16 Proteins/Vitamins
advertisement

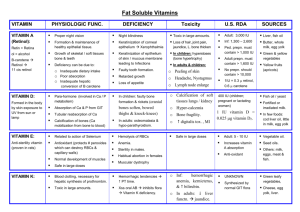
PROTEINS IN THE DIET Humans have about 10kg protein and need to replace about 300g daily: recycle ~230g need to eat ~30g ~40g Most of us >100g/day meat/fish/egg protein grain protein per day FOOD Meat Beef Chicken Salmon Grain Bread Rice, cooked Dairy Milk, whole Cheese Eggs Fruits Apples Bananas Nuts – Almonds Vegetables Potato Corn Tomato WATER PROT FAT CARB kcal /100g 62 71 64 32 24 27 5 4 7 0 0 0 180 140 180 36 70 10 3 3 0 50 26 250 120 87 37 74 3 25 13 3 32 11 5 2 1 65 400 160 84 76 5 0.2 1 19 0 0.2 54 15 22 20 60 85 600 75 74 94 2 3 1 0.1 1 0.2 21 21 5 90 90 22 Some grains lack some amino acids CORN RICE WHEAT SOY lacks lysine and tryptophan lacks lysine and threonine lacks lysine lacks methionine (need 2g/day of this one) KWASHIORKOR is common in Africa where corn is almost the exclusive food consumed: characterized by bloated and swollen belly, scaly skin, retarded growth and mental apathy Not generally a problem with a balanced vegan diet in North America as a variety of seeds and nuts provide all necessary amino acids From an efficiency standpoint, consuming animal proteins is not necessarily the best option: To produce 1kg of animal protein requires the following kg of feed: Beef Chicken Catfish/Carp 20 5 2.5 Pork Eggs 8 4 Animal protein sources have changed a lot over the last few decades (chicken was ~ equal to mutton in 1950): Beef Pork Mutton Chicken Ocean Fish Farm Fish 1990 (M tons) 53 70 10 41 85 13 2003 59 96 12 76 93 40 Growth/y World 0.8 2.5 1.6 4.9 0.8 9.7 High protein – low carb diets (Atkins, Zone, Protein Power…) Result in quick weight loss because eliminating carbohydrates results in loss of body fluids – but, according to the American Heart Association, are not effective long term: impede fat metabolism, generally substitute carbohydrates with fats, restricts mineral intake, causes ketosis (and nausea) Some people can’t metabolize excess protein resulting in liver and kidney disorders 2002: Acrylamide, a potent carcinogen, identified in many popular foods such as fries, potato chips, cakes, bread, coffee, cookies Comes from carb rich foods that are fried or baked Source identified from amino acid asparagine + dicarbonyl compound from browned sugars H2N-CO-CH2CH<COOH NH2 + R-CO-CHO heat H2N-CO-CH=CH2 Is this a risk? Maybe not: NOAEL (no observed adverse affect limit) is 500x higher at 0.5 mg/kg body weight than the amount in a normal portion of the worst offender, french fries (ca. 50 mg/serving) FOOD - MINERALS AND VITAMINS RDA/DRI=800/ 1000-1300*mg 2mg *generally higher values are for 15-18 yr olds, and 50+ RDA is old recommended daily allowance, DRI is new joint Canada/US intake values 3(F)-4(M)mg 100-150/150mg 10-18/10(M)-15(F)mg 300-400/320(F)-420(M) 800-1200/700-1250 (15-18y) /55(F)-70(M)mg 15/12(F)-15(M) IODINE Iodine required for Thyroxine which controls the thyroid gland: regulates rate at which cells use O2 and the base metabolic rate GOITER = swollen neck (size of head) caused by too much or too little iodine. All salt in NA has 0.1% KI added to avoid this problem I HO I NH2 COOH O I I thyroxine L-form is active amino acid VITAMINS OIL (FAT) SOLUBLE = A, D, E, F, K WATER SOLUBLE = B, C. VITAMIN A = RETINOL: derived in body from b-carotene (orange pigment in carrots) liver CHO CH2OH oxn b-carotene b-carotene 2 retinol (vitamin A alcohol) retinol citral citral Commercially, citral from lemon grass can be converted to Vitamin A or carotene US uses RDA (recommended dietary allowance), CAN uses RNI (recommended nutrient intakes) RDA = 5000 IU (International units) (~1500 RE) = 1.5 mg retinol = 1.72 mg of Vit A acetate ≡ 3 mg carotene NOW 1000 RE (retinol equivalents) = 1 mg (1000mg) of retinol These differ by country, eg. UK = 800RE = 0.8 mg; Canada = 870 RE = 0.87mg and by gender: F = 80% of male Function: