Facts about Vitamins
advertisement

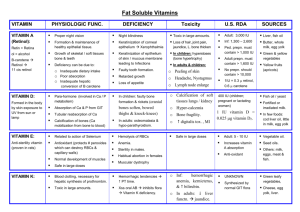
Facts About Vitamins 2/17/2016 Vitamin Important Dietary Sources Liver, milk, Vitamin butter, cheese, A and fortified margarine; carrots, spinach, and other orange and deep-green vegetables and fruits Fortified milk Vitamin and margarine, D fish liver oils, butter egg yolks(sunlight on skin also produces vitamin D) Vitamin E Vegetable oils, whole grains, nuts and seeds, green leafy vegetables, asparagus, peaches Vitamin K Green leafy vegetables, smaller amounts wide spread in other foods Vitamin C Peppers, broccoli, spinach, Brussels sprouts, citrus fruits, strawberries, tomatoes, potatoes, cabbage, other fruits and vegetables Major Functions Signs of Prolonged Deficiency Toxic Effects of Megadoses Maintenance of vision skin, linings of the nose mouth, digestive and urinary tracts, immune function Night blindness’ dry, scaling skin, increased susceptibility to infection, loss of appetite, anemia and kidney stones Development and maintenance of bones and teeth, promotion of calcium absorption Rickets(bone deformities) in children, bone softening, loss and fractures in adults Headache, vomiting and di8arrhea, vertigo, double vision, bone abnormalities, liver damage, miscarriage and birth defects Kidney damage, calcium deposits in soft tissues, depression, death Protection and maintenance of cellular membranes Red blood cell breakage and anemia, weakness, neurological problems, muscle cramps Production of factors essential for blood clotting Hemorrhaging Maintenance and repair of connective tissue, bones, teeth and cartilage. Promotion of healing aid in iron absorption Scurvy, anemia, reduced resistance to infection, loosened teeth, joint pain, poor wound healing, hair loss, poor iron absorption Relatively nontoxic, but may cause excess bleeding or formation of blood clots Anemia, jaundice Urinary stones in some people, acid stomach from ingesting supplements in pill form, nausea, diarrhea, headache, fatigue Facts About Vitamins 2/17/2016 Thiamin Whole-grain and enriched breads and cereals, organ meats, lean pork, nuts, legumes Conversion of carbohydrates into usable forms of energy, maintenance of appetite and nervous system function Riboflavin Dairy Energy products, metabolism, enriched breads maintenance of and cereals, skin, mucous organ meats, membranes, and lean meats, nervous system poultry, fish, structures green vegetable Niacin Eggs, poultry, Conversion of fish, milk, carbohydrates, whole grains, fats, and protein nuts, enriched into usable forms breads and of energy cereals, meats, legumes Vitamin Eggs, poultry, Protein and B-6 fish, whole neurotransmitter grains, nuts, metabolism, red soybeans, liver, blood cell kidney, pork synthesis Folate Green leafy Amino acid vegetables, metabolism yeast, oranges, synthesis of RNA whole grains, and DNA, new legumes, liver cell synthesis Vitamin Eggs, milk, Synthesis of B-12 meats, other blood cells and animal foods other metabolic reactions Biotin Cereals, yeast, Metabolism of egg yolks, soy fats, flour, liver, carbohydrates, widespread in and proteins foods Beriberi (symptoms include muscle wasting, mental confusion, anorexia, enlarged heart, nerve changes) None Reported Cracks at corners of mouth, sore throat, skin rash, hypersensitivity to light, purple tongue None Reported Pellagra(symptoms include diarrhea, dermatitis, inflammation of mucous membranes, dementia) Flushing of the skin, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, liver dysfunction, glucose intolerance Neurological abnormalities and damage Anemia, convulsions, cracks at corners of mouth, dermatitis, nausea, confusion Anemia, weakness, fatigue, irritability, shortness of breath swollen tongue Masking of Vitamin B-12 deficiency Anemia, fatigue, nervous system damage, sore tongue None reported Rash, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, depression, fatigue, hair loss None Reported