vitamin - WordPress.com
advertisement

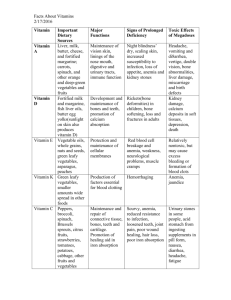
Fat Soluble Vitamins VITAMIN VITAMIN A (Retinol): PHYSIOLOGIC FUNC. B-carotene Retinol 11 cis retinol Proper night vision Night blindness Toxic in large amounts. Formation & maintenance of healthy epithelial tissue. Keratinization of corneal epithelium Xerophthalmia Loss of hair, joint pain, Growth of skeletal / soft tissues bone & teeth Keratinization of epithelium of skin / mucous membrane leading to Infections In children: hyperstoses Deficiency can be due to: o Inadequate dietary intake o Poor absorption o Inadequate hepatic Formed in the body by skin exposure to UV from sun or lamp Para-hormone (involved in Ca / P metabolism) jaundice, L. bone thicken (bone hypertrophy) Faulty tooth formation. o Peeling of skin Retarded growth o Headache, Nystagmus Loss of appetite o Lymph node enlarge In children: faulty bone formation & rickets (cranial Absorption of Ca & P from GIT o Calcification of soft tissues lungs / kidney bones soften, bowed thighs & knock-knees) o Hyper-calcemia Tubular reabsorption of Ca Calcification of bones (Ca mobilization from bone to blood) In adults: osteomalasia & hypo-parathyroidism. o VITAMIN E: Related to action of Selenium Hemolysis of RBCs Anti-sterility vitamin (proven in rats) Antioxidant (protects # peroxides which can destroy RBCs & capillary walls) Anemia. Sterility in males. Habitual abortion in females Muscular dystrophy Hemorrhagic tendencies PT time. VITAMIN K: Normal development of muscles Safe in large doses Blood clotting, necessary for hepatic synthesis of prothrombin. Toxic in large amounts. Xss oral AB inhibits flora Vitamin K deficiency. U.S. RDA o Bone fragility. digitalis tox. , MI Safe in large doses o Inf: hemorrhagic anemia, kernicterus, & bilirubin. o In adults: liver functn. jaundice. SOURCES Adult: 3,000 IU Liver, fish oil Inf: 1,300 – 2,600 Butter, whole Ped. prepn. must contain > 1,000 IU Adult prepn. must contain > 1,600 IU No prepn. should contain > 10,000 1IU = 0.3 retinol, 0.6 carotene In adults & children: conversion of B carotene VITAMIN D: Toxicity Retin = Retina ol = alcohol DEFICIENCY 400 IU (children; pregnant or lactating women) milk, egg yolk Green & yellow vegetables Yellow fruits (apricots) Fish oil / yeast Fortified or irradiated milk. 1 IU vitamin D = 0.025 g vitamin D2. In few foods: Adult: 5 - 10 IU Vegetable oil. Increases vitamin A absorption Seed oils. Anti-oxidant UNKNOWN Synthesized by normal GIT flora cod liver oil, little in milk, egg yolk Others: milk, eggs, meat & fish. Green leafy vegetables, Cheese, egg yolk, liver. Water Soluble Vitamins VITAMIN PHYSIOL. FUNCTIONS THIAMINE (B 1) Anti-beriberi factor Coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism (2 C atom metabolism getting rid of pyruvic). (Oral / IM / SC) RIBOFLAVIN (B 2) The yellow green florescent pigment in milk NIACIN (B 3) As nicotinic acid or nicotinamide (when vasodilatation is contraindicated we can use nicotinamide instead of nicotinic a PYRIDOXINE (B 6) Pyridoxal is more stable than pyridoxine Coenzyme in protein metabolism (proton carrier). Deficiency tissue inflammation. (def. occurs in conjunctn. with other B vit.) Coenzyme in tissue oxidation as H+ carrier energy (ATP productn in respiratory chain). Metabolism of Fat, protein, glucose. Uses: ttt Nicot. a (not nicotinamide) > 3 gm / day, hypocholest. of pellagra. Coenzyme in amino acid metabolism (in decarboxylation & transamination) Production of GABA (a neurotransmitter inhibitor that prevents convulsions) Deficiency Results from eating white wheat polished rice & alcoholics Beriberi Toxicity Very safe; toxicity not marked. U.S. RDA Adults > 0.6 mg Uses: GI: Anorexia, HCl Beriberi CNS: Fatigue, Mental Disorders, Periph neuritis, Periph neuritis in DM CV: Card. failure / LVH, TC Mental Disorders Wound aggravation Adults > 1.0 mg Cheilosis (cracks at corners of mouth). Infants > 0.6 mg Glossitis, eye irritation. Pellagra characterized by scaly dermatitis, photosensitivity & fatal effects on CNS Neuralgia Never given alone but with other B vit. (Oral, IM, SC) Seborrheic dermatitis. Vasodilatatn, flushing Adults: > 6 - 45 mg Hepatotoxicity GI irritatn/ ulceration Weakness, lassitude Hyperuricemia Infants > 4 mg (niacin equivalent) 60 mg tryptophan = 1 mg nicotinic acid Anorexia, indigestion. Glucose intolerance interrelated in cell (hyperglycemia) metabolism. If one is CNS: neuritis, confusion, apathy, schizophrenia. Anemia (hypo chromic, microcytic). CNS: epileptic convulsions, peripheral neuritis. Beef, liver, pork, fish, eggs. Whole or enriched grains. Yeast Milk, liver, kidney Enriched cereals Meats Enriched grains. Infants > 0.4 mg SOURCES Vitamin B1 is thermolabile. Absorbed from upper GIT Peanuts, beans, peas B3 & B2 are closely deficient the other is. B6 is contraindicated wit Ldopa (Why) 2 mg (Pregnancy & estrogen/progest OC B6 additional B6) INH, hydralazine & penicillamine deplete tryptophan B6 def. Wheat, corn, yeast Meat, liver, Kidney GIT flora B6 but significance not determined VITAMIN PANTOTHENIC ACID Found throughout body tissues PHYSIOLOGIC FUNC. Coenzyme in overall body metabolism Deficiency U.S. RDA Contributes to: Converted to Co-A (Ac Ch synthesis & fatty a metabolism) Amino acid activation Locally to aid wound healing. IM to aid motility of the intestine after surgical op (post-op paralytic ileus. SOURCES GIT flora syn. a considerable amount + wide spread in nat. sources def. not common Liver, kidney Yeast, egg yolk Skimmed milk. Leafy vegetable 50 ug Liver, kidney Formation of Cholesterol Excretion of drugs Megaloplasic anemia Not toxic by oral route Sprue (GIT disease characterized by severe diarrhea). Pern. anemia (doesn’t control neurologic sym) Green leafy vegetables Megaloblastic anemia. Asparagus. Sprue treatment. 6 ug. Liver, meat, egg. milk, cheese. “micronutrient” bec minute traces metabolic task Egg yolk, Liver, kidney. Tomato, yeast . FOLIC ACID Important in cell growth & blood forming factors. Essential for synth. of purine & pyrimidine nucleotides COBOLAMINE (B12) Coenzyme in protein synthesis Pernicious anemia Formation of red blood cells. Sprue treatment + folic a BIOTIN Coenzyme in CO2 reactions in energy metabolism. Undetermined. Involved in fatty a synthesis & in carboxylation reactns. CHOLINE Essential for synthesis of phosphatidyl-choline involved in lipid transport & acetylcholine synthesis Synthesized by GIT flora or with ingested food (nat. def. unknown) Large amounts of white deficiency. egg Synth. in body from amino acid methionine VITAMIN C Building & maintaining collagen, cartilage, bone matrix & connective tissue. Scurvy * Wound healing, tissue Wound healing, tissue GIT absorption of iron Redox reactions in the body Cellular respiration formation (cementing connective tissue) Megahemoglobinemia (bec of its reducing properties) Fever, infections stored vitamin C Stress reactions Growth period. ttt of alcohol overdose stimulates alcohol dehydrogenase Increased formation in UT. stone Adult > 150 mg Child > 20 mg Diarrhea 10 gm daily of vit C followed by rapid withdrawal frank symptoms of scurvy. Women have higher vitamin C levels than men. Smoking vitamin Scurvy develops in C levels in blood. newborns to mothers who suddenly stop large daily doses of vitamin C. Citrus fruits, tomatoes, green & yellow vegetables (cabbage, potatoes) & strawberries.