Vitamin A protects against invading bacteria - makes mucus secreting cells produce sticky stuff which trap bacteria; - prevents night blindness - (regeneration of retinal pigments); - keeps skin and tear ducts healthy DEFICIENCY: Light sensitivity, night blindness, infections ~ 1 million people in India suffer night blindness EXCESS: probably most toxic vitamin in excess irritability, dry peeling skin, pressure in head severe liver injury if >25,000 IU. only 5x normal dose also TERATOGENIC: birth defects of eyes, ears, heart avoid liver if pregnant (limit 8,000 IU) SOURCES: CAROTENE: fish liver oils, egg yolks, apricots, peaches not poisonous, present in carrots, green vegetables VIT A is fat soluble so passes up food chain: highest in polar bear liver (~20,000 IU/g!!) Adults store a year’s supply in fat India: diet is deficient; GM modified rice to produce carotene trans-RETINOIC ACID; RETIN-A; TRETINOIN Causes the skin to peel: used in cosmetics as an anti-acne agent, anti-skin damage, anti-wrinkle...OK in limited doses topically Some questions as to its efficacy: see the FDA site on RENOVA: http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/label/2000/21108lbl.pdf cis-RETINOIC ACID; ISOTRETINOIN; ACCUTANE Orally for severe acne, BUT it has severe side effects and is powerful TERATOGEN: requires two pregnancy tests to start see: http://www.aocd.org/skin/dermatologic_diseases/accutane.html Tretinoin Isotretinoin VITAMIN D (calciferol) 400 IU = 10 mg of Vit D3 US = 5-10 mg; UK 5-7 mg; CAN 3-5 mg sunlight HO 7 HO 7-dehydrocholesterol Sources: Vit D3 cholecalciferol Pre-vitamin in cereals, bread, milk sunlight converts it to active vitamin Function: Vitamin D controls Ca and P absorption from foods, metabolism, transport of Ca in bloodstream and formation of bones DEFICIENCY: soft, deformed bones (RICKETS) not enough Ca3(PO4)2 to stiffen them; poor teeth Stored in fat Excess is toxic: 250 mg/d for 4 weeks or 5 mg/d for 2 weeks causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache Too much Ca/P: stiffens joints a-TOCOPHEROL VITAMIN E USRDA = 30 IU (30 mg) old racemic RH/LH mixture now use d-(RH) a-tocopherol = 16.7 mg O HO Function: prevents oxidation of fats maintains red blood cell membranes necessary for proper functioning of: genitals, lungs, liver, kidneys Not destroyed by heat but sensitive to O2 Not as fat soluble as A or D so storage in body is shorter DEFICIENCY: edema (water under skin), anaemia in kids, muscular dystrophy EXCESS Vitamin E: recently recognized as a potential health hazard increases LDL, depresses platelet formation by causing Vit K deficiency (slows blood clotting), shows immunosuppresant properties (see for eg. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/126268-overview) Sources: plenty in grains, meats, eggs, nuts, salmon (oily fish) VITAMIN F = (w-6)-linoleic acid (see fats section) D9,12-octadecadienoic acid HO O Function: Important for structural cell membranes Sources: present in all fats, some vegetable oils and many expensive supplements DEFICIENCY coarse sparse hair, eczema (RDA = 1.3 g) O VITAMIN K H O n n = 5-13 Function: Synthesis of prothrombins (blood coagulants) DEFICIENCY: haemorrhages, slow blood clotting (RDA ~ 80 mg/d) EXCESS: clotting Sources: Found in leafy veg like cauliflower, broccoli Must watch intake if on blood thinners ANTI-VITAMIN K: dicoumarol is found in clover, alfalfa substitute is warfarin (blood thinner, rat poison) O O OO O OH O HO O OH Dicoumarol [Dicumarol] Warfarin Inhibits Vit K dependent synthesis of blood clotting factors WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS: washed out so need more frequently B-GROUP B1 co-enzymes in growth and energy production THIAMINE RDA = 1.5mg N NH2 N S OH N + Cl - Function: carbohydrate metabolism (decarboxylation of pyruvate and ketoglutarate), energy production, ATP levels, heart and