FILL IN THE BLANKS: ENDOCRINE HORMONES (Student Copy
advertisement
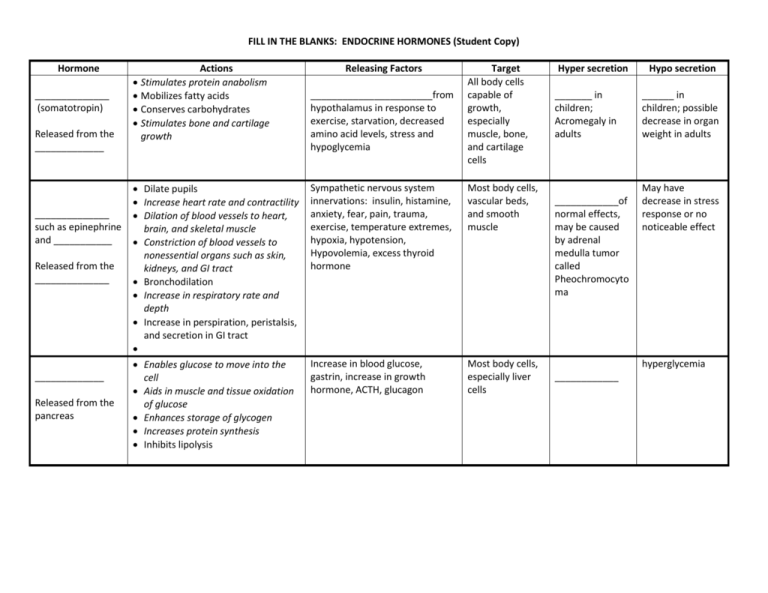
FILL IN THE BLANKS: ENDOCRINE HORMONES (Student Copy) Hormone ______________ (somatotropin) Released from the _____________ ______________ such as epinephrine and ___________ Released from the ______________ _____________ Released from the pancreas Actions Stimulates protein anabolism Mobilizes fatty acids Conserves carbohydrates Stimulates bone and cartilage growth Dilate pupils Increase heart rate and contractility Dilation of blood vessels to heart, brain, and skeletal muscle Constriction of blood vessels to nonessential organs such as skin, kidneys, and GI tract Bronchodilation Increase in respiratory rate and depth Increase in perspiration, peristalsis, and secretion in GI tract Enables glucose to move into the cell Aids in muscle and tissue oxidation of glucose Enhances storage of glycogen Increases protein synthesis Inhibits lipolysis Releasing Factors _______________________from hypothalamus in response to exercise, starvation, decreased amino acid levels, stress and hypoglycemia Target All body cells capable of growth, especially muscle, bone, and cartilage cells Sympathetic nervous system innervations: insulin, histamine, anxiety, fear, pain, trauma, exercise, temperature extremes, hypoxia, hypotension, Hypovolemia, excess thyroid hormone Most body cells, vascular beds, and smooth muscle Increase in blood glucose, gastrin, increase in growth hormone, ACTH, glucagon Most body cells, especially liver cells Hyper secretion _______ in children; Acromegaly in adults ____________of normal effects, may be caused by adrenal medulla tumor called Pheochromocyto ma Hypo secretion ______ in children; possible decrease in organ weight in adults May have decrease in stress response or no noticeable effect hyperglycemia ____________ ______________ (T3) and Thyroxine (T4) Released from the _____________ _______________ Released from the _____________ _____________ (__________) Released from the _____________ ____________ (vasopressin) Released from the ______________ Stimulate metabolic rate Increase protein synthesis Increase carbohydrate and fat metabolism Increase bone growth Increase oxygen consumption Increase metabolism and clearance of drugs Most body cells ______________________from anterior pituitary; thyrotropin releasing hormone from hypothalamus; cold temperature Increase blood glucose by stimulating gluconeogenesis in the liver Inhibit glucose use by the cell Inhibit protein anabolism Promote fatty acid mobilization Inhibit inflammatory response Corticotrophin releasing hormone from hypothalamus: ACTH from anterior pituitary Most body cells Increases serum calcium by accelerating bone breakdown with release of calcium into the blood, increasing calcium reabsorption from intestine, and decreasing kidney tubule reabsorption of calcium Decreases blood phosphate levels by increasing phosphate loss in urine Increases reabsorption of magnesium by the renal tubules Low serum calcium; high serum magnesium or phosphate level; catecholamines; cortisol Bone cells and cells of the GI tract and kidney ______in serum osmolality; hypernatremia; Hypovolemia; hypoxia; hypotension; pain; trauma; stress; nausea; pharmacologic agents Distal renal tubules and collecting ducts; smooth muscle of arterioles and GI tract Increases water reabsorption (inhibits dieresis) by kidney tubules and collecting ducts Vasoconstriction of arterioles Abdominal cramping Hyperthyroidism (chronic), ________(acute) _____________ ___________ and hypophosphatem ia; possibly renal calculi Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone Hypothyroidism (chronic) Addison’s disease (chronic); adrenal crisis (acute) Hypocalcemia and bone decalcification; ____________ ______________ _______(from alpha cells) Released from the _____________ ______________ (calcitonin) Stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to increase blood glucose Inhibits glycolysis Increases lipolysis __________ in blood glucose, elevated blood amino acid, catecholamines, exercise, starvation Most body cells, especially liver cells Hypoglycemia ___________ Reduces plasma calcium levels by inhibiting bone lysis and decreasing calcium resorption by the kidney Increase in serum calcium, magnesium, or glucagon Bone cells and kidney cells Stimulates growth and function of adrenal gland Controls production and release of glucocorticoid hormones Stimulates mineralcorticoid production Stimulates androgen production Increases size and growth of thyroid cells Increases synthesis of thyroid hormones Releases stored thyroid hormones Increase sodium and water reabsorption and potassium excretion Corticotropin releasing hormone from hypothalamus in response to hypoglycemia, decrease in cortisol levels, hypoxia, trauma, surgery, and physical and/or psychological stress Cells of the adrenal cortex Thyrotropin releasing hormone from hypothalamus in response to cold temperature or a decrease in thyroid hormone levels Cells of thyroid gland Hyperthyroidism Distal and collecting tubules of kidney; sweat glands; salivary glands; intestines Hyperaldosteroni sm Not significant Not significant Released from the _____________ _______________ hormone Released from the _____________ _____________ (thyrotropin) Released from the _______________ _______________ such as Aldosterone Released from the _________from anterior pituitary (minor effect), primary stimulus is renin-angiotension system; decrease in serum sodium; increase in serum potassium ____________ Adrenal insufficiency (chronic) and/or adrenal crisis (acute) _____________ _______(chronic); adrenal crisis (acute) ANSWERS Thyroid stimulating hormone Glucagon Hypercalcemia Diabetes Insipidus Increase Glucocorticoids such as cortisol Dwarfism Parathormone thyroid storm Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) ACTH parathyroid gland Exaggeration or prolongation anterior pituitary Hyperglycemia Decrease Addison’s disease adrenal cortex Insulin (from beta cells) Adrenocorticotropic thyroid gland Giantism Thyrocalcitonin Hypothyroidism Antidiuretic hormone Growth hormone releasing hormone pancreas thyroid gland Parathyroid hormone hyperphosphatemia Triiodothyronine Cushing’s disease anterior pituitary Mineralocorticoids adrenal medulla posterior pituitary norepinephrine Catecholamines adrenal cortex Growth hormone anterior pituitary Cushing’s syndrome Hypoglycemia