CHAPTER_4_POWER
advertisement

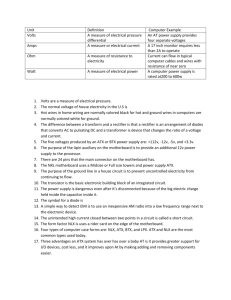
CHAPTER 4 POWER MOTHERBOARDS Form Factor – This designates a particular type of motherboard in re guard to Size Shape Major features FORM FACTORS AT – outdated ATX – most popular MICRO ATX NLX BTX – newest AT form factor is outdated and rarely seen today, but dominated the industry for more than 10 years Had a smaller version called the baby AT Used two power connectors P8 & P9 ATX – most popular form factor today Uses 1 power connector: P1 Has a number of variations Mini – ATX Flex ATX Micro ATX – major differences But BTX may beat it BTX (balanced technology extended) Newest form factor Supports newest standards (usb 2.0 sata) 1 P1 power connector but can support auxiliary power connectors as well. Specifically designed to improve air folw LPX mini LPX Becoming outdated Low profile computers only 1 expansion slot uses a riser card into which expansion slots are plugged Heat is a problem Difficult to upgrade NLX Improved version of lpx Also uses a riser card, sometimes called a daughter board Fixed some of the problems of the LPX Supports AGP Can have larger dims Uses ATX power supply BACK PLANE SYSTEMS No true motherboard The back plane is a board that may contain basic bus and power circuitry to support the circuit boards that plug into its connects Back plane computers=dedicated servers:multiple processor board TYPES OF CASES TOWER – offers most flexibility for expansion Offers most flesibility for expansion Large footprint Has 2 smaller sizes – midsized tower – mini tower DESKTOP – becoming less popular Smaller size is called a slimline. Use lpx, mini lpx, nlx boards NOTE BOOK CASES Very proprietary Emphasize less power, heat, space & more portable PROPERTIES OF ELECTRICITY VOLTS – (V) a measure of electrical pressure differential AMPERE or AMP (A) a measure of electrical current OHMS – a measure of the resistance to the flow of electricity Watts – (W) a measure of electrical power # volts X # of amps = # of watts 10V X 50A = 500W Watts are used to measure the total amount of electrical power needed to operate a device SIGNAL DISTORTION Damage to a signal caused by interference, either EMI or RFI ATTENUATION The decrease in strength of a signal over a distance. More resistance means more attenuation AC – alternating current A cheap way of moving electricity great distances DC – direct current Electricity that only flows in one direction DC is what electronic equipment uses HOT – electricity coming in NEUTRAL – electricity going out GROUND – an escape route for out of control electricity American AC power – 110 volts Europe AC power – 220 volts ELECTRONIC DEVICES Transistor – a gate or switch that can serve to amplify the flow of electricity Capacitor – a device that can hold a charge. Used to smooth or even out the folw of electricity Diode – a semiconductor that allows electricity to flow in only 1 direction Resistor – a device that can limit the amount of electricity that can flow through it ELECTRICAL THREATS ESD EMI The flow of electricity through metal generates a magnetic field SPIKES & SURGES in electrical current Devices that can protect against threats Surge protectors Dataline protectors Line conditioners – protect against spikes & sags but not blackouts Ups – uninterruptible power supply Ups protect against almost all spikes & surges, provide power conditioning and will provide power for a short time in case of a blackout. 2 types Standard Intelligent – comes with it’s own software. Can perform monitoring, diagnostics and will shut down the computer in case of a black out.