Nutrition Deficiencies
advertisement

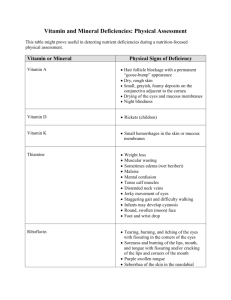
Name:________________ Date:_________________ Class:_________________ Worksheet Nutrition Deficiencies Topic #3041 Ashlee Gibson Read the situations or symptoms described below. Answer the questions by looking at the deficiency charts included in the packet. With these situations, we are assuming everything is caused by some type of deficiency. 1. Uncle Joe has a ewe that has had really stiff joints, if it isn’t arthritis, would there be any vitamins or minerals you could suggest to check out? 2. The neighbor’s horse has constant diarrhea. By looking at the chart, would this more likely be a vitamin deficiency or a mineral deficiency? And, what specifically? 3. Bob’s cow has a few bald spots on her body. He can’t really find anywhere where she is rubbing. Could you suggest any deficiencies? 4. Triple T Ranch has a horse in their herd that seems to have a constant nasal discharge. They have ruled out any type of cold or sickness. Look at the chart and decide what type of deficiency this could be. 5. Would poor, slow or retarded growth be an easily diagnosable deficiency from this chart? Why/why not? 6. Mrs. Shim has 2 horses in a wooded corral for the winter. In spring she notices that the horses had chewed the fencing? What would the deficiency be for these horses? 7. What is anemia? 8. Define the following words found in the chart. AnemiaCoagulation Scurvy Mineralization Retinol- Vitamin Deficiencies Fat Soluble Vitamins Vitamin A Function Deficiency Signs Required in retinol for night vision; needed in epithelial cells that cover body surfaces; needed for bone growth Vitamin D Enhanced calcium and potassium levels allowing bone mineralization; prevents tetany Vitamin E Promotes health Vitamin K Required for blood clotting Night blindness; dry and irritated eyes; respiratory infection; reproductive problems Abnormal skeletal development- lameness, bowed, and crooked legs; slowed growth Failure of the reproductive system; changed cell permeability; muscular lesions Long blood clot time; hemorrhages; in severe cases, death Thiamin (B1) Promotes health Riboflavin (B2) Niacin Functions in coenzymes Pantothenic Acid Needed in energy metabolism Vitamin B6 Vitamin B12 Help with protein and nitrogen metabolism; involved in formation of red blood cells Need in several enzyme systems Folacin Biotin Used in a variety of metabolic reactions Needed for several enzyme systems Choline Aids in transmission of nerve impulses Vitamin C Prevents scurvy; causes several metabolic reactions to occur Used by cells in energy metabolism Anorexia, numbness, weakness, and stiffness in thighs, unsteady walk, edema in feet and legs, and painful along the spine Reduced growth rate; skin lesions; hair loss Retarded growth; decreased appetite; diarrhea; vomiting; dermatitis Slowed growth; dermatitis; graying of the hair; fetal death; skin lesions Convulsions; lesions around feet, face, and ears Anemia, retardation; skin pigmentation Slow growth rate; anemia Scaly skin; abnormalities of the circulatory system Fatty liver; hemorrhaging kidney Scurvy-edema, weight loss, and diarrhea Mineral Deficiencies Macrominerals Function Calcium (Ca) Structural component of the skeleton; controls the excitability of the nerves and muscles; required for coagulation of the blood Phosphorus (P) Magnesium (Mg) Component of the skeleton providing structural support; aids in lipid transport and metabolism Needed for skeletal growth; needed for chemical reactions in the muscles Potassium (K) Required to move sodium; helps to uptake glucose and carbohydrates Iodine (I) Component of the thyroxin Deficiency symptoms Rickets or osteomalacia develop- the bones become soft and deformed; milk fever occurs in cows; blood clotting time increases Rickets; depressed appetite; may chew on wood or other objects Anorexia; reduced weight gain; hyperemia of the ears and other extremities Slowed growth, unsteady walk, overall muscle weakenss Goiter- enlargement of the thyroid gland; dry skin, brittle hair; young born Iron (Fe) Found in the hemoglobin in the blood Selenium (Se) Component of numerous enzymes without hair; reproduction problems Amenia- common problem among newborns; pale color; shallow breathing; rough hair; slow growth; Nutritional muscular dystrophy