circulatory system functioning Deficiency: Beriberi*, muscular atrophy, nervous disorders Sources: grain skin, soybeans, bran, peanuts, meat, liver, eggs (bread and cerials are enriched: 2.1 mg/100g) *Beriberi: laboured breathing, enlarged heart, mental confusion, paralysis of arms/legs – common with exclusive white rice diet B2 RIBOFLAVIN RDA = 1.2-1.8 mg HO OHOH OH N N O NH N O Function: used as part of co-enzyme FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide); metabolism of fats and proteins DEFICIENCY: cracks around mouth, sore eyelids, oily skin around nose, DERMATITIS, fatigue, stops tissue growth Sources: liver, milk, eggs, leafy veg Added to enriched bread, cereals: 3.6 mg/100g B3 COOH (orCONH 2) NIACIN RDA 13-20mg N Function: part of co-enzyme NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) metabolism and synthesis of carbs, fats, proteins, (alcohol) Deficiency – the three D’s: Diarrhea, dermatitis and dementia (Pellagra) Sources: yeasts, liver, peanuts, whole grains, potatoes Corn is deficient in niacin so people in SE USA used to get pellagra Added to enriched bread, cereals: 21 mg/100g High levels of Niacin have been shown to raise HDL and lower LDL but high levels of niacin can also cause liver damage: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002409.htm OH B5 PANTOTHENIC ACID H N Incorporated into Co-enzyme A O Function: Deficiency: Sources: OH HO O transfers C2 units in metabolism of fats and carbs retarded growth liver, salmon, eggs, nuts, yeasts, broccoli, cauliflower OH B6 PYRIDOXINE 1.7-2.0 mg/d Function: Deficiency: Sources: HO OH N metabolism/synthesis of proteins oily dermatitis, nausea, vomiting, weakness, dizziness yeasts, bran, carrots, bananas, liver, eggs, meats Morning sickness during pregnancy is reduced with extra B6 EXCESS: (100 mg/d): loss of balance, numbness (sold 100-500 mg) O B7 BIOTIN 0.3-1 mg/d NH HN COOH S Function: Deficiency: Sources: carboxylase coenz (transfer CO2 in food metabolism) sleepiness, muscle pains, aversion to food, increase in blood cholesterol, dry scaly skin most vegetables, liver, milk, nuts B9 FOLIC ACID 0.15-0.4 mg/d N (2x pregnant F) Function: Deficiency: Sources: N H2N N N OH NH CONH CHCH2CH2COOH COOH coenzymes of growth, especially red blood cells anaemia, fatigue, poor appetite, forgetfulness liver, whole grains, yeast, green veg Folic Acid Controversies Pregnant women: protects baby from spina bifida BUT Swedish study suggests increased chance of twins and cerebral palsy Is this risk > spina bifida risk? US has made folic acid a compulsory additive in cereals: reduces blood homocysteine, reduces heart disease http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/iyh-vsv/med/folic-folique_e.html http://www.marchofdimes.com/professionals/690_1403.asp B12 COBALAMIN RDA = 6 mg/d Function: catalyzes synthesis of nucleic acids, red and white blood cells, RNA to DNA conversion Deficiency: pernicious anaemia inability to absorb vitamin from food (need to have them injected) Sources: Meat and dairy, seafood No significant plant sources Needs to be formed by bacteria or consumed in meat C ASCORBIC ACID RDA = 50-60 mg/d Deficiency – Scurvy: bleeding hair follicles, edges of nails, bleeding stinking gums, weight loss, black lungs, damaged liver, swollen legs... Only need ~ 10 mg/d to prevent scurvy Sources: all citrus fruit, potatoes, tomatoes, cabbage English sailors corrected the deficiency with limes: ‘limeys’ Need 300mg of Vit C in body, of which need to replenish ~60 mg/d Cannot be stored for long: excrete excessive doses (>200 mg/d) Pauling advocated (and took) > 2 g/d Function: ANTI-OXIDANT that scavenges free radicals slows or prevents invading viruses (VIT C – Common Cold connection) regenerates Vit E in the body heat and oxygen sensitive (old bottles are not good) OH HO HO O HO O O O HO O O HO + 2 e- + 2 H+ O2 + 2 H+ + 2 e- H2O2