -> V/Q mismatch -> pulmonary vasoconstriction to optimize gas exchange - pulmonary infarction CLINICAL FEATURES - subclinical -> massive History - SOB pleuritic chest pain apprehension cough haemotypsis leg pain collapse = massive PE - acute cardiovascular collapse Examination - pale, mottled skin tachypnoea tachycardia signs of DVT hypotension altered LOC elevated JVP parasternal heave loud P2 central cyanosis Jeremy Fernando (2011) Risk factors Major (relative risk 5-20) - SLOMMM Surgery – major abdominal/pelvic, hip/knee replacements, post ICU Lower limb problems - #, varicose veins Obstetrics – late pregnancy, C/S, puerperium Malignancy – abdominal/pelvic, advanced/metastatic Mobility – hospitalization, institutional care Miscellaneous – previous VTE Minor (relative risk 2-4) - COM Cardiovascular – congenital heart disease, CHF, HT, superficial venous thrombosis, CVL Oestrogens – OCP, HRT Miscellaneous – COPD, neurological disability, occult malignancy, thrombotic disorder, long distance travel, obesity, other (IBD, nephrotic syndrome, dialysis, myeloproliferative disorders, paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria, Bechet’s diseas) Thrombophillia’s - Factor V Leiden mutation Prothombin gene mutation Hyperhomocysteinaemia Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Deficiency of antithrombin III, protein C or protein S High concentrations of factor VIII or XI Increased lipoprotein (a) -> test in those < 50years with recurrent or a strong FHx INVESTIGATIONS - goal = confirm diagnosis + assess severity - normal compliance and peak pressures on ventilator - increased PACO2 -> ETCO2 to gradient - hypoxaemia - ECG: -> -> -> -> -> -> -> -> -> mostly normal sinus tachycardia SI, QIII, TIII non specific ST changes or TWI in anterior leads (right heart strain), right axis deviation s wave (I and aVL) > 1.5mm Q wave in III and aVF p pulmonale RBBB - CXR: rules out other pathology, focal oligaemia, wedge density (pulmonary infarction) - ABG: reduced PaO2 in keeping with size of PE, metabolic acidosis with circulatory collapse, respiratory alkalosis - D-Dimer: reassuring if negative to exclude PE, use in conjunction with clinical probability Jeremy Fernando (2011) - TNT: elevation is associated with adverse outcome even in normotensive patients, also associated with haemodynamic instability in patients with non-massive PE - BNP and NT-terminal BNP: if low correlates well with uneventful course - CTPA: as good as pulmonary angiography (gold standard), can calculate RV/LV ratio (>0.9) = severe - ECHO: RV dialation, paradoxical septal motion towards the LV, TR, RVF, PHT or PA thrombus on TOE, - US: leg veins (not as accurate as initially thought -> have low threshold to re-scan) - V/Q scan: only really used now when CT is contraindicated, (normal scan, low, intermediate and high probability with various criteria) - MRI – high rate of technical difficulty and insufficient sensitivity (PIOPED III study) MANAGEMENT Grade severity of PE MASSIVE – haemodynamically unstable -> thrombolyse/embolectomy SUB-MASSIVE – haemodynamically stable with evidence of RV dysfunction -> strongly consider thrombolysis/embolectomy but need to balance risk of bleeding MILD – haemodynamically stable with normal RV function -> anticoagulation Management Goals (1) prevent further embolism (2) removal of emboli (massive or sub-massive) (3) haemodynamic support (massive) Jeremy Fernando (2011) Resuscitate A – may need intubation if in cardiovascular collapse or cardiac arrest B – high flow O2 as a pulmonary vasodilator, ventilation to optimize V/Q mismatch, hyperventilation to clear CO2 C – invasive monitoring, fluid management to optimize right ventricular function, inotropic support, cautious fluid boluses, use milrinone, noradrenaline or adrenaline (rather than alpha agonists) Electrolyte + Acid-base - proportional to the degree of shock - may have a metabolic acidosis from hyperlactataemia from circulatory compromise Antidotes THROMBOLYSIS - not used in small or sub-massive (although this is contentious – doesn’t reduce mortality but does reduce deterioration) Jeremy Fernando (2011) - can be used up to 14 days after symptoms begin - PE resolve more quickly than with heparin alone - as successful as embolectomy in massive PE (earlier the better) - indicated in patients with RV compromise + haemodynamically unstable - rTPA 1.5mg/kg is maximum dose (as good through peripheral IV or CVL) - 50mg bolus of alteplase IV - contraindications: absolute - bleeding, recent stroke, HI, current GI bleeding, relative – PUD, surgery within 7 day, prolonged CPR - follow straight away with heparin - if bleeds -> FFP and anti-fibrinolytics ANTICOAGULATION - use UFH as first dose, in massive PE and where reversal may be required start immediately when there is a suspicion (prior to imaging) LMWH as good as heparin give straight after thrombolysis then needs warfarin (INR 2-3) SURGICAL - embolectomy (massive PE and unresponsive to thrombolysis or is contraindicated) - right heart catheterisation with clot destruction - IVC filter (high risk of further embolic or recurrent PE despite adequate anticoagulation, contraindications to anticoagulation, extensive DVT, massive PE) OTHER THERAPIES - ECMO – its place in PE is unknown - IABP – has been used with vasoactive medications - NO – has been used with some effect Underlying cause - prophylaxis - modify risk factors - diagnose thrombophillias Jeremy Fernando (2011)