Holt Physics Chap 1 Highlights
advertisement

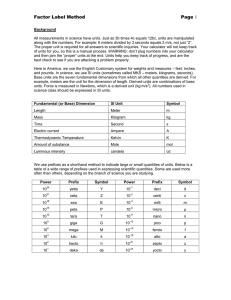
Holt Physics Chap 1 Highlights Physics A broad field of study that presents an organized way of modeling and interpreting nature and uses a small number of basic assumptions and equations to describe the physical world. Areas Within Physics Mechanics Motion and its causes. Thermodynamics Heat and temperature. Vibrations and wave phenomena. Sound, light, and RF (radio frequency) repetitive motions. Electromagnetism Electricity, magnetism, and light. Optics Light Relativity Particles moving at speeds approaching the speed of light. Quantum Mechanics Subatomic particle behavior. Scientific Method Observations and data collecting are done to: ask a question Hypotheses are formulated and objectively tested by: experiments Diagrams Drawings that simplify a physical situation by an illustration that does not include detailed images of the objects. Diagrams do not measure an event or a situation. Models Used by physicists to: explain basic features of a complex phenomena. are not used to manipulate variables in an experiment. SI Basic Units of Measurement Mass – kg Length – meter Time – second Prefixes for units of measurement Prefixes are used to easily state very large and very small numbers. See chap 1 test cover sheet. Be able to pick an appropriate prefix for a measurement. e.g. a tall building would be measured in meters, a butterfly’s wings would be measured in cm, the length of a car would be measured in meters. Precision of Measurement The repeatability of the measurement. Typically is dependent on the limitations of the measuring instrument. Accuracy of Measurement How close it is to the accepted value of the measurement. The frequency of human error is reduced and the minimizing of accuracy is reduced by: o repeating measurements o using the same method of measurement maintaining instruments in good working order Know the Greek letters uses to represent the sum or total and the change in an amount of numbers. Know how to add, subtract, divide, and multiply in scientific notation. Know how to determine the number of significant figures. Know how to interpret graphs. Know the basic equations of different graph shapes. Know how to do conversions between prefixes in the metric system. Know how to determine the resulting unit from given units in an equation. e.g. in the expression ( v)2 / x, what is the resultant unit of measurement? e.g. what is the dimension (unit of measurement) of the constant A in the equation x = Av? Know how to make a diagram and how to arrive at a logical conclusion. e.g. how many 1cm3 blocks are there in a 1 m3 volume block?