Disorders of the Endocrine System
advertisement

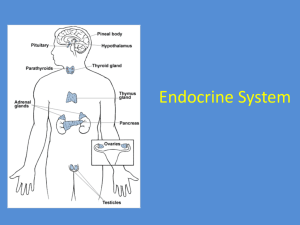
Disorders of the Endocrine System Addison’s disease Caused by undersecretion of adrenal steroid hormones. Results in weakness, nausea, low circulation, and bronzing of the skin. Adenoma A tumor of a gland. Adrenogenital syndrome Oversecretion of adrenal sex hormones, resulting in intense masculinizing of the body. Aldosteronism Overproduction of the adrenal hormone aldosterone, resulting in a decrease in the body’s potassium store. Cretinism Dwarfism and mental retardation caused by too little thyroxine in childhood. Cushing’s syndrome Caused by oversecretion of glucocorticoid hormones from the adrenals. Results in a redistribution of body fat and other effects. Diabetes insipidus Effect of underproduction of the hormone ADH. Diabetes mellitus Condition characterized by frequent thirst and urination and due to excess amounts of sugar in the blood. Results from a lack of insulin. Gigantism Oversecretion of growth hormone in childhood, resulting in taller-than-average stature. If the oversecretion occurs in adulthood, the condition is acromegaly, resulting in a thickening of facial bones and fingers. Goiter An abnormal growth of thyroid tissue due to lack of iodine. Gynecomastia Excessive growth of the male mammary gland caused by oversecretion of feminizing hormones. Hypersecretion Overproduction (of a hormone). Underproduction is called hyposecretion. Hyperthyroidism Oversecretion of thyroxine, resulting in increased metabolic and heart rates, circulation, and blood pressure. © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. Hypoglycemia Low blood sugar, which can cause anxiety, tremors, weakness, and even unconsciousness and death. Hypothyroidism Undersecretion of thyroxine, resulting in a very low metabolic rate and sluggish activity, sometimes accompanied by obesity. Myxedema Accumulation of water in skin resulting from thyroid hormone deficiency in adults. Pituitary dwarfism Undersecretion of growth hormone from the pituitary gland in childhood, resulting in smaller-than-average stature. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) Condition resulting from changes in the body’s level of the hormone melatonin. The level varies seasonally: it is higher in winter and lower in summer, when increased daylight inhibits its production. Symptoms include tiredness and depression. Simmond’s disease Undersecretion of pituitary hormones during adulthood, resulting in symptoms of deficiency of thyroid, adrenal, and sex hormones. Tetany Muscle twitches, spasms, and convulsions resulting from a lack of calcium in the blood. It may be caused by a dysfunction in the parathyroid glands (hypoparathyroidism). Thyrotoxicosis Overactivity of the thyroid gland, often due to an autoimmune disease of the thyroid.