Cell Test 1 – Review Sheet

Name: _________________
Date: _________________
Period: ________________
Cell Test 1 – Review Sheet
1) State the three parts of the Cell Theory: a. All cells come from cells. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
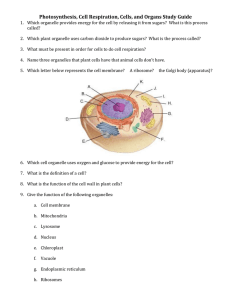
2) What two organelles are only in a plant cell?
Cell wall and chloroplasts
3) What organelle is larger in the plant than the animal? Why?
Vacuole – Because plants need to be able to store more water because they can’t get it when they need it.
4) Explain the function(s) of the following organelles: a. Nucleusdirects all of the cell’s activities b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions c. Cell membrane – the next barrier within the cell wall – all cells have membranes - controls what substances come into and out of the cell d. Chloroplast – green organelles in plants that capture energy from the sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell e. Cell wall – a rigid layer of nonliving material (composed of cellulose) that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms f. Vacuole – storage areas within the cell for food, wastes and water
5) Cell Processes a. What is selective permeability? the cell membrane allows some substances to pass through while others cannot b. Define passive transport: the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without the use of cellular energy ex. Define diffusion: the process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Example of diffusion: candle, chocolate milk, air freshener, etc. ex. Define osmosis: the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane c. Define active transport: the movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy
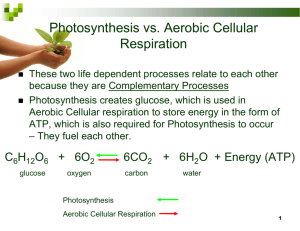
6) How does photosynthesis help living things?
It creates food they can eat and oxygen they can breathe.
7) What happens during photosynthesis? a. What types of living things carryout photosynthesis? Plants (autotrophs)
b.
Define - the process by which a cell captures energy in sunlight and uses it to make food. c.
Equation 6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2 carbon dioxide water d.
Organelle used : __Chloroplasts sugar oxygen e.
What would happen to the cell if this organelle stopped working?
The cell would be unable to produce food for itself which would make it impossible to survive.
8) What happens during respiration? a.
What types of living things carryout cellular respiration? Both plants and animals (autotrophs and heterotrophs) b.
Define – the process by which cells breakdown sugar and release the energy it contains.
c.
Equation
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + Energy
sugar oxygen carbon water dioxide d.
Organelle used : __Cytoplasm, Mitochondria e.
What would happen to the cell if this organelle stopped working?
The cell would not have the energy necessary to carry out its cell processes, resulting in death.
9) What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
They are opposite processes. The raw materials for photosynthesis are the products of cellular respiration and vice versa. This important because oxygen is in .limited supply in the environment.
10) The six characteristics of living things
1. Cells
2. Reproduce
3. Respond to the Environment
4. Grow and Develop
5. Energy Use (autotroph/heterotroph)
6. Chemicals of life
** Be sure you can match these with examples.
11) Basic needs of all living things
1. Food
2. Water
3. Shelter
4. Oxygen
12) Make sure you can identify the 7 major organelles in a picture of a cell. (see below)
13) Be sure you know the major parts of a microscope and how find total magnification of a specimen when viewed using the microscope. Eyepiece X Objective