Energy Systems & Training Adaptations: Aerobic & Anaerobic
advertisement
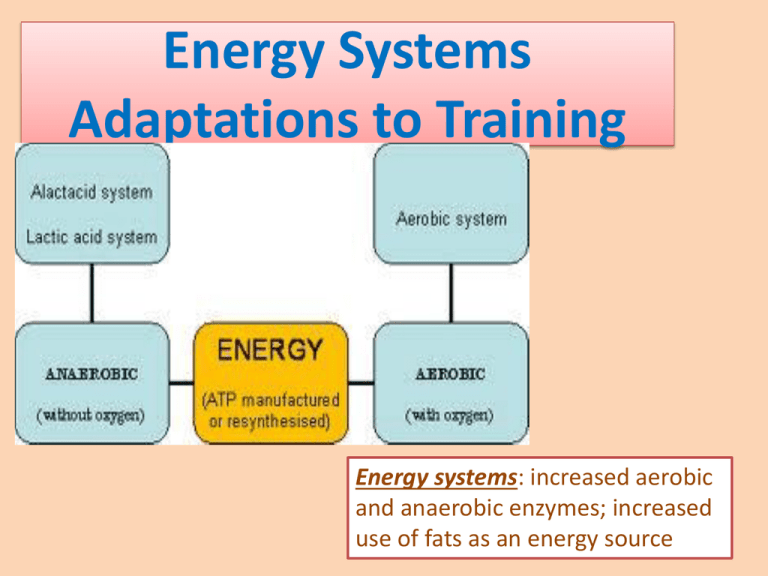
Energy Systems Adaptations to Training Energy systems: increased aerobic and anaerobic enzymes; increased use of fats as an energy source Energy System Adaptations to Anaerobic Training •ATP – CP –Will increase stores of ATP & CP •Anaerobic Glycolysis (Lactic Acid System) – in levels of glycolytic enzymes –Less Lactic Acid produced, more efficient Cori cycle (converting lactic acid in the liver back to glucose to use) –Increased buffering capacity (acidbase balance) more able to tolerate lactic acid for longer! –More energy can be produced through these systems Adaptation to Aerobic Training -↑ the availability of carbohydrate and fats as substrate to meet cellular needs for ATP resynthesis. -↑ capillary density -↑ myoglobin content (increases extract of O2 to the muscle cells) -↑ activity of oxidative enzymes (aerobic pathways) -↑ oxidative capacity linked to ↑ numbers of mitochondria -Therefore O2 ↑ utilization Adaptation to Aerobic Training Increased capacity to oxidize Fats shifts the energy source from glucose to fat (to spare glucose) Decreased utilisation of the anaerobic glycolysis (LA) system ↓ lactate concentration ↑ clearance of lactate during exercise