Note 17
advertisement

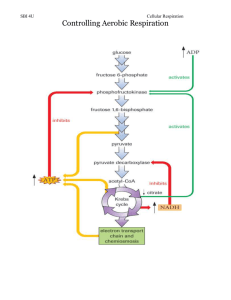
South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School Biology Revision Note 17 Respiration - is the process by which energy is given out Aerobic respiration - the release of energy using oxygen - take place in nearly ALL living organisms Glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water [overall reaction] (energy is released as heat and it is used to do phosphorylation : ADP + [P] ATP]) Anaerobic respiration - the release of energy without oxygen Alcoholic fermentation - takes place in yeast, bacteria, lower organisms, green plants Glucose ethanol (alcohol) + carbon dioxide (energy is released as heat and for phosphorylation) Accumulation of ethanol (alcohol) can kill the living organisms. Lactic acid fermentation – takes place in skeletal muscle of man / mammal and some bacteria Heavy exercise increases the energy demand of skeletal muscle. The rate of aerobic respiration increases. Aerobic respiration requires glucose and oxygen. When the highest rate and depth of breathing cannot provide enough oxygen to meet the energy demand, lactic acid fermentation takes place (at the same time with aerobic respiration) to supply extra energy to the skeletal muscle. Glucose lactic acid (energy is released as heat and for phosphorylation) Accumulation of lactic acid will lead to fatigue of skeletal muscles. After heavy exercise, lactic acid is removed: Lactic acid + oxygen carbon dioxide + water energy lactic acid glucose glycogen Therefore oxygen is used to remove lactic acid. The amount of oxygen required to remove lactic acid is called oxygen debt. Biochemical pathway of aerobic respiration: (I) Glycolysis – the splitting of glucose (6-C compound) into 2 x 3-C compound The products of glycolysis are pyruvate (3-C compound), ATP and NADH. The process of glycolysis does not need oxygen. (II) Krebs cycle (1) the change of _____________________ into acetyl-CoA (2-C) [this is not a part of the Krebs cycle] The products are NADH, acetyl-CoA, CO2 (carbon dioxide). (2) Krebs cycle The products are CO2, NADH, FADH, ATP and regeneration of coenzyme A. (III) Oxidative phosphorylation In oxidative phosphorylation, NADH and FADH will move the hydrogen atoms through different hydrogen carriers. Eventually, hydrogen is accepted by oxygen to form water (H2O). Energy is given out to form ATP. 1 NADH is used to make 3 ATP, 1 FAD makes 2ATP. As a conclusion, in aerobic respiration, a total of 38 ATP is produced. Biochemical pathway of anaerobic respiration: (i) Alcohol fermentation In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate accepts hydrogen from NADH to make ethanol and gives out carbon dioxide. A total of 2 ATP is produced. (ii) Lactic acid fermentation In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate accepts hydrogen from NADH to make lactic acid. A total of 2 ATP is produced. Structure of mitochondrion: Function of : Outer membrane – control the passage of substances in and out of the mitochondrion; Inner membrane – highly folded to carry more enzymes for oxidative phosphorylation. Matrix – contains enzymes to carry out the chemical reactions of the Krebs cycle. Daily application of anaerobic respiration: Brewing of beer + making wine [alcohol fermentation produces ethanol / alcohol in the drink] Making bread [alcohol fermentation to make carbon dioxide that produces pores in the bread soft] Making yoghurt [lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid to give the sour taste of the food] Making cheese [lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid to lower pH and coagulate the proteins of dairy products] Making biofuel [alcoholic fermentation produces alcohol / ethanol as fuel] Comparison between aerobic and anaerobic respiration Similarities: Both use glucose as a substrate. Both give out energy to make ATP. Both are catalysed by enzymes. Differences: Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration takes place in both cytoplasm and mitochondria takes place in cytoplasm only requires oxygen does not require oxygen produces carbon dioxide, water produces ethanol / alcohol and carbon dioxide or produces lactic acid complete oxidation incomplete oxidation more energy released to form 38 ATP less energy released to form 2 ATP