Endocrine Summary for the quiz

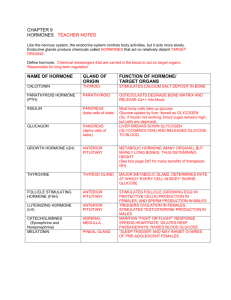
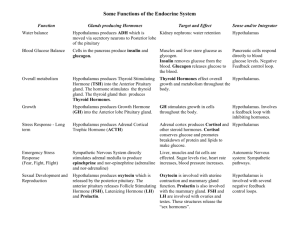
ENDOCRINE SUMMARY
(Note: compared to other organs, all endocrine organs are well vascularized)
1.
HYPOTHALAMUS a.
SECRETES: Releasing or Inhibiting hormones that affect anterior pituitary
2.
ANTERIOR
PITUITARY
(adenohypophysis) a.
Growth hormone: causes growth i.
Increased fat breakdown and protein synthesis, increases blood glucose
1.
Oversecretion: gigantism (child) or acromegaly (adults)
2.
Undersecretion: Pituitary dwarfism b.
Prolactin: Causes lactation in females; effect in males not understood (low levels may reduce desire to cry) c.
TSH: Causes thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormone d.
ACTH: Causes adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol e.
MSH: Causes melanocytes to increase production of pigmentation f.
LH: Causes ovulation g.
FSH: Causes maturation of spermatocytes and oocytes
3.
POSTERIOR PITUITARY (neurohypophysis) a.
Oxytocin: Causes childbirth contractions b.
ADH: Increases blood volume (raises blood pressure) by causing kidneys to reabsorb water (no salt involved) i.
Undersecretion: Diabetes insipidus
4.
THYROID GLAND a.
Thyroid hormone (hormonal mechanism): Increases metabolism in all cells. Iodine is needed for thyroxin (precursor to thyroid hormone) i.
Undersecretion: Hypothyroidism
1.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune) ii.
Oversecretion: Hyperthyroidism
1.
Graves’ disease(autoimmune) b.
Calcitonin: Lowers blood calcium
5.
PARATHYROID GLAND a.
Parathyroid hormone: Increases calcium reabsorption from bone to raise blood calcium
(humoral mechanism)
6.
THYMUS: stimulated maturation of T-cells (white blood cells)
7.
ADRENAL GLAND a.
MEDULLA i.
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine: speeds up heart rate (neuronal mach) b.
CORTEX (the major source of steroid hormones in the body) i.
Aldosterone: Raises blood pressure by causing kidneys to reabsorb salt, and water follows ii.
Cortisol: Anti-inflammation, anti-stress (helps the body cope with stress. It can be converted to prednisone, which suppresses immune system
1.
Increased fat and protein breakdown, increases blood glucose a.
Oversecretion: Cushing’s Disease or Syndrome i.
Round moon face, buffalo hump, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, masculinization in females b.
Under secretion: Addison’s disease i.
Low blood pressure and low glucose, hyperpigmentation c.
Under-secretion of cortisol in fetus i.
CAH (lack of enzymes to make cortisol) iii.
Sex hormones for opposite sex: males make estrogen, females make testosterone here.
8.
PANCREAS a.
Insulin: lowers blood glucose i.
Undersecretion: Diabetes mellitus b.
Glucagon: raises blood glucose by glycogenolysis (breaking down glycogen into glucose) and by gluconeogenesis (making new glucose from amino acids and fatty acids)
9.
OVARIES (stores enough of its hormones to last several months) a.
Progesterone: Causes uterus lining to thicken b.
Estrogen: Causes oocytes to develop; causes female 2° sex characteristics
10.
TESTES a.
Testosterone: Causes male 2° sex characteristics
11.
PINEAL GLAND a.
Melatonin: influences sleep cycles b.
Pineal mineral deposits (“sand”) is seen on x-rays and helps radiologists get oriented in the